Abstract
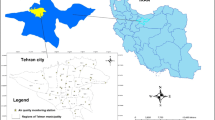
This paper presents a methodology of determining the air pollution potential based on pollutant source identification and meteorological parameters, using as a case study the Isfahan Province in Iran. First, taking the county as the evaluation unit, the regional air pollution information system database of Isfahan Province was established, supported by Geographic Information Systems. Then, the air pollution potential of the study area was assessed based on the analysis of regional air pollution, review of available literature, seeking advice from experts, and using determining factors such as population density, traffic, industries, wind speed, precipitation, temperature and humidity. A layer for each factor was prepared in GIS. After data acquisition, criteria were set and weighted by experts. Finally, all criteria were integrated using the Weighted Linear Combination method to obtain the spatial distribution of air pollution potential. The results showed that 55 % of the total land area in Isfahan Province maintains a high to moderate level of air pollution potential resulting from unsuitable meteorological conditions along with high density of emissions from human activities. However, winds counteract the serious air pollution in some parts. The results suggest that very strict air quality management is needed in days of low wind speed, especially at places of increased air pollution resulting from human activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achillas C, Vlachokostas C, Moussiopoulos N, Banias G (2011) Prioritise strategies to confront environmental deterioration in urban areas: multicriteria assessment of public opinion and experts' views. Cities 28:414–423
Asgharpour M (2006) Multicriteria analysis, 4th edn. Tehran press, University of(in Farsi)
Bahattinn G, Ibrahim K (2007) The relation between meteorological factors and pollutants concentrations in Karabük city. G.U. Journal of Science 20(4):87–95
Bay Area Air Quality Management District (1998) Climate, Physiography, and air Pollution Potential, Bay Area and its sub-Regions http://www.baaqmd.gov/~/media/files/board-of-directors/2008/brd_agenda_120308.pdf?la=en
Bayat R (2005) Source apportionment of Tehran’s air pollution. Sharif University of Technology, Dissertation(in Farsi)
Brown B (1968) Delphi process: a methodology used for the elicitation of opinions of experts, an earlier paper published by RAND (document no: P-3925, 1968, 15 pages) Sta. Monica, California
Cairncross E, John J, Zunckel MA (2007) Novel air pollution index based on the relative risk of daily mortality associated with short-term exposure to common air pollutants. Atmos Environ 41:8442–8454
Cox, W (2000) How urban density intensifies traffic congestion and air pollution. Golden Water Institute. americandreamcoalition.org/landuse/denseair.pdf
Curtis L, Rea W, Smith-Willis P, Fenyves E, Pan Y (2006) Adverse health effects of outdoor air pollutants. Environ Int 32(6):815–830
Dalkey NC, Helmer O (1963) An experimental application of the Delphi method to the use of experts. Manag Sci 9(3):458–467
Drobne S, Lisec A (2009) Multi-attribute decisions analysis in GIS, weighted linear combination and ordered weighted averaging. Informatica 33:459–474
EPA Report (2010) Density, Traffic Density and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) Emission Air Pollution Density in Major Metropolitan Areas of the United States. http://www.demographia.com/db-countynox.pdf
Ezatiean V (2007) Investigation of atmospheric parameters on air pollution, case study, Isfahan city, Iran. Isfahan University, Dissertation(in Farsi)
Gassmann M, Mazzeo N (2000) Air pollution potential: regional study. Environ Manag 25(4):375–382
Gouveia NC, Maisonet M (2005) Health Effects of Air Pollution: An overview. In Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update ; World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe: Geneva, Switzerland: 87–109
Gregory C, Davis JC (2003) Using multiple logistic regression and GIS technology to predict landslide hazard in northeast Kansas, USA. Eng Geol 69:331–343
Henschel S, Atkinson A, Zeka A, Tertre A, Analitis A, Katsouyanni K, Chanel O, Pascal M, Forsberg B, Medina S, Goodman PG (2012) Air pollution interventions and their impact on public health. Int J Public Health 57:757–768
Heuvelink M (1993) Error propagation in quantitative spatial modeling: applications in geographical information systems. University of Utrecht, Dissertation
Hosseiniebalam F, Ghaffarpasand O (2014) The effect of emission sources and meteorological factors on Sulphur dioxide concentration of great Isfahan, Iran. Atmos Environ 100:94–101
Jayamurugan R, Kumaravel B, Palanivelraja S, Chockalingam MP (2013) Influence of temperature, relative humidity and seasonal variability on ambient air quality in a coastal urban area. International Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, Article ID 264046, 7 pages
Khedairia S, Khadir MT (2012) Impact of clustered meteorological parameters on air pollutants concentrations in the region of Annaba, Algeria. Atmos Res 113:89–101
Latza U, Gerdes S, Baur X (2009) Effects of nitrogen dioxide on human health: systematic review of experimental and epidemiological studies conducted between 2002 and 2006. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212(3):271–287
Lin M, Lin Y (2002) Application of GIS to air quality analysis in Taichung city, Taiwan. Environ Model Softw 17:11–19
Mahini AS, Gholamalifard M (2006) Siting MSW landfill with a weighted linear combination methodology in a GIS environment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3(4):435–445
Malczewski J (1999) GIS and multi criteria decision analysis. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Matejicek L (2005) Spatial modeling of air pollution in urban areas with GIS: a case study on integrated database development. Adv Geosci 4:63–68
Mendoza GA, Martins H (2006) Multi-criteria decision analysis in natural resource management: a critical review of methods and new modeling paradigms. For Ecol Manag 230:1–22
Moeinaddini M, Khorasani N, Danehkar A, Darvishsefat A, Zienalyan M (2010) Siting MSW landfill using weighted linear combination and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) methodology in GIS environment (case study: Karaj). Waste Manag 30:912–920
Mofarrah A T, Husain Badr H (2011) Design of urban air quality monitoring network: fuzzy based multi-criteria decision making approach. Air Quality Monitoring, Assessment and Management, Dr. Nicolas Mazzeo (Ed.), ISBN: 978–953-307-317-0
Mui-How P, Mitsuhiro M (2005) GIS-based multi-criteria decision making approach to forest conservation planning at a landscape scale: a case study in the kinabalu area, Sabah, Malaysia. Urban and Landscape Planning 71:207–221
Mulaku GC, Kariuki LW (2001) Mapping and analysis of air pollution in Nairobi. Kenya. International Conference on Spatial Information for Sustainable Development, Nairobi, Kenya
Nas B, Cay T, Iscan F, Berktay A (2010) Selection of MSW landfill site for Konya, Turkey, using GIS and multi-criteria evaluation. Environ Monit Assess 160(1–4):491–500
Norouzi M (2012) Mapping environmental quality statues of Isfahan province using multi criteria evaluation. Dissertation, Isfahan University of Technology (in Farsi)
Pisoni E, Carnevale C, Volta M (2009) Multi-criteria analysis for PM10 planning. Environment 43:4833–4842
Rowe G, Wright G (1999) The Delphi technique as a forecasting tool: issues and analysis. Int J Forecast 15(4):353–375
Safavi SY, Alijani B (2006) Investigate meteorological and geographical parameters in air pollution, Tehran, Iran. Geogr Res 58:99–112(in Farsi)
Sanaei M, Falah Shamsi S (2010) Range product site selection using WLC and OWA, case study, farokhzad-e- shiraz, Iran. Journal of Range and Watershed Sciences 2:216–227(in Farsi)
Setayesh B, Sadeqian B (2012) Investigation of mining industries concentrated on air pollution of Isfahan city. National conference of sustainable development and urban development. Isfahan, Iran(in Farsi)
Statistical Center of Iran (2013) National census of population and housing, technical report. http://www.amar.org.ir/english
Stephen C, Hurlock J (2004) GIS in air pollution research, the role of building surfaces. ESRI International User Conference San Diego, California
Thapa RB, Murayama Y (2008) Land evaluation for peri-urban agriculture using analytical hierarchical process and geographic information system techniques: a case study of Hanoi. Land Use Policy 25:225–239
Ventura AT, Ellis JH (1991) Multiobjective air pollution monitoring network design. Atmos Environ 25:469–479
Viswanathanand P, Krishna C (1989) Ecotoxicology and climate, effects of temperature and humidity on ecotoxicology of chemicals. Ed. by P. Bourdeau, J. A. Haines, W. Klein and C. R. Krishna, John Wiley & Sons, pp:139–152
UNEP/WHO (1992) Urban air pollution in megacities of the world. Blackwell, Oxford. http://alpha.chem.umb.edu/chemistry/ch471/documents/mageetal.pdf
Ying B, Minga Z, Qiua CL (2007) Combining AHP with GIS in synthetic evaluation of eco-environment quality, a case study of Hunan province, China. Ecol Model 209:97–109
Zambelli P, Geneletti D, Ragazzi M, Ciolli M (2012) Using spatial multi criteria analysis to design an air quality monitoring network considering source pollutants and receptors. Submitted to journal of Environment Management. http://www.ing.unitn.it/~zambelli/ftp/misc/PietroSMCA4AQMN.pdf
Zarkesh M, Almasi N, Taghizadeh F (2011) Ecotourism land capability evaluation using spatial multi criteria evaluation. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 3(7):693–700
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Department of Natural Resources at Isfahan University of Technology. The authors wish to thank Iran Meteorology Organization, Department of Isfahan Environment, and Mine, Industry and Commerce Organization of Isfahan for supplying the data used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi, H., Soffianian, A., Mirghaffari, N. et al. Determining Air Pollution Potential Using Geographic Information Systems and Multi-criteria Evaluation: A Case Study in Isfahan Province in Iran. Environ. Process. 3, 229–246 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0136-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0136-4