Abstract
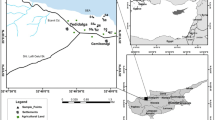
High levels of heavy metals in the environment pose threat to the ecosystem, due to their deleterious effects on humans, animals and plants. The present study aims at determining the extent of pollution of heavy metals such as Fe, Pb, Cr, Zn, Co, Cu and Al in surface soil from Aboabo and Santasi abandoned landfill sites and examining the quality of the soil using pollution indices. In all, 30 soil samples were collected from two study sites and a control sample was also taken from KNUST Botanic Gardens. Concentration of heavy metals were determined using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) after acid digestion. Analyses of the physicochemical parameters revealed that pH of soils from both study sites were slightly alkaline and the soils have a sandy loam texture. At such pH, precipitation of hydroxides and carbonate is induced, leading to limitation in metal mobility. Mean organic matter contents of soil samples were 8.67 ± 7.19 % at Aboabo site and 19.23 ± 4.80 % at Santasi site. High organic content can lead to cation adsorption and reduced metal bioavailability. The study further revealed that mean concentrations of all the heavy metals exceeded their respective levels in the control samples. Correlation analysis of metal concentrations indicated that Pb/Cu correlated at the Aboabo, whereas Cu/Zn, Fe/Pb and Cr/Co showed strong correlation in Santasi site. Heavy metals pollution was assessed using Igeo, contamination factor and PLI, and the results indicated elevated levels of all the metals in soil samples from both areas. Finally, the results indicate that pH and organic content are important barriers to metal distribution in the environment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adedosu HO, Adewuyi GO, Adie GU (2013) Assessment of heavy metals in soil, leachate and underground water samples collected from the vicinity of Olusosun Landfill in Ojota, Lagos, Nigeria. Transnatl J Sci Technol 3(6):73–85
Agyarko K, Darteh E, Berlinger B (2010) Metal levels in some refuse dump soils and plants in Ghana. Plant Soil Environ 56(5):244–251
Akoto O, Ephraim JH, Darko G (2008) Heavy metals pollution in surface soils in the vicinity of abandoned railway servicing workshop in Kumasi, Ghana. Int J Environ Res 2(4):359–364
Appel C, Ma L (2002) Concentration, pH, and surface charge effects on cadmium and lead sorption in three tropical soils. J Environ Qual 31:581–589
Awokunmi EE, Asaolu SS, Ipinmoroti KO (2010) Effect of leaching on heavy metals concentration of soil in some dumpsites. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 4(8):495–499
Bahaa-Eldin EAR, Yusoff I, Abdul Rahim S, Wan Zuhairi WY, Abdul Ghani MR (2008) Heavy metal contamination of soil beneath a waste disposal site at Dengkil, Selangor, Malaysia. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 17(5):449–466
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils. Agro J 54:464
Brady NC, Weil RR (1996) The nature and properties of soils, 11th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
CCME (1999) Canadian council of ministers of the environment updated 2001. Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health. Canadian environmental quality guidelines, 1299
Chang LW (1992) The concept of toxic metal / essential element interactions as a common biomechanism underlying metal toxicity. Toxins in food. Plenum Press, New York, p 61
de Vries W, Römkens PFAM, Schütze G (2007) Critical soil concentrations of cadmium, lead, and mercury in view of health effects on humans and animals. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 191:91–130
Devi CB, Reddy GH, Prasanthi RP, Chetty CS, Reddy GR (2005) Developmental lead exposure alters mitochondrial monoamine oxidase and synaptosomal catecholamine levels in rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 23(4):375–381
Forstner UW, Calmano W (1993) Sediment quality objectives and criteria development in Germany. Water Sci Technol 28:307–316
Kanmani S, Gandhimathi R (2013) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil due to leachate migration from an open dumping site. Appl Water Sci 3(1):193–205
Kumasi Metropolitan Assembly (KMA) (2010) Data for purposes of planning waste management intervention programmes. Kumasi Waste Management Department, Kumasi
Loganathan P (1984) Laboratory manual of soil and plant analysis. Rivers State University of Science and Technology, Port- Harcourt
Ministry of Food and Agriculture (MoFA) (2014) Kumasi metropolitan, background and location. http://mofa.gov.gh. Accessed on 15 March 2015
Mudipalli A (2007) Lead hepatotoxicity and potential health effects. Indian J Med Res 126(6):518–527
Müller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. Geo J 2:108–118
Nriagu JO (1991) Human influence on the global cycling of the metals. In: Farmer JG (ed) Heavy metals in the environment, vol 1. CEP consultants Ltd, Edinburgh, pp 1–5
Ogundiran OO, Afolabi TA (2008) Assessment of the physicochemical parameters and heavy metals toxicity of leachates from municipal solid waste open dumpsite. Int J Environ Sci Technol 5(2):243–250
Okoronkwo NE, Odemelam SA, Ano OA (2006) Levels of toxic elements in soils of abandoned waste dump site. Afr J Biotechnol 5(13):1241–1244
Oluyemi EA, Feuyit G, Oyekunle JAO, Ogunfowokan AO (2008) Seasonal variations in heavy metal concentrations in soil and some selected crops at a landfill in Nigeria. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 2(5):89–96
Opaluwa OD, Aremu MO, Ogbo LO, Abiola KA, Odiba IE, Abubakar MM, Nweze NO (2012) Heavy metal concentrations in soils, plant leaves and crops grown around dump sites in Lafia Metropolis, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Adv Appl Sci Res 3(2):780–784
Owusu-Sekyere E, Harris E, Bonyah E (2013) Forecasting and planning for solid waste generation in the Kumasi Metropolitan Area of Ghana: An ARIMA time series approach. Int J Sci 2:69–83
Oyedele DJ, Gasu MB, Awotoye OO (2008) Changes in soil properties and plant uptake of heavy metals on selected municipal solid waste dump sites in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 3(5):107–115
Porteus A (1985) Hazardous waste management handbook. Butterworth and Co Publishers, UK, pp 146–166
Shepherd KD, Walsh GM (2002) Development of reflectance spectral libraries for characterization of soil properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:988–998
Sherene T (2010) Mobility and transport of heavy metals in polluted soil environment. Biol Forum 2(2):112–121
Storer AD (2008) A simple high sample volume ashing procedure for determination of soil organic matter. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 15:759–772
Sukop H, Blume HP, Kunick W (1979) In: Laurie IC (ed) The soil, flora and vegetation of Berlin’s waste land, Nature in cities- The natural environment in the design and development of urban green space. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, pp 115–132
Thomilson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problem in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol Mar Res 33:566–575
Tumuklu AY, Sonmez MG (2007) Detection of heavy metal concentrations in soil caused by Nigde City Garbage Dump. Pol J Environ Stud 16(4):651–658
Uba SA, Uzairu G, Harrison FS, Balarabe ML, Okunola OJ (2007) Assessment of heavy metals bioavailability in dumpsites of Zaria Metropolis, Nigeria. Afr J Biotechnol 7(2):122–130
Vandana P, Murthya NN, Praveen RS (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil around hazardous waste disposal sites in Hyderabad city (India): natural and anthropogenic implications. J EnvironRes Manag 2(2):27–34
Xiaoli C, Shimaoka T, Xianyan C, Qiang G, Youcai Z (2007) Characteristics and mobility of heavy metals in an MSW landfill: implications in risk assessment and reclamation. J Hazard Mater 144(1–2):485–491
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Ghana Government Research Allowance and the MSc. Fellowship awarded to Mr. Collins Nimako by the Scholarship secretariat in Ghana. We thank the staff of the ECOLAB at the University of Ghana for their help during the chemical analysis of the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akoto, O., Nimako, C., Asante, J. et al. Heavy Metals Enrichment in Surface Soil from Abandoned Waste Disposal Sites in a Hot and Wet Tropical Area. Environ. Process. 3, 747–761 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0183-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0183-x