Abstract
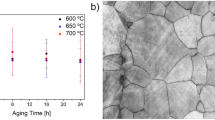
The effect of thermomechanical treatments on grain size and precipitate evolution as well as their impact on the shape memory properties of cold-drawn Fe41–Ni28–Co17–Al11.5–Ti2.5–B0.05 (at. %) wires were studied. Cold drawing produces a strong {hkl} < 111 > /{hkl} < 001 > texture in this alloy. Different thermal treatments promote the evolution of specific recrystallisation textures as well as grain growth, while ageing at 600 °C to 650 °C leads to the formation of γ’ precipitates. Variation in size and distribution of the precipitates via ageing significantly affect the functional properties. A maximum transformation strain of 1.3% without fracture was obtained on sample tested on heating–cooling experiments.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset used in this study is available upon reasonable request.
References
Otsuka K, Wayman CM (eds) (1998) Shape Memory Materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tanaka Y, Himuro Y, Kainuma R, Sutou Y, Omori T, Ishida K (2010) Ferrous polycrystalline shape-memory alloy showing huge superelasticity. Science 327:1488–1490. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183169
Ma J, Kockar B, Evirgen A, Karaman I, Luo ZP, Chumlyakov YI (2012) Shape memory behavior and tension-compression asymmetry of a FeNiCoAlTa single-crystalline shape memory alloy. Acta Mater 60:2186–2195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.12.047
Omori T, Ando K, Okano M, Xu X, Tanaka Y, Ohnuma I, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2011) Superelastic effect in polycrystalline ferrous alloys. Science 333:68–71. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1202232
Omori T, Abe S, Tanaka Y, Lee DY, Ishida K, Kainuma R (2013) Thermoelastic martensitic transformation and superelasticity in Fe–Ni–Co–Al–Nb-B polycrystalline alloy. Scr Mater 69:812–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.09.006
Tseng LW, Ma J, Karaman I, Wang SJ, Chumlyakov YI (2015) Superelastic response of the FeNiCoAlTi single crystals under tension and compression. Scr Mater 101:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.12.021
Geng Y, Jin M, Ren W, Zhang W, Jin X (2013) Effects of aging treatment on martensitic transformation of Fe-Ni-Co-Al-Ta-B alloys. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.03.033
Karaca HE, Turabi AS, Chumlyakov YI, Kireeva I, Tobe H, Basaran B (2016) Superelasticity of [001]-oriented Fe42·6Ni27.9Co17·2Al9.9Nb2.4 ferrous shape memory alloys. Scr Mater 120:54–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.04.008
Lee D, Omori T, Kainuma R (2014) Ductility enhancement and superelasticity in Fe–Ni–Co–Al–Ti-B polycrystalline alloy. J Alloys Compd 617:120–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.07.136
Ma J, Hornbuckle BC, Karaman I, Thompson GB, Luo ZP, Chumlyakov YI (2013) The effect of nanoprecipitates on the superelastic properties of FeNiCoAlTa shape memory alloy single crystals. Acta Mater 61:3445–3455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.02.036
Krooß P, Niendorf T, Karaman I, Chumlyakov Y, Maier HJ (2012) Cyclic deformation behavior of aged FeNiCoAlTa single crystals. Funct Mater Lett. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793604712500452
Zhang C, Zhu C, Shin S, Casalena L, Vecchio K (2019) Grain boundary precipitation of tantalum and NiAl in superelastic FeNiCoAlTaB alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 743:372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.077
Fu H, Li W, Song S, Jiang Y, Xie J (2016) Effects of grain orientation and precipitates on the superelasticity in directionally solidified FeNiCoAlTaB shape memory alloy. J Alloys Compd 684:556–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.209
Sobrero CE, La Roca P, Roatta A, Bolmaro RE, Malarría J (2012) Shape memory properties of highly textured Cu–Al–Ni–(Ti) alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.12.104
Bhattacharyya JJ, Agnew SR, Muralidharan G (2015) Texture enhancement during grain growth of magnesium alloy AZ31B. Acta Mater 86:80–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.12.009
Sobrero CE, Lauhoff C, Wegener T, Niendorf T, Krooß P (2020) On the Impact of texture and grain size on the pseudoelastic properties of polycrystalline Fe–Ni–Co–Al–Ti Alloy. Shape Mem Superelasticity 6:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-020-00280-4
Lee D, Omori T, Han K, Hayakawa Y, Kainuma R (2018) Effect of thermomechanical Processing on texture and superelasticity in Fe–Ni-Co-Al–Ti-B alloy. Shape Mem Superelasticity 4:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-018-0160-5
Fu H, Zhao H, Song S, Zhang Z, Xie J (2016) Evolution of the cold-rolling and recrystallization textures in FeNiCoAlNbB shape memory alloy. J Alloys Compd 686:1008–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.273
Choi WS, Pang EL, Choi PP, Schuh CA (2020) FeNiCoAlTaB superelastic and shape-memory wires with oligocrystalline grain structure. Scr Mater 188:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.06.067
Omori T, Okano M, Kainuma R (2013) Effect of grain size on superelasticity in Fe-Mn-Al-Ni shape memory alloy wire. APL Mater 10(1063/1):4820429
Ozcan H, Ma J, Wang SJ, Karaman I, Chumlyakov Y, Brown J, Noebe RD (2017) Effects of cyclic heat treatment and aging on superelasticity in oligocrystalline Fe–Mn–Al–Ni shape memory alloy wires. Scr Mater 134:66–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.02.023
Dippel AC, Liermann HP, Delitz JT, Walter P, Schulte-Schrepping H, Seeck OH, Franz H (2015) Beamline P021 at PETRA III for high-resolution and high-energy powder diffraction. J Synchrotron Radiat 22:675–687. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600577515002222
Bachmann F, Hielscher R, Schaeben H (2010) Texture analysis with MTEX- Free and open source software toolbox. Solid State Phenom 160:63–68. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.160.63
Zhang C, Zhu C, Harrington T, Vecchio K (2018) Design of non-equiatomic high entropy alloys with heterogeneous lamella structure towards strength-ductility synergy. Scr Mater 154:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.05.020
Coelho RS, Klaus M, Genzel C (2014) Analysis of texture depth distribution by energy-dispersive diffraction. Mater Sci Forum 768–769:36–43. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.768-769.36
Zhao H, Fu H, Xie J, Zhang Z (2018) Effects of solution treatment on microstructure and superelasticity of FeNiCoAlTaB alloy. Res Express Mater. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaa1fd
Annealing R (1995) Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena. Recryst Relat Annealing Phenom. https://doi.org/10.1016/c2009-0-07986-0
Zhang C, Zhu C, Cao P, Wang X, Ye F, Kaufmann K, Casalena L, MacDonald BE, Pan X, Vecchio K, Lavernia EJ (2020) Aged metastable high-entropy alloys with heterogeneous lamella structure for superior strength-ductility synergy. Acta Mater 199:602–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.043
Krooß P, Somsen C, Niendorf T, Schaper M, Karaman I, Chumlyakov Y, Eggeler G, Maier HJ (2014) Cyclic degradation mechanisms in aged FeNiCoAlTa shape memory single crystals. Acta Mater 79:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.06.019
Czerny M, Maziarz W, Cios G, Wójcik A, Chumlyakov YI, Schell N, Fitta M, Chulist R (2020) The effect of heat treatment on the precipitation hardening in FeNiCoAlTa single crystals. Mater Sci Eng A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139327
Evirgen A, Ma J, Karaman I, Luo ZP, Chumlyakov YI (2012) Effect of aging on the superelastic response of a single crystalline FeNiCoAlTa shape memory alloy. Scr Mater 67:475–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.06.006
Tseng LW, Tzeng YC, Tsai YL, Chumlyakov Y (2021) Microstructure investigation of new iron-based FeNiCoAlTiNb shape memory alloys. Res Mater 10:100188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinma.2021.100188
Zhang C, Wang X, Xu M, MacDonald BE, Hong R, Zhu C, Dai X, Vecchio KS, Apelian D, Hahn H, Schoenung JM, Lavernia EJ (2021) Orientation-dependent superelasticity of a metastable high-entropy alloy. Appl Phys Lett 10(1063/5):0066130
Fu H, Zhao H, Zhang Y, Xie J (2017) Enhancement of superelasticity in Fe–Ni–Co-Based shape memory alloys by microstructure and texture control. Procedia Eng 207:1505–1510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.1084
Sobrero CE, La Roca P, Roatta A, Bolmaro RE, Malarría J (2012) Shape memory properties of highly textured Cu–Al–Ni–(Ti) alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 536:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.12.104
Krooß P, Holzweissig MJ, Niendorf T, Somsen C, Schaper M, Chumlyakov YI, Maier HJ (2014) Thermal cycling behavior of an aged FeNiCoAlTa single-crystal shape memory alloy. Scr Mater 81:28–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.02.020
Kireeva IV, Chumlyakov YI, Kirillov VA, Karaman I, Cesari E (2011) Orientation and temperature dependence of superelasticity caused by reversible γ-α′ martensitic transformations in FeNiCoAlTa single crystals. Tech Phys Lett 37:487–490. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785011050221
Abuzaid W, Sehitoglu H (2018) Superelasticity and functional fatigue of single crystalline FeNiCoAlTi iron-based shape memory alloy. Mater Des 160:642–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.10.003
Tseng L-W, Chen C-H, Chen W-C, Cheng Y, Lu N-H (2021) Shape memory properties and microstructure of new iron-based FeNiCoAlTiNb shape memory alloys. Crystals 11:1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11101253
Sobrero C, Lauhoff C, Langenkämper D, Somsen C, Eggeler G, Chumlyakov YI, Niendorf T, Krooß P (2021) Impact of test temperature on functional degradation in Fe–Ni–Co–Al–Ta shape memory alloy single crystals. Mater Lett 291:129430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129430
Tsai CY, Tseng LW, Tzeng YC, Lee PY (2022) Magnetic properties of FeNiCoAlTiNb shape memory alloys. Crystals. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010121
Chumlyakov YI, Kireeva IV, Pobedennaya ZV, Krooß P, Niendorf T (2021) Shape memory effect and superelasticity of [001]-oriented fenicoalnb single crystals aged under and without stress. Metals (Basel) 11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060943
Chulist R, Prokopowicz M, Maziarz W, Ostachowski P, Schell N (2019) Effect of heat treatment on the precipitation hardening in FeNiCoAlTaB shape memory alloys. Int J Mater Res 110:70–74. https://doi.org/10.3139/146.111688
Zhang C, Zhu C, Harrington T, Casalena L, Wang H, Shin S, Vecchio KS (2019) Multifunctional non-equiatomic high entropy alloys with superelastic, high damping, and excellent cryogenic properties. Adv Eng Mater 21:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201800941
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge DESY (Hamburg, Germany), a member of the Helmholtz Association HGF, for the provision of experimental facilities. Parts of this research were carried out at P02.1 and authors would like to thank Dr. Martin Etter for assistance in using the line. Beamtime was allocated for proposal I-20191495. PK acknowledges Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (project ID 449930948).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sobrero, C., Remich, V., Cassineiro, J. et al. Functional Properties of Highly Textured Fe–Ni–Co–Al–Ti–B Shape Memory Alloy Wires. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 9, 531–541 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-023-00449-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-023-00449-7