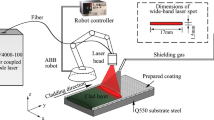
Abstract
Laser metal deposition (LMD) has attracted global interest due to its capacity to fabricate wear-resistant materials. However, the magnitude of heat input is crucial during the manufacturing of hard-facing alloys. This study explores the potential of LMD to deposit Co/WC composite coatings using different laser beam emission modes—specifically, continuous and pulsed waves. Co-based coatings without WC were also fabricated for comparative analysis. The primary characteristics of the coatings, including macro- and microstructural evaluations, chemical and phase composition, hardness, and wear resistance, were systematically studied and compared to laser emission type, track overlapping percentage, and laser delay time. Results indicate the homogeneous distribution of hard WC particles along the coatings, regardless of the process parameters. A notable finding is the fine-grained microstructure developed when employing a pulsed-wave laser condition, further enhanced with increased delay time. The pulsed-wave mode inhibits the dissolution of WC particles, whereas secondary carbides are formed in the coatings under continuous-wave mode. The hardness of Co/WC composite coatings is 1.2 to 1.5 times higher than that of Co coatings. Partial WC dissolution positively influences the wear rate of composite coatings, reducing its value by 1.9 to 3.7 times.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Hasan, M.S., Mazid, A.M., Clegg, R.: The basics of stellites in machining perspective. Int. J. Eng. Mater. Manuf. 1, 35–50 (2016). https://doi.org/10.26776/IJEMM.01.02.2016.01
Pauzi, A.A., Husin, S.: Study on the effect of wear resistant materials applications in reducing wear damage of gas turbine combustor components. Appl. Mech. Mater. 575, 17–21 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/AMM.575.17
Foster, J., Cullen, C., Fitzpatrick, S., Payne, G., Hall, L., Marashi, J.: Remanufacture of hot forging tools and dies using laser metal deposition with powder and a hard-facing alloy stellite 21®. J. Remanufacturing. 9, 189–203 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/S13243-018-0063-9
Davis, J.R.: Nickel, Cobalt, and their alloys. ASM Int. Mater. Park OH (2000)
Bartkowski, D., Bartkowska, A.: Wear resistance in the soil of Stellite-6/WC coatings produced using laser cladding method. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 64, 20–26 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.12.013
Lian, G., Yao, M., Liu, Z., Yang, S., Chen, C., Wang, H., Xiang, Y., Cong, W.: Near-net shaping control of triangular stacking in laser cladding process. Procedia Manuf. 34, 233–238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROMFG.2019.06.144
Li, W., Xu, P., Wang, Y., Zou, Y., Gong, H., Lu, F.: Laser synthesis and microstructure of micro- and nano-structured WC reinforced co-based cladding layers on titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 749, 10–22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2018.03.235
Moradi, M., Ashoori, A., Hasani, A.: Additive manufacturing of stellite 6 superalloy by direct laser metal deposition – part 1: Effects of laser power and focal plane position. Opt. Laser Technol. 131, 106328 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106328
Zieliński, A., Smoleńska, H., Serbiński, W., Kończewicz, W., Klimpel, A.: Characterization of the co-base layers obtained by laser cladding technique. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 164–165, 958–963 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMATPROTEC.2005.02.093
Díaz, E., Amado, J.M., Montero, J., Tobar, M.J., Yáñez, A.: Comparative study of co-based alloys in repairing low cr-mo steel components by laser cladding. Phys. Procedia. 39, 368–375 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHPRO.2012.10.050
Toyserkani, E., Khajepor, A., Corbin, S.: Laser Cladding. CRC Press LLC, USA (2005)
Morrow, W.R., Qi, H., Kim, I., Mazumder, J., Skerlos, S.J.: Environmental aspects of laser-based and conventional tool and die manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 15, 932–943 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2005.11.030
Dev Singh, D., Arjula, S., Raji Reddy, A.: Functionally graded materials manufactured by direct energy deposition: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 47, 2450–2456 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2021.04.536
Ghosal, P., Majumder, M.C., Chattopadhyay, A.: Study on direct laser metal deposition. Mater. Today Proc. 5, 12509–12518 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2018.02.232
Amado, J.M., Tobar, M.J., Alvarez, J.C., Lamas, J., Yánez, A.: Laser cladding of tungsten carbides (Spherotene®) hardfacing alloys for the mining and mineral industry. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 5553–5556 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2008.07.198
Shah, K., Pinkerton, A.J., Salman, A., Li, L.: Effects of melt pool variables and process parameters in laser direct metal deposition of aerospace alloys. Mater. Manuf. Process. 25, 1372–1380 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2010.480999
Wu, T., Shi, W., Xie, L., Gong, M., Huang, J., Xie, Y., He, K.: Effect of preheating temperature on geometry and mechanical properties of laser cladding-based stellite 6/wc coating. Materials. 15, 3952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113952
Ahmed, N.: Direct metal fabrication in rapid prototyping: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 42, 167–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.05.001
Moradi, M., Hasani, A., Malekshahi Beiranvand, Z., Ashoori, A.: Additive manufacturing of stellite 6 superalloy by direct laser metal deposition – part 2: Effects of scanning pattern and laser power reduction in differrent layers. Opt. Laser Technol. 131, 106455 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OPTLASTEC.2020.106455
Zhang, H., Zou, Y., Zou, Z., Zhao, W.: Comparative study on continuous and pulsed wave fiber laser cladding in-situ titanium-vanadium carbides reinforced Fe-based composite layer. Mater. Lett. 139, 255–257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.10.102
Wang, G., Zhang, J., Shu, R., Yang, S.: High temperature wear resistance and thermal fatigue behavior of Stellite-6/WC coatings produced by laser cladding with co-coated WC powder. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 81, 63–70 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2019.02.024
Li, B., Jin, Y., Yao, J., Li, Z., Zhang, Q.: Solid-state fabrication of WCp-reinforced Stellite-6 composite coatings with supersonic laser deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 321, 386–396 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.04.062
Thawari, N., Chandak, G.C., Gupta, A.: Influence of laser cladding parameters on distortion, thermal history and melt pool behaviour in multi-layer deposition of stellite 6: In-situ measurement. J. Alloys Compd. 860, 157894 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2020.157894
Ostolaza, M., Zabala, A., Arrizubieta, J.I., Llavori, I., Otegi, N., Lamikiz, A.: High-temperature tribological performance of functionally graded Stellite 6/WC metal matrix composite coatings manufactured by laser-directed energy deposition. Friction. 12, 522–538 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/S40544-023-0790-2/METRICS
Bartkowski, D., Kinal, G.: Microstructure and wear resistance of Stellite-6/WC MMC coatings produced by laser cladding using yb:YAG disk laser. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 58, 157–164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.04.017
Sun, S., Durandet, Y., Brandt, M.: Parametric investigation of pulsed nd: YAG laser cladding of stellite 6 on stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 194, 225–231 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFCOAT.2004.03.058
Wang, X., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Hu, Z., Li, X.: Macroscopic morphology and properties of cobalt-based laser cladding layers on rail steel based on pulse shaping. Opt. Laser Technol. 168, 109940 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OPTLASTEC.2023.109940
Sun, S., Durandet, Y., Brandt, M.: Melt pool temperature and its effect on clad formation in pulsed nd:Yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser cladding of stellite 6. J. Laser Appl. 19, 32–40 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.2402524
Sun, S., Brandt, M.: Comparison between continuous wave and pulsed Nd:YAG laser cladding of stellite 6. ICALEO 2004–23rd Int Congr Appl Laser Electro-Optics, Congr. Proc. (2004). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.5060303/1002632
Cuevas-Mercado, C.E.: Fabricación De recubrimientos de aleación base Co Y Co/WC mediante la técnica de deposición de Metal por Laser (in Spanish). Autonomous University of Zacatecas (2023)
E384 Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. Accessed 15 Feb 2023. https://www.astm.org/e0384-17.html
G99 Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin: -on-Disk Apparatus. https://www.astm.org/g0099-17.html. Accessed 10 Jul 2023
Easterling, K.E.: Introduction to the Physical Metallurgy of Welding, 2nd edn. Butterworth Heinemann Ltd (1992)
Ganesh, P., Moitra, A., Tiwari, P., Sathyanarayanan, S., Kumar, H., Rai, S.K., Kaul, R., Paul, C.P., Prasad, R.C., Kukreja, L.M.: Fracture behavior of laser-clad joint of Stellite 21 on AISI 316L stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 527, 3748–3756 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2010.03.017
Hemmati, I., Ocelík, V., De Hosson, J.T.M.: Dilution effects in laser cladding of Ni–Cr–B–Si–C hardfacing alloys. Mater. Lett. 84, 69–72 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.06.054
Zanzarin, S., Bengtsson, S., Molinari, A.: Study of dilution in laser cladding of a carbon steel substrate with Co alloy powders. Powder Metall. 59, 85–94 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/00325899.2015.1118842
Vilar, R.: Laser cladding. J. Laser Appl. 11, 64–79 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.521888
Pacheco, J.T., da Silva, L.J., Barbetta, L.D., Santos Ferreira, H., Taveira Veiga, M., Forni, R., Teixeira, M.F.: Laser cladding of stellite-6 on AISI 316 L austenitic stainless steel: Empirical-statistical modeling and parameter optimization. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 8, 1–14 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S40516-020-00132-0/METRICS
Gan, Z., Yu, G., He, X., Li, S.: Numerical simulation of thermal behavior and multicomponent mass transfer in direct laser deposition of co-base alloy on steel. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 104, 28–38 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEATMASSTRANSFER.2016.08.049
Kurz, W., Bezençon, C., Gäumann, M.: Columnar to equiaxed transition in solidification processing. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2, 185–191 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1468-6996(01)00047-X
Xiao, H., Li, S., Han, X., Mazumder, J., Song, L.: Laves phase control of Inconel 718 alloy using quasi-continuous-wave laser additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 122, 330–339 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.004
Li, S., Xiao, H., Liu, K., Xiao, W., Li, Y., Han, X., Mazumder, J., Song, L.: Melt-pool motion, temperature variation and dendritic morphology of Inconel 718 during pulsed- and continuous-wave laser additive manufacturing: A comparative study. Mater. Des. 119, 351–360 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.01.065
Kazymyrovych, V., Kryzhanivskyy, V.: Thermal properties of cemented carbides used for metal cutting. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 111, 106097 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2022.106097
Zhou, Y., Wen, S., Wang, C., Duan, L., Wei, Q., Shi, Y.: Effect of TiC content on the Al-15Si alloy processed by selective laser melting: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Opt. Laser Technol. 120, 105719 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105719
De Lovelock, V.: Powder/Processing/Structure relationships in WC-Co thermal spray coatings: A review of the published literature. J. Therm. Spray. Technol. 7, 357–373 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1361/105996398770350846
Zanzarin, S., Bengtsson, S., Molinari, A.: Study of carbide dissolution into the matrix during laser cladding of carbon steel plate with tungsten carbides-stellite powders. J. Laser Appl. 27, S29209 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4906480
Sassatelli, P., Bolelli, G., Lassinantti Gualtieri, M., Heinonen, E., Honkanen, M., Lusvarghi, L., Manfredini, T., Rigon, R., Vippola, M.: Properties of HVOF-sprayed Stellite-6 coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 338, 45–62 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFCOAT.2018.01.078
Ates, S., Aslan, O., Tümer, M., Arisoy, C.F.: Impact sliding wear behavior of stellite 6 and stellite 12 hardfacings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 313, 128762 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2023.128762
Wang, R., Ye, S., Cheng, P., Xie, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, G., Wu, W., Lu, X.: Microstructure and wear resistance of in-situ TiC reinforced Stellite 6 coating using PTA cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 27, 2656–2669 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMRT.2023.10.053
Navas, C., Conde, A., Cadenas, M., De Damborenea, J.: Tribological properties of laser clad stellite 6 coatings on steel substrates. Surf. Eng. 22, 26–34 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1179/174329406X84949
Acknowledgements
Authors are gratefully acknowledged to Consejo Nacional de Humanidades Ciencias y Tecnologías (CONAHCyT) for financial support. The authors also thank the program Investigadores por México- CONAHCyT (Project number 2015-85 and 2018-131).
Funding
Funding provided by Consejo Nacional de Humanidades Ciencias y Tecnologías (CONAHCyT) under projects 275,781, 297,265 and 296,384, and master’s scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: H.R.L., C.F.M.; Supervision: H.R.L., C.F.M.; Formal analysis: H.R.L., J.M.G.C.; Visualization: H.R.L., J.M.G.C.; Writing- Original draft preparation: H.R.L., C.F.M.; Writing- Reviewing and Editing: H.R.L., C.F.M., J.M.G.C., J.M.A.O.; Methodology: C.E.C.M., C.F.M., J.R.O.; Investigation: C.E.C.M., J.R.O.; Resources: C.F.M., J.M.A.O.; Funding acquisition: J.M.A.O.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known conflict of interest or competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Luna, H., Cuevas-Mercado, C.E., Félix-Martínez, C. et al. Co-based and Co/WC Laser Metal Deposition: A Comparative Study between Continuous and Pulsed Wave Laser Process Conditions. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 11, 447–468 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-024-00255-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-024-00255-8