Abstract
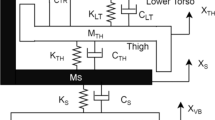
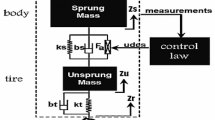
This paper uses two MacPherson struts and one fluidic muscle actuator (FMA) to design a fluidic muscle active suspension system (FMASS), allowing to provide active complementary force to suppress road vibration and improve ride comfort for passengers. The FMA outputs an additional force accompanying with the MacPherson struts so that FMASS has much powerful strength to stabilize the vehicle body. To regulate the vehicle body, a parallel type adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control (parallel-AIT2FSC) is presented in this paper. It has two AIT2FSCs in parallel: one controls the position and the other reduces acceleration. A fully functional test-rig is constructed to verify the feasibility of the FMASS using self-generated road conditions. In the experiments, the characteristics of the FMASS, such as the position and the vertical acceleration of the sprung mass, are demonstrated on two different road conditions and are presented in the time and frequency domains. The experimental results show that the vibration on the chassis is greatly reduced.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gohrle, C., Schindler, A., Wagner, A., Sawodny, O.: Design and vehicle implementation of preview active suspension controllers. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 22(3), 1135–1142 (2014)
Cao, D., Song, X., Ahmadian, M.: Editors’ perspectives: road vehicle suspension design, dynamics, and control. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 49(1–2), 3–28 (2011)
Patil, S.A., Joshi, S.G.: Experimental analysis of 2 DOF quarter car passive and hydraulic active suspension systems for ride comfort. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. Open Access J. 2(1), 621–631 (2014)
Van der Sande, T.P.J., Gysen, B.L.J., Besselink, I.J.M., et al.: Robust control of an electromagnetic active suspension system: simulations and measurements. Mechatronics 23(2), 204–212 (2013)
Kang, R., Guo, Y., Chen, L., Branson, D.T., Dai, J.S.: Design of a pneumatic muscle based continuum robot with embedded tendons. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22(2), 751–761 (2017)
Daerden, F., Lefeber, D.: Pneumatic artificial muscles: actuators for robotics and automation. Eur. J. Mech. Environ. Eng. 47(1), 11–21 (2002)
Anakwa, W.K.N., Thomas, D.R., Jones, S.C., et al.: Development and control of a prototype pneumatic active suspension system. IEEE Trans. Educ. 45(1), 43–49 (2002)
Nieto, A.J., Morales, A.L., González, A., et al.: An analytical model of pneumatic suspensions based on an experimental characterization. J. Sound Vib. 313, 290–307 (2008)
Alireza, K.: Improving control mechanism of an active air-suspension system. Master Thesis, Eastern Mediterranean University (2013)
Graf, G., Kieneke, R., Maas, J.: Pneumatic push–pull actuator for an active suspension. In: 5th IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems 2010, Cambridge, MA, USA, Step 13–15.
D’Amato, F.J., Viassolo, D.E.: Fuzzy control for active suspensions. Mechatronics 10(8), 897–920 (2000)
Lin, J., Lian, R.J., Huang, C.N., Sie, W.T.: Enhanced fuzzy sliding mode controller for active suspension systems. Mechatronics 19, 1178–1190 (2009)
Ostasevicius, V., Sapragonas, J., Rutka, A., Staliulionis, D.: Investigation of Active Car Suspension with Pneumatic Muscle. SAE MOBILUS, 01-2206 (2002)
Zhong, X.F., Han, S.Y., Zhou, J., Chen, Y.H.: Design of optimal disturbance attenuation controller for networked T-S fuzzy vehicle active suspension with control delay. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 676–684 (2019)
Bijan, R.S., Mohammad, S., Mehdi, R.: Control of active suspension system: an interval type-2 fuzzy approach. World Appl. Sci. J. 12(12), 2218–2228 (2011)
Krauze, P., Kasprzyk, J., Kozyra, A., Rzepecki, J.: Experimental analysis of vibration control algorithms applied for an off-road vehicle with magnetorheological dampers. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 37(3), 619–639 (2018)
Tang, X., Du, H., Sun, S., Ning, D., Xing, Z., Li, W.: Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy control for semi-active vehicle suspension with a magnetorheological damper and experimental validation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22(1), 291–300 (2017)
Chou, C.P., Hannaford, B.: Measurement and modeling of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1(2), 90–102 (1996)
Bouri, M., Thomasset, D.: Sliding control of an electropneumatic actuator using an integral switching surface and modeling of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 9, 368–375 (2001)
Slotine, E.J., Li, W.: Applied Nonlinear Control. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1991)
Acknowledgements
This research is sponsored by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C. under Grants Nos. MOST 109-2221-E-032-022, 110-2221-E-032-036. I would like to greatly thank Dr. Lian-Wang Lee for providing equipment for experiments and appreciate L.C. Jin and C.W. Wang for organizing the experimental data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, IH. Design for a Fluidic Muscle Active Suspension Using Parallel-Type Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sliding Control to improve Ride Comfort. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 1719–1734 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01229-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01229-0