Abstract
The hydrogenation of CO to synthetic natural gas (SNG) needs a high molar ratio of H2/CO (usually large than 3.0 in industry), which consumes a large abundant of hydrogen. The reverse dry reforming reaction (RDR, 2H2 + 2CO ↔ CH4 + CO2), combining CO methanation with water-gas-shift reaction, can significantly decrease the H2/CO molar ratio to 1 for SNG production. A detailed thermodynamic analysis of RDR reaction was carried out based on the Gibbs free energy minimization method. The effect of temperature, pressure, H2/CO ratio and the addition of H2O, CH4, CO2, O2 and C2H4 into the feed gas on CO conversion, CH4 and CO2 selectivity, as well as CH4 and carbon yield, are discussed. Experimental results obtained on homemade impregnated Ni/Al2O3 catalyst are compared with the calculations. The results demonstrate that low temperature (200–500 °C), high pressure (1–5 MPa) and high H2/CO ratio (at least 1) promote CO conversion and CH4 selectivity and decrease carbon yield. Steam and CO2 in the feed gas decrease the CH4 selectivity and carbon yield, and enhance the CO2 content. Extra CH4 elevates the CH4 content in the products, but leads to more carbon formation at high temperatures. O2 significantly decreases the CH4 selectivity and C2H4 results in the generation of carbon.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Natural gas is a highly efficient and clean fossil fuel due to its high calorific value, low sooting tendency and slag free products, leading to its increasing consumption year by year (Gao et al. 2015; Meng et al. 2015a; Rönsch et al. 2016). In 2014, the consumption of natural gas in China increased to 197.3 billion cubic meters, with a growth rate of 30.9% every year in the last decade (BP 2016). Recently, the consumption of natural gas has raised a serious concern regarding its depletion because of its limited reserves (Kopyscinski et al. 2010; Huo et al. 2013), in comparison, coal is considered as a much more abundant energy resource in many countries. The production of synthetic natural gas (SNG) from coal has been developed to be a potential route to circumvent the limited supply of natural gas, especially in China (Li et al. 2014a, b; Lu et al. 2014).
Among the coal-to-SNG production processes, SNG is produced through the four major steps, i.e., coal gasification, water-gas-shift (WGS) reaction (CO + H2O ↔ H2 + CO2), gas cleaning and CO methanation (3H2 + CO ↔ CH4 + H2O) (Shinde and Madras 2014; Wang et al. 2015). The CO methanation reaction is a key process for increasing SNG production (Meng et al. 2015b; Götz et al. 2016; Gao et al. 2016). If one mole of CO is converted to methane, three moles of H2 are stoichiometrically required. However, the content of carbon in coal is usually more than 60 wt% (up to more than 90 wt% in bituminous coal) whereas that of hydrogen is <5 wt% (Martelli et al. 2011; Shen et al. 2016). The high content of carbon in coal results in low H2/CO molar ratios, usually less than one, of produced gas from coal gasification (Messerle et al. 2016). For example, the produced gas of the British Gas-Lurgi (BGL) coal gasification process is composed of 60%–70% CO, 27%–30% H2, 0%–7% CH4, 1%–4% CO2, and trace amounts of O2 and light hydrocarbons (Yu and Wang 2010). To increase the H2/CO ratio, the WGS reaction should be well controlled. It is worthwhile to mention, in order to enhance the CO conversion and CH4 yield during industry processes, an even higher H2/CO ratio is usually used. For instance, the H2/CO ratio of the Lurgi process for methanation was optimized at about 3.2, and that of the Topsøe Recycle Energy Efficient Methanation (TREMP) process reached about 3.5 (Kopyscinski et al. 2010). More amount of CO needs to be converted to produce H2 by WGS reaction in order to get a high H2/CO ratio, which results in the high operating cost and energy consumption.
The reverse dry reforming (RDR) reaction (2CO + 2H2 ↔ CH4 + CO2), which is the combination of CO methanation with WGS reaction, can be used to produce SNG. Recently, many studies have focused on the RDR reaction with the H2/CO ratio of one. Yan et al. (2013) found that the catalyst preparation methodologies significantly affected the activity and stability of Ni/SiO2 catalysts. Jiang et al. (2013, 2014) investigated the stepwise sulfidation and sulfidation temperature on the catalytic activity of MoO3/CeO2–Al2O3. It is because there are many advantages of this reaction. First, the feed gas has a low H2/CO ratio of one, which needs less hydrogen; Secondly, the water-free products can diminish the damage of steam on methanation catalyst, and the by-product CO2 can be easily removed by employing low-temperature methanol purification process. In other words, less H2 is needed from the gas of coal gasification, which simplifies the SNG production process and reduces the cost.
In literatures, data are available for the thermodynamic analysis of methanation reactions. Miguel et al. (2015) and Sahebdelfar et al. (2015) conducted a thermodynamic calculation of CO2 methanation based on the method of Gibbs free energy minimization and compared with the experimental data. Gao et al. (2012) analyzed the thermodynamic properties of several reactions during the complete methanation of CO and CO2. However, these thermodynamic studies were carried out based on the complete methanation reactions. To our knowledge, there is little information on the thermodynamic analysis of the RDR reaction that occurs at low temperatures. Therefore, it needs to perform the calculations based on the Gibbs free energy minimization method and validate the data through experimental means.
It is well known that the produced gas from coal contains many impurities, such as steam, CO2, CH4, O2 and light hydrocarbons of C2H4 and C2H6. In order to increase the production of SNG and optimize the H2/CO ratio of the produced gas, effects of these substances on the catalytic performance of the RDR reaction have to be investigated. Moreover, the yield of solid carbon should be taken into account during the thermodynamic analysis.
The objective of this work is to elucidate, through a thermodynamic study supported by experimental data, the effects of temperature, pressure and the other factors affecting the RDR reaction, such as the H2/CO molar ratio and addition of H2O, CH4, CO2, O2, and C2H4 in feed gas on the catalytic activity and selectivity and the yield. For this purpose, this study does not take into account of reaction kinetics, practical heat and mass transfer processes. It is expected to produce necessary thermochemical data to describe the effectiveness of the RDR reaction and to provide useful guidance to chemical engineers for optimizing the individual processes.
2 Methods
2.1 Thermodynamic analysis software
The HSC Chemistry software 6.0 allows simulating chemical reactions and processing on the thermochemical data basis. In this study, the modules of reaction equations and equilibrium compositions were utilized to calculate the effects of various substances in conversion, selectivity and yield. The calculations were performed based on an extensive thermochemical database, which contains enthalpy (H), entropy (S) and heat capacity (C p) data of more than 17000 chemical compounds (Roine 2010; Kumar et al. 2016).
2.2 Thermodynamic analysis method
The equilibrium products at different temperatures and pressures were calculated using the Gibbs free energy minimization method, which has been widely applied for thermodynamic calculations (Adhikari et al. 2007; Nahar and Madhani 2010; López Ortiz et al. 2015). The detailed interpretation of this theory can be referenced by Wang et al. (Wang and Cao 2012; Wang et al. 2014).
The total Gibbs free energy is expressed as Eq. (1). As to chemical reaction equilibrium state, f Θ i = p Θ, f i = y i φ i p, and G Θ i = ΔG Θ fi are supposed. With the Lagrange multiplier method, Eqs. (2) and (3) indicate the minimum Gibbs free energy of each gas and total system without solid ones, respectively. Equation (4) is the constraining condition. The vapor–solid phase equilibrium is applied to the Gibbs free energy of carbon, as shown in Eq. (5). Thus, the minimization formation of Gibbs free energy Eq. (6) is obtained by substituting Eq. (1) with Eqs. (3) and (5).
In the HSC Chemistry software 6.0, the reaction system needs to be specified, in terms of its phases and species, and the amount of the reactants. The program calculates the amount of products at equilibrium in isothermal or isobaric condition for a heterogeneous system. At the equilibrium state, the free energy of the system is minimized.
It should be noted that these thermodynamic analyses do not include any reaction kinetic limitation or transport process in the real process. However, thermochemical calculations show a great importance in adjusting the feasibility of a reactive process under certain conditions. Here, possible reactions are summarized in Table 1 for the calculations which were carried out based on different types of gases including CO, H2, CO2 and CH4, and the solid product of deposition carbon (graphite). Other substances such as alcohols, acids and high hydrocarbons are not taken into account due to their trace contents in the equilibrium gas mixture. The elemental mass balance is evaluated by carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
The conversion of CO, selectivities of CH4 and CO2, yields of CH4 and solid carbon are calculated as follows:
Here, i indicates all carbon containing species (CO, CO2, CH4 and C2H4) at inlet, and N i indicates the number of carbon atom of i-th species.
2.3 Experimental study
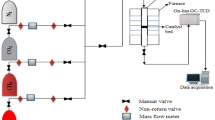
The alumina (191 m2/g, Shandong Aluminum Co., China) supported homemade Ni-based catalyst was prepared by the co-impregnation method, as described in Meng’s works (Meng et al. 2017). The Ni-based catalyst, with the Ni loading of 20 wt% and La loading of 4 wt%, showed the specific surface area of 128 m2/g and pore size of 5.1 nm, and the catalyst was denoted as ExCat. To validate the thermodynamic calculations, the RDR reaction was carried out in a stainless steel, high-pressure fixed-bed tube reactor (10 mm × 2 mm × 500 mm) within the temperature range of 300–550 °C. 300 mg of Ni/Al2O3 catalyst (20–40 mesh) was placed in the reactor. Prior to the RDR reaction, the catalyst was reduced at 550 °C in a H2 (99.99%, purchased from Taiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., China) flow diluted with 25% N2 (99.995%, purchased from Taiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., China) for 6 h. A mixed feed gases of H2/CO = 1 (the gas of CO with a purity of 99.9% was purchased from Taiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., China) were introduced and controlled with the mass flow controller (MFC), preheat treatment was finished at 200 °C in first oven at a space velocity of 20000 mL/(g h)−1. In the second oven, two thermocouples are employed for the reaction. One is placed closely to the reactor, in the middle of the oven to control the oven temperature. The other one is placed inside of the catalyst bed for the measurement of reaction temperature of catalyst bed. The outlet gas steam was cooled by condenser (2 °C) and quantitatively analyzed by an online gas chromatography (GC, Agilent 7890A) using helium (99.999%, purchased from Taiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., China) as the carrier gas. The GC equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) with an HP-AL/S column was employed to analyze CH4, and a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) equipped with a Porapak-Q column, HP-PLOT/Q column, and HP-MOLESIEVE column was employed to analyze CO2, CO, and N2.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Equilibrium analysis of the reactions
The equilibrium constants K of R1–R8 at various temperatures are shown in Fig. 1. The value of K is calculated using the Van’t Hoff equation:
It can be seen in Fig. 1, as the temperature increases, all the K values decrease except that of R6, which agrees with the Le Chatelier’s principle. R1, R2, R3, R5, and R7 play important roles in the RDR reaction system. When the temperature is lower than 500 °C, the equilibrium constant K reduces in the order of R1 > R2 > R5 > R3 > R7 > R8 > R4 > R6. Among all these reactions, R1 and R2 show elative high K values at low temperatures, which will lead to the high conversions of CO. CO2 could be converted via reactions of R3 and R8; however, the CO2 cannot be fully converted, which is due to that the reactions of R1, R4, and R5 generate CO2. Moreover, the solid carbon generated from the reaction of R5 to R8, and the Boudouard reaction (R5) acts a dominant role due to its largest K value. Importantly, all these reactions may occur simultaneously in the system, resulting in a balanced composition of the products.
3.2 Equilibrium compositions
Figure 2 shows the methanation products with their mole fractions at equilibrium temperatures at 0.1 MPa. The feed gas contains H2 and CO with a H2/CO stoichiometric ratio of 1. The products mainly consist of CH4 and CO2 in the temperature range of 200–400 °C. The mole fractions of CH4 and CO2 decrease as the temperature increases, whereas the mole fractions of H2 and CO exhibit the opposite trend. This can be explained by that the methane-generating reactions (R1–R3) are exothermic reactions and a higher temperature inhibits them. It is also found that the mole fraction of CH4 is lower than that of CO2. At a low H2/CO ratio, the Boudouard reaction (R5) is more preferable, leading to a large amount of CO2 and solid carbon. On the other side, the amount of H2 is higher than that of CO, as shown in Fig. 2. when the temperature over 550 °C, the CO mole fraction increases linearly with temperature, which is due to the inhibition of the RDR reaction and the CO produced by the reverse Boudouard reaction (Nahar and Madhani 2010). The solid carbon is produced between 300 and 800 °C, with a maximum amount around 575 °C. Boudouard reaction will not occur when the temperature reaches 700 °C or higher, as shown in Fig. 1, from which the solid carbon is mainly derived from the methane cracking reaction R6. Once the solid carbon produced, it may cover the active sites and results in catalyst deactivation (Takenaka et al. 2008). Thus to emphasize, a proper temperature below 600 °C for RDR reaction is focused, in looking for a high yield of methane.
3.3 Effect of temperature and pressure
The effects of temperature and pressure on RDR reaction are shown in Fig. 3. Figure 3a shows that the CO can be fully converted when the temperature was below 400 °C, further increasing the temperature resulted in the decrease of CO conversion, from the reason of the exothermic nature of RDR reaction. At a constant temperature, a higher pressure promotes the CO conversion due to the volume reducing nature of RDR reaction. The above results indicate that a lower temperature and a higher pressure are favorable for the RDR reaction, in terms of increasing CO conversion. On the other hand, the increasing range of CO conversion is not obvious when the pressure is higher than 1 MPa. In Fig. 3b, high CH4 selectivity is obtained at low temperatures and high pressures. This is because all the methane producing reactions are volume reducing and exothermic. When the temperature is higher than 550 °C, the K value of R5 is comparatively larger than that of R1 (Fig. 1), and the Boudouard reaction (R5) becomes dominantly in the reaction system, leading to a high CH4 selectivity at relative low temperatures. In Fig. 3c, a CH4 yield close to 50% is obtained in the temperature ranges of 200–300 °C from 1 to 5 MPa. Thus, to get a comparatively high CO conversion and CH4 yield, the conditions of high pressure and low temperature are recommended. Knowing that low temperature is not benefit to accelerate the reaction rate and high pressure is harmful for the equipment, a pressure range of 2–3 MPa and a temperature range of 300–500 °C are favorable for the RDR reaction.
The variation of carbon yield is presented in Fig. 3d. All these carbon yield curves exhibit a volcano characteristic, with less yield of carbon at high pressures. The solid carbon results from many reactions, including R5, R6, R7, and R8 (as shown in Table 1), from which have different K values. Since the K value of R6 is negative at 200–550 °C and the value of R5 is higher than that of R7 and R8 at 200–800 °C (Fig. 1), so R5 is the main reason for the deposition of carbon. At the point of 0.1 MPa and around 575 °C, the carbon yield reaches the maximum (23%). Accordingly, at this condition, the occurrence of R6 triggered a higher production of carbon. However, further increase the temperature results in the decrease of carbon yield, possibly because the reverse reactions of R5, R7 and R8 consumes a comparable amount of solid carbon.
3.4 Effect of H2/CO ratio
Since the produced gas derived from coal gasification has a varying ratio of H2/CO (Zheng and Furinsky 2005), there is a need to investigate the effect of H2/CO ratio on performance of RDR reaction. Figure 4a exhibits the effect of H2/CO molar ratio on CO conversion. The CO conversion changes slightly as the H2/CO ratio increases. When the pressure is 3 MPa, the CO conversion reaches nearly 100% in the temperature range of 200–550 °C. Figure 4b shows the changes of CH4 selectivity. A high H2/CO ratio improves the selectivity of CH4, as it can be found when the H2/CO ratio is 0.8, the maximum CH4 selectivity of 40% can be obtained. Considering the nearly 100% CO conversion below 450 °C, there should be much carbon deposition (see Fig. 4d). When the H2/CO ratio increased to 1, the corresponding initial CH4 selectivity increases to 50%. Further increase H2/CO ratio to 3, the CH4 selectivity enhanced remarkably to 100%. In addition, high pressure is favorable to improve the CH4 selectivity. So a high H2/CO ratio or pressure value is useful for SNG production. Figure 4c reveals the variations of CH4 yield. Higher H2/CO ratio or pressure and lower temperature lead to a higher CH4 yield. Figure 4d demonstrates the variation of carbon yield. When the H2/CO ratio is 0.8, a significant amount of carbon is produced, because a large amount of unreacted CO is converted to solid carbon via R5. The highest carbon yield is 28 mol% at 0.1 MPa. To avoid such carbon deposition, high H2/CO ratio and high pressure are recommended for the RDR reaction.
3.5 Effect of H2O content
Steam controls the H2/CO ratio via WGS reaction (R4), which is mostly used in methanation and ammonia synthesis industrial process. Moreover, it can be also used for eliminating the carbon deposition to some extent via reverse R7 and R8.
The effect of steam content in feed gas is shown in Fig. 5. As can be found in Fig. 5a, the introduction of steam slightly decreases the CO conversion at 0.1 and 3 MPa. Although the steam does not participate in the RDR reaction, it can inhibit the methanation reaction R2 and thus decrease the CO conversion. As shown in Fig. 5b, steam has a small effect on the selectivity of CH4. However, the selectivity of CO2 significantly increases as the amount of steam increases at 0.1 MPa (Fig. 5c). From Fig. 5d, the additional steam decreases the yield of carbon, especially at high pressures. When the steam ratio reaches 0.4 at 3 MPa, only trace amount of carbon is formed at the temperature higher than 650 °C. This is because the added steam promotes the reverse R8 reaction. This is also verified by Fig. 5c, where the addition of steam results in the increase of CO2 selectivity. In industrial methanation processes, such as High Combined Shift Methanation (HICOM) (Ensell and Stroud 1983) and Ralph M. Parsons (RMP) (G. A White et al. 1975), certain amount of steam is required to eliminate the solid carbon.
3.6 Effect of CH4 content
The syngas, derived from gasification of coal, frequently contains a certain amount of CH4. In addition, the contained CH4 in methanation products is generally cycled to dilute the feed gas, in order to avoid reaction temperature run away from the fixed-bed technology (Rönsch et al. 2016). Thus, to study the effect of CH4 on the RDR reaction is of necessity. Figure 6a shows the effect of CH4 content on CO conversion. Additional CH4 results in slight decrease of CO conversion at both 0.1 and 3 MPa. The reason is that CH4 is the product of reactions R1, R2 and R3. Introduction of CH4 can inhibit these reactions (R1, R2 and R3), and thus decrease the CO conversion. In Fig. 6b and c, additional CH4 greatly improves the CH4 content in the product and reduces the CO2 selectivity at both 0.1 and 3 MPa, especially at low temperatures. However, the introduction of CH4 into the feed gas sharply exacerbates the deposition of solid carbon, especially at high temperatures (Fig. 6d). Increasing pressure is very effective to reduce the carbon deposition. Comparing to 0.1 MPa, the carbon yield has been greatly reduced at 3 MPa. Interestingly, increasing the CH4 ratio from 1 to 2 increases slightly the carbon yield, when the temperature was lower than 600 °C. Therefore, to enhance the CH4 yield and avoid the deposition of carbon, a certain content of CH4 in feed gas or product gas for recycling should not be ignored and the temperature should not exceed 600 °C.
3.7 Effect of CO2 content
Usually, the syngas needs to be purified to remove the acidic gas, such as CO2. In this section, the effect of CO2 on the RDR reaction is elucidated. Figure 7 shows the effect of CO2 content on the performance. In Fig. 7a, the increasing of CO2 ratio results in a slightly decrease of CO conversion, because the addition of CO2 inhibits the RDR reaction and probably accelerates the reaction rate of CO2 methanation (R3), based on the Le Chatelier’s principle. Figure 7b, c reveal the effect of CO2 on the selectivities of CH4 and CO2, respectively. As the CO2 amount increases, the selectivity of CH4 decreases gradually at 0.1 and 3 MPa. However, the selectivity of CO2 exhibits the opposite trend, especially when the temperature is higher than 600 °C at 0.1 MPa, the selectivity of CO2 increases significantly under the high CO2 amount. Meanwhile, the carbon yield (see Fig. 7d) drops gradually with an increasing of CO2 ratio, due to the inhibition of Boudouard reaction (R5). To decrease the carbon yield, the addition of CO2 could work at both pressures. In brief, high pressure inhibits carbon formation, however, it is better to remove the CO2 in the syngas to get a high methane yield.
3.8 Effect of O2 content
In addition to steam, air and oxygen are also used as the feed gases for the coal gasification to produce the syngas. Thus, the effect of O2 amount on the RDR reaction is necessary to be studied. The results are shown in Fig. 8. Figure 8a depicts the effect of O2 amount on CO conversion. The CO conversion exhibits almost no change at 200–500 °C at a constant pressure. However, when the temperature is higher than 500 °C, as the O2 amount increases, the CO conversion decreases slightly at 3.0 MPa. It is probably due to that a small amount of O2 reacts with the CH4 (partial oxidation of methane, 1/2O2 + CH4 ↔ CO + 2H2), which changes the CO conversion. Figure 8b shows the effect of O2 amount on CH4 selectivity. In the range of 200–500 °C, as the O2 content rises, the selectivity of CH4 decreases especially at a high pressure. It is because that, when O2 is introduced into the reaction system, it reacts with CO to generate CO2, resulting in the decrease of CH4 selectivity. Another reason could be the reaction of partial oxidation of methane that consumes CH4, which also decreases the CH4 selectivity. From Fig. 8c, the CO2 selectivity increases as the O2 content rises, especially when the temperature is higher than 500 °C at 0.1 MPa. It is due to that the CO and the produced solid carbon are oxygenated by O2, especially at high temperatures. Both of the possibilities result in the increase of CO2 selectivity. In Fig. 8d, the addition of O2 reduces the carbon yield to a large extent at 0.1 and 3 MPa, due to the fact that solid carbon reacts with the O2. It is noticeable that no carbon is formed at 3 MPa when the O2 ratio is 0.1 or 0.2. Therefore, to obtain a high CH4 yield, from the thermodynamic point of view, the feed gas should contain none of O2.
3.9 Effect of C2H4 content
In the process of coal gasification, some trace amounts of high hydrocarbons are produced, such as C2H6 and C2H4. Here, C2H4 is taken as a typical hydrocarbon to study the effect on performance. From Fig. 9a, b, C2H4 slightly affects the CO conversion and CH4 selectivity. This is mainly due to that, C2H4 is not involved in the reactions (R1, R2, R4 and R5), and in which CO is a reactant. This observation agrees with Gao’s results (Gao et al. 2012). However, as shown in Fig. 9c, the CO2 selectivity decreases as the C2H4 ratios increases. Figure 9d shows that the carbon yield rises rapidly with increasing the C2H4 ratio, especially at 0.1 MPa. The temperature corresponding to the maximum carbon yield is around 600 °C. It can be concluded that at low pressure (0.1 MPa) and high temperatures (about 600 °C), the reaction of C2H4 cracking (C2H4 ↔ C + 2H2) should not be ignored. Whereas at high pressure (3 MPa), the carbon yield is remarkably reduced. Therefore, as an impurity, the C2H4 content must be controlled to prevent the formation of solid carbon.
3.10 Comparison between thermodynamic calculations and experimental results
The RDR activity test was carried out on ExCat to compare the experimental results with thermodynamic calculations. Both the results at various temperatures and pressures are shown in Fig. 10. Figure 10a shows the comparisons of CO conversion. Thermodynamically, the equilibrium conversion of CO is almost 100% between 200 and 400 °C, further increasing the temperature decreases the CO conversion, especially at a low pressure (0.1 MPa). Experimental results show that the CO conversion firstly increases and then decreases as the temperature rises and the highest CO conversion was obtained around 400 °C. The high pressure is benefit to improve the CO conversion. It should be noted that the experimental conversion of CO at 400 °C or below is much lower than that of the calculated values, which may be due to the low reaction rate at low temperatures. When the temperature is 400 °C or higher, the experimental results show good accordance with the calculated ones.
Figure 10b shows the CH4 selectivity at various temperatures and pressures. The calculated results shows that increasing temperature decreases the CH4 selectivity, whereas the increasing pressure enhances the CH4 selectivity. At low temperature and pressure, the experimental results are slightly higher than the calculation ones, while at high temperature, the experimental CH4 selectivity is much higher than the calculated one. Figure 10c shows the comparison of CO2 selectivity. The calculation results exhibit that the selectivity of CO2 is constant at various temperatures and pressures, and the experimental results are slightly lower than the calculation ones. The above comparison show that more amount of CO2 converted to CH4 during the reaction. Figure 10d shows the comparison of carbon yields. The calculated carbon yields rose as the temperature increased, and decreased as the pressure increased, which means a large amount of CO is converted to carbon. However, the experimental results show that the yields of carbon were nearly zero, probably due to the catalyst inhibit the formation of carbon. The above discussion show that the experimental results are generally in accordance with the calculated ones at different temperatures and pressures. The result also indicates that the Gibbs free energy minimization method is an ideal tool for thermodynamic analysis of the RDR process.
4 Conclusions
A detailed thermodynamic equilibrium analysis of reverse dry reforming (RDR) reaction by minimizing the Gibbs free energy method in the range of 200–800 °C and 0.1–3 MPa, and an experimental results in the range of 300–550 °C and 0.1–3 MPa are studied. The calculation results demonstrate that low temperature and high pressure are beneficial for the CO conversion and CH4 yield, and high H2/CO ratio (at least 1) promotes CH4 yield and decreases carbon yield. In the range of 200–500 °C and 1–5 MPa, the CO conversion and CH4 yield reach 95%–100% and 43%–50%, respectively. Steam in the feed gas enhances the CO2 selectivity and inhibits the generation of carbon, almost no carbon formed at the H2/CO/H2O ratio of 1/1/0.4, when the temperature is below 600 °C at 3 MPa. CH4 contained in the recycling product gas elevates the CH4 content in the products, but also leads to more solid carbon at 500–800 °C, especially at 0.1 MPa. CO2 has a negative effect on CH4 selectivity, but it could result in a slightly decrease of carbon yield at the temperature higher than 500 °C. O2 is not preferable for increasing CH4 selectivity and decreasing the CO2 selectivity although it decreases the carbon yield. C2H4 is prone to crack, creating a high carbon yield. As impurities, O2 and C2H4 should be completely removed to get a high CH4 yield. The experimental data are consistent with the calculation ones, indicating that minimizing the Gibbs free energy is effective to analyze the RDR reaction thermodynamically. This work is expected to provide a valuable suggestion in the process optimization for SNG production by combining CO methanation with WGS reaction.
Abbreviations
- A k :
-
Total mass of k element in the feed
- f Θ i :
-
Standard-state fugacity of species i (Pa)
- f i :
-
Fugacity of species i (Pa)
- G i :
-
Gibbs free energy of species i (J/mol)
- G Θ i :
-
Standard Gibbs free energy of species i (J/mol)
- ΔG Θ fi :
-
Standard-state Gibbs free energy of formation of species i (J/mol)
- G C(g) :
-
Partial molar Gibbs free energy of gas carbon (J/mol)
- G C(s) :
-
Partial molar Gibbs free energy of solid carbon (J/mol)
- G Θ fC(s) :
-
Standard-state Gibbs function of formation of solid carbon (J/mol)
- △r H Θm :
-
Standard-state reaction enthalpy change (J/mol)
- K Θ :
-
Standard-state equilibrium constant
- n i :
-
Mole of species I (mol)
- n C :
-
Mole of carbon (mol)
- N :
-
Number of components
- P :
-
System pressure (Pa)
- p Θ :
-
Pressure of the standard state (Pa)
- R :
-
Molar gas constant (J/(mol K)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- y i :
-
Mole fraction of species i
- α ik :
-
Number of atoms of the k element present in each molecule of species i
- μ i :
-
Chemical potential of species i (J/mol)
- ϕ i :
-
Fugacity coefficient of species i
- λ k :
-
Lagrange multiplier
References
Adhikari S, Fernando S, Haryanto A (2007) A Comparative Thermodynamic and Experimental Analysis on Hydrogen Production by Steam Reforming of Glycerin. Energy Fuels 21:2306–2310
BP (2016) Statistical Review of World Energy. June
Ensell R, Stroud H (1983) The British gas HICOM methanation process for SNG production. In: Proceedings of the international gas research conference, UK: British Gas Corporation pp 472–481
Gao J, Wang Y, Ping Y, Hu D, Xu G, Gu F, Su F (2012) A thermodynamic analysis of methanation reactions of carbon oxides for the production of synthetic natural gas. RSC Adv 2:2358–2368
Gao J, Liu Q, Gu F, Liu B, Zhong Z, Su F (2015) Recent advances in methanation catalysts for the production of synthetic natural gas. RSC Adv 5:22759–22776
Gao Y, Meng F, Li X, Wen J, Li Z (2016) Factors controlling nanosized Ni-Al2O3 catalysts synthesized by solution combustion for slurry-phase CO methanation: the ratio of reducing valences to oxidizing valences in redox systems. Catal Sci Technol 6:7800–7811
Götz M, Lefebvre J, Mörs F, McDaniel Koch A, Graf F, Bajohr S, Reimert R, Kolb T (2016) Renewable Power-to-Gas: a technological and economic review. Renew Energy 85:1371–1390
Huo J, Yang D, Xia F, Tang H, Zhang W (2013) Feasibility analysis and policy recommendations for the development of the coal based SNG industry in Xinjiang. Energy Policy 61:3–11
Jiang M, Wang B, Lv J, Wang H, Li Z, Ma X, Qin S, Sun Q (2013) Effect of sulfidation temperature on the catalytic activity of MoO3/CeO2–Al2O3 toward sulfur-resistant methanation. Appl Catal A: Gen 466:224–232
Jiang M, Wang B, Yao Y, Wang H, Li Z, Ma X, Qin S, Sun Q (2014) Effect of stepwise sulfidation on a MoO3/CeO2–Al2O3 catalyst for sulfur-resistant methanation. Appl Catal A: Gen 469:89–97
Kopyscinski J, Schildhauer TJ, Biollaz SMA (2010) Production of synthetic natural gas (SNG) from coal and dry biomass—A technology review from 1950 to 2009. Fuel 89:1763–1783
Kumar N, Roy A, Wang Z, L’Abbate EM, Haynes D, Shekhawat D, Spivey JJ (2016) Bi-reforming of methane on Ni-based pyrochlore catalyst. Appl Catal A: Gen 517:211–216
Li H, Yang S, Zhang J, Kraslawski A, Qian Y (2014a) Analysis of rationality of coal-based synthetic natural gas (SNG) production in China. Energy Policy 71:180–188
Li S, Ji X, Zhang X, Gao L, Jin H (2014b) Coal to SNG: technical progress, modeling and system optimization through exergy analysis. Appl Energ 136:98–109
López Ortiz A, Pallares Sámano RB, Meléndez Zaragoza MJ, Collins-Martínez V (2015) Thermodynamic analysis and process simulation for the H2 production by dry reforming of ethanol with CaCO3. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:17172–17179
Lu B, Ju Y, Kawamoto K (2014) Conversion of producer gas using NiO/SBA-15 obtained with different synthesis methods. Int J Coal Sci Technol 1:315–320
Martelli E, Kreutz T, Carbo M, Consonni S, Jansen D (2011) Shell coal IGCCS with carbon capture: conventional gas quench vs. innovative configurations. Appl Energ 88:3978–3989
Meng F, Li Z, Ji F, Li M (2015a) Effect of ZrO2 on catalyst structure and catalytic methanation performance over Ni-based catalyst in slurry-bed reactor. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:8833–8843
Meng F, Li Z, Liu J, Cui X, Zheng H (2015b) Effect of promoter Ce on the structure and catalytic performance of Ni/Al2O3 catalyst for CO methanation in slurry-bed reactor. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 23:250–258
Meng F, Li X, Li M, Cui X, Li Z (2017) Catalytic performance of CO methanation over La-promoted Ni/Al2O3 catalyst in a slurry-bed reactor. Chem Eng J 313:1548–1555
Messerle VE, Ustimenko AB, Lavrichshev OA (2016) Comparative study of coal plasma gasification: simulation and experiment. Fuel 164:172–179
Miguel CV, Soria MA, Mendes A, Madeira LM (2015) Direct CO2 hydrogenation to methane or methanol from post-combustion exhaust streams – A thermodynamic study. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 22:1–8
Nahar GA, Madhani SS (2010) Thermodynamics of hydrogen production by the steam reforming of butanol: analysis of inorganic gases and light hydrocarbons. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:98–109
Roine A (2010) Chemical reaction and equilibrium software with extensive thermo-chemical database. Outokumpu HSC 6.0, Chemistry for Windows
Rönsch S, Schneider J, Matthischke S, Schlüter M, Götz M, Lefebvre J, Prabhakaran P, Bajohr S (2016) Review on methanation – From fundamentals to current projects. Fuel 166:276–296
Sahebdelfar S, Takht Ravanchi M (2015) Carbon dioxide utilization for methane production: a thermodynamic analysis. J Petrol Sci Eng 134:14–22
Shen F, Liu J, Zhang Z, Yang Y (2016) Temporal measurements and kinetics of selenium release during coal combustion and gasification in a fluidized bed. J Hazard Mater 310:40–47
Shinde VM, Madras G (2014) CO methanation toward the production of synthetic natural gas over highly active Ni/TiO2 catalyst. AIChE J 60:1027–1035
Takenaka S, Orita Y, Umebayashi H, Matsune H, Kishida M (2008) High resistance to carbon deposition of silica-coated Ni catalysts in propane stream reforming. Appl Catal A: Gen 351:189–194
Wang W, Cao Y (2012) Combined Carbon Dioxide Reforming with Steam Reforming of Ethanol for Hydrogen Production: thermodynamic Analysis. Int J Green Energy 9:503–516
Wang B, Liu S, Hu Z, Li Z, Ma X (2014) Active phase of highly active Co3O4 catalyst for synthetic natural gas production. RSC Adv 4:57185–57191
Wang Y, Su Y, Zhu M, Kang L (2015) Mechanism of CO methanation on the Ni4/γ-Al2O3 and Ni3Fe/γ-Al2O3 catalysts: a density functional theory study. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:8864–8876
White GA, Roszkowski TR, Stanbridge DW (1975) The RMProcess. Methanation of Synthesis Gas, Advances in Chemistry, American Chemical Society 146:138–148
Yan X, Liu Y, Zhao B, Wang Z, Wang Y, Liu C (2013) Methanation over Ni/SiO2: effect of the catalyst preparation methodologies. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38:2283–2291
Yu Z, Wang F (2010) The technology of Coal gasification. Chemical industry Press, Beijing
Zheng L, Furinsky E (2005) Comparison of Shell, Texaco, BGL and KRW gasifiers as part of IGCC plant computer simulations. Energ Conver Manag 46:1767–1779
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Youth Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 2013021007-4) and National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB723105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, F., Li, X., Lv, X. et al. CO hydrogenation combined with water-gas-shift reaction for synthetic natural gas production: a thermodynamic and experimental study. Int J Coal Sci Technol 5, 439–451 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-017-0177-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-017-0177-y