Abstract
Background
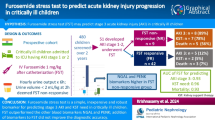
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common among critically ill children and these children are at risk of developing acute kidney disease (AKD).
Methods
A prospective cohort study was conducted on children aged > 1 month to ≤ 18 years old admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (ICU) of Hong Kong Children’s Hospital from 6/2020 to 6/2021. The incidences and risk factors of both AKI and AKD were determined.
Results
There were 254 eligible admissions (58.3% in males, with a median age of 4.9 [9.7] years). The overall AKI incidence was 41.7% and 56% of children who remained hospitalized in the pediatric ICU for ≥ 7 days after acquiring AKI developed AKD. Cardiac surgery, bone marrow transplantation and requirement of inotropes were risk factors for both AKI and AKD. The requirement of non-invasive ventilation [relative risk (RR): 2.625 (1.361, 5.064)], total medication dose [RR 1.006 (1.002, 1.010)] and maximal medication intensity [RR 1.154 (1.038, 1.283)] were additional determinants of AKI. Factors indicating more severe AKI and AKI progression were predictive of AKD development. The overall mortality in the pediatric ICU was 3.1%. AKI was significantly associated with mortality (p < 0.001), longer length of hospitalization in the pediatric ICU (p < 0.001) and hospital stay (p < 0.001). AKD was associated with a lower estimated glomerular filtration rate at discharge from the pediatric ICU (p = 0.036).
Conclusion
AKI and AKD were common among critically ill children, and were associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Few modifiable risk factors, especially those related to nephrotoxic medication exposure, were associated with AKI development and AKD progression.
Graphical abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 May 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-023-01656-2
References
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002231
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11:R31. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc5713
Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl 2:1–138
Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, Goldstein SL, Investigators AWARE (2017) Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N Engl J Med 376(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1611391
De Zan F, Amigoni A, Pozzato R, Pettenazzo A, Murer L, Vidal E (2020) Acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a retrospective analysis of risk factors. Blood Purif 49(1–2):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502081
Naik S, Sharma J, Yengkom R, Kalrao V, Mulay A (2014) Acute kidney injury in critically ill children: risk factors and outcomes. Indian J Crit Care Med 18(3):129–133. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-5229.128701
Slater MB, Gruneir A, Rochon PA, Howard AW, Koren G, Parshuram CS (2016) Risk factors of acute kidney injury in critically ill children. Pediatr Crit Care Med 17(9):e391-398. https://doi.org/10.1097/PCC.0000000000000859
Alkandari O, Eddington KA, Hyder A, Gauvin F, Ducruet T, Gottesman R, Phan V, Zappitelli M (2011) Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for pediatric intensive care unit mortality, longer length of stay and prolonged mechanical ventilation in critically ill children: a two-center retrospective cohort study. Crit Care 15(3):R146. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc10269
Louzadaa CF, Ferreira AR (2021) Evaluation of the prevalence and factors associated with acute kidney injury in a pediatric intensive care unit. J Pediatr 97:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jped.2020.08.003
Sigurjonsdottir VK, Chaturvedi S, Mammen C, Sutherland SM (2018) Pediatric acute kidney injury and the subsequent risk for chronic kidney disease: is there cause for alarm? Pediatr Nephrol 33(11):2047–2055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3870-6
Chawla LS, Bellomo R, Bihorac A, Goldstein SL, Siew ED, Bagshaw SM, Bittleman D, Cruz D, Endre Z, Fitzgerald RL, Forni L, Kane-Gill SL, Hoste E, Koyner J, Liu KD, Macedo E, Mehta R, Murray P, Nadim M, Ostermann M, Palevsky PM, Pannu N, Rosner M, Wald R, Zarbock A, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Acute Disease Quality Initiative Workgroup 16 (2017) Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(4):241–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.2
Menon S, Goldstein SL, Mottes T, Fei L, Kaddourah A, Terrell T, Arnold P, Bennett MR, Basu RK (2016) Urinary biomarker incorporation into the renal angina index early in intensive care unit admission optimizes acute kidney injury prediction in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 31(4):586–594. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfv457
Fitzgerald JC, Ross ME, Thomas NJ, Weiss SL, Balamuth F, Anderson AH (2018) Risk factors and inpatient outcomes associated with acute kidney injury at pediatric severe sepsis presentation. Pediatr Nephrol 33(10):1781–1790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3981-8
Schwartz GJ, Muñoz A, Schneider MF, Mak RH, Kaskel F, Warady BA, Furth SL (2009) New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(3):629–637. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2008030287
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A (1976) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58(2):259–263
Joannidis M, Forni LG, Klein SJ, Honore PM, Kashani K, Ostermann M, Prowle J, Bagshaw SM, Cantaluppi V, Darmon M, Ding X, Fuhrmann V, Hoste E, Husain-Syed F, Lubnow M, Maggiorini M, Meersch M, Murray PT, Ricci Z, Singbartl K, Staudinger T, Welte T, Ronco C, Kellum JA (2020) Lung-kidney interactions in critically ill patients: consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 21 Workgroup. Intensive Care Med 46(4):654–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05869-7
Antonelli M, Conti G, Rocco M, Bufi M, de Blasi RA, Vivino G, Gasparetto A, Meduri GU (1998) A comparison of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation and conventional mechanical ventilation in patients with acute respiratory failure. N Engl J Med 339(7):429–435. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199808133390703
Ehrmann S, Helms J, Joret A, Martin-Lefevre L, Quenot JP, Herbrecht JE, Benzekri-Lefevre D, Robert R, Desachy A, Bellec F, Plantefeve G, Bretagnol A, Dargent A, Lacherade JC, Meziani F, Giraudeau B, Tavernier E, Dequin PF, Clinical research in intensive care and sepsis-Trial group for global evaluation and research in sepsis (CRICS-TRIGGERSEP network) (2019) Nephrotoxic drug burden among 1001 critically ill patients: impact on acute kidney injury. Ann Intensive Care 9(1):106. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-019-0580-1
Goldstein SL, Mottes T, Simpson K, Barclay C, Muething S, Haslam DB, Kirkendall ES (2016) A sustained quality improvement program reduces nephrotoxic medication-associated acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 90(1):212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.03.031
Bhatraju PK, Zelnick LR, Chinchilli VM, Moledina DG, Coca SG, Parikh CR, Garg AX, Hsu CY, Go AS, Liu KD, Ikizler TA, Siew ED, Kaufman JS, Kimmel PL, Himmelfarb J, Wurfel MM (2020) Association between early recovery of kidney function after acute kidney injury and long-term clinical outcomes. JAMA Netw Open 3(4):202682–7. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.2682
Siew ED, Abdel-Kader K, Perkins AM, Greevy RA Jr, Parr SK, Horner J, Vincz AJ, Denton J, Wilson OD, Hung AM, Robinson-Cohen C, Matheny ME (2020) Timing of recovery from moderate to severe AKI and the risk for future loss of kidney function. Am J Kidney Dis 75(2):204–213. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.05.031
Forni LG, Darmon M, Ostermann M, Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Pettilä V, Prowle JR, Schetz M, Joannidis M (2017) Renal recovery after acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med 43(6):855–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-017-4809-x
Goldstein SL (2014) Renal recovery at different ages. Nephron Clin Pract 127(14):21–24. https://doi.org/10.1159/000363679
van de Eynde J, Salaets T, Louw JJ, Herman J, Breysem L, Vlasselaers D, Desmet L, Meyns B, Budts W, Gewillig M, Mekahli D (2022) Persistent markers of kidney injury in children who developed acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc 11(7):024266–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.121.024266
Lugthart G, Jordans CCE, de Pagter APJ, Bresters D, Jol-van der Zijde CM, Bense JE, van Rooij-Kouwenhoven RWG, Sukhai RN, Louwerens M, Dorresteijn EM, Lankester AC (2021) Chronic kidney disease ten years after pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Kidney Int 100(4):906–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.05.030
Vanmassenhove J, Steen J, Vansteelandt S, Morzywolek P, Hoste E, Decruyenaere J, Benoit D, Van Biesen W (2021) The importance of the urinary output criterion for the detection and prognostic meaning of AKI. Sci Rep 11(1):11089. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-90646-0
Kellum JA, Sileanu FE, Murugan R, Lucko N, Shaw AD, Clermont G (2015) Classifying AKI by urine output versus serum creatinine level. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(9):2231–2238. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014070724
Macedo E, Bouchard J, Soroko SH, Chertow GM, Himmelfarb J, Ikizler TA, Paganini EP, Mehta RL for the Program to improve care in acute renal disease study (2010) Fluid accumulation, recognition and staging of acute kidney injury in critically-ill patients. Crit Care 14(3):R82. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc9004
Paquette F, Bernier-Jean A, Brunette V, Ammann H, Lavergne V, Pichette V, Troyanov S, Bouchard J (2015) Acute kidney injury and renal recovery with the use of aminoglycosides: a large retrospective study. Nephron 131(3):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1159/000440867
Cooper DJ, Plewes K, Grigg MJ, Patel A, Rajahram GS, William T, Hiemstra TF, Wang Z, Barber BE, Anstey NM (2021) An evaluation of commonly used surrogate baseline creatinine values to classify AKI during acute infection. Kidney Int Rep 6(3):645–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2020.12.020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. The authors did not receive any financial support from any organization for the submitted work.
Human and animal rights
The study complied with Declaration of Helsinki and was conducted in accordance with the approved protocol of the research ethics committee of the Hong Kong Children’s Hospital (HKCH-REC-2020-007).
Informed consent
Informed consent has been obtained from the parents.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, W.F., Chan, V.P.Y., Cheung, W.L. et al. Risk factors for development of acute kidney injury and acute kidney disease in critically ill children. J Nephrol 36, 1425–1434 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-023-01613-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-023-01613-z