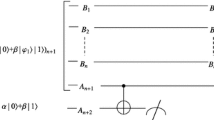
Abstract
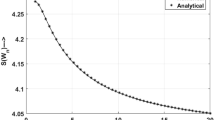
In this work, we have applied the entanglement concentration protocols to partially entangled subsets of classes of highly entangled multi-qubit states, created on IBM quantum computer. The highly entangled multi-qubit states like Z-states and cluster states act as a powerful resource in measurement based computation model. The success of the protocol is analysed through calculating the success probability obtained from the IBM quantum computer and simulator with which the protocol can generate maximally entangled states. The results of the protocol obtained from the IBM simulator are in close agreement with the theoretical predictions of the protocol, however, the results of IBMQ computer show comparative deviations due to large amount of gate errors, qubit errors and readout errors.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Einstein, A., Rosen, N., Podolsky, B.: Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete?. Phys. Rev. 47, D (1935)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s Theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography. Sci. Am. 267, 50–57 (1992)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one-and two-particle operators on Einstein Podolsky Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2881 (1992)
Menicucci, N. C., Loock, P. V., Gu, M., Weedbrook, C., Ralph, T. C., Nielsen, M. A.: Universal quantum computation with continuous-variable cluster states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 110501 (2006)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829–1834 (1999)
Shukla, C., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Semi-quantum communication: protocols for key agreement, controlled secure direct communication and dialogue. Quant. Inf. Process. 16, 295 (2017)
Hu, J.Y., Yu, B., Jing, M.Y., Xiao, L.T., Jia, S.T., Qin, G.Q., Long, G.L.: Experimental quantum secure direct communication with single photons. Light Sci. Appl. 5, e16144 (2016)
Horodecki, R., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, K.: Quantum enatanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865–942 (2009)
Schlosshauer, M.: Decoherence and the Quantum to Classical Transition. Springer (2007)
Bennett, C.H., Bernstein, H.J., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B.: Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys. Rev. A 53, 2046–2052 (1996)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wooters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722–725 (1996)
Sheng, Y. B., Deng, F. G., Zhou, H. Y.: Single-photon entanglement concentration for long distance quantum communication (2009). arXiv:0907.0050
Kimble, H.J.: The quantum internet. Nature 453, 1023–1030 (2008)
Gyongyosi, L., Imre, S.: Entanglement concentration services for quantum internet. Quant. Inf Process 19, 221 (2020)
Zhao, Z., Yang, T., Shen, Y.A., Zhang, A.N., Pan, J.W.: Experimental realization of entanglement and quantum repeaters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 207901 (2003)
Liu, J., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Logic Bell state concentration with parity check measurement. Front. Phys. 14(2), 21601 (2019)
Shukla, C., Malpani, P., Thapliyal, K.: Hierarchical quantum network using hybrid entanglement. Quant. Inf. Process 20, 121 (2021)
Yan, P.S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Feasible measurement based entanglement purification in linear optics. Opt. Express 29, 9363–9384 (2021)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012304 (2001)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88, 012302 (2013)
Bandyopadhyay, S.: Qubit-and entanglement -assisted optimal entanglement concentration. Phys. Rev. A 62, 032308 (2000)
Bose, S., Vedral, V., Knight, P.L.: Purification via entanglement swapping and conserved entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 60, 194–197 (1999)
Horodecki, P., Horodecki, R.: Distillation and bound entanglement. Quant. Inf. Comp. 1, 45–75 (2001)
Chaudhari, B.S., Dhara, A.: A three-qubit state entanglement concentration protocol assisted by two-qubit systems. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 3965–3969 (2013)
Zhao, S.Y., Liu, J., Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Two- step entanglement concentration for arbitrary electronic cluster state. Quant. Inf. Process. 12, 3633–3647 (2013)
Gu, Y.-J., Li, W.-D., Guo, G.-C.: Protocols and quantum circuits for realizing deterministic entanglement concentration. Phys. Rev. A 73, 022321 (2006)
Zhao, Z., Yang, T., Shen, Y.A., Zhang, A.N., Pan, J.W.: Experimental realization of entanglement concentration and a quantum repeater. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 207901 (2003)
Chaudhary, B.S., Dhara, A.: An entanglement concentration protocol for Cluster states. Quant. Inf. Process. 12, 2577–2585 (2013)
Sisodia, M., Shukla, C., Long, G.L.: Linear optics based entanglement concentration protocols for cluster-type entangled coherent state. Quant. Inf. Process. 18, 1–16 (2019)
Banergee, A., Patel, K., Pathak, A.: Comment on teleportation via GHZ-like state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 507–510 (2011)
Vedral, V., Plenio, M.B.: Entanglement measures and purification procedures. Phys. Rev. A 57, 1619–1633 (1998)
Kwiat, P.G., Lopez, S.B., Stefanov, A., Gisin, N.: Entanglement distillation andhidden nonlocality. Nature 409, 1014–1017 (2001)
Nielsen, M.A.: Conditions for class of entanglement transformations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 436 (1999)
Shukla, C., Banergy, A., Pathak, A.: Protocols and quantum circuits for implementing entanglement concentration in cat state, GHZ-like state and nine families of 4-qubit entangled states. Quant. Inf. Process. 14, 2077–2099 (2015)
Banerjee, A., Shukla, C., Pathak, A.: Maximal entanglement concentration for a set of (n+1)-qubit states. Quant. Inf. Process. 14, 4523–4536 (2015)
IBM quantum experience. http://quantumexperience.ng.bluemix.net/qx/exp
Satyajit, S., Srinivasan, K., Bahera, B.K., Panigarhi, P.K.: Nondestructive discrimination of a new family of highly entangled states in IBM quantum computer. Quant. Inf. Process. 17, 212 (2018)
Gangopadhyay, S., Manabputra., Behera, B. K., Panigrahi, P. K.: Generalization and demonstration of entanglement based Deutch–Jozsa-like algorithm using a five-qubit computer. Quant. Inf. Process. 17, 160 (2018)
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Design and experimental realization of an optimal scheme for teleportation of an n-qubit quantum state. Quant. Inf. Process. 16, 292 (2017)
Behera, B.K., Seth, S., Das, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Demonstration of entanglement purification and swapping to design quantum repeater in IBM quantum computer. Quant. Inf. Process. 18, 108 (2017)
Anagha, M., Mohan, A., Muruganandan, T., Behera, B. K., Panigrahi, P. K.: A new scheme of teleportation using highly entangled Brown et. al. state using IBM quantum experience. Quant. Inf. Process. 19, 147 (2020)
Pradhan, S., Behera, T. S., Behera, B. K., Panigrahi, P. K.: Simulating quantum synchronization of atomic spin model on ibm Q experience. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.22783.15521
Srinivasan, K Satyajit, S., Bahera, B. K., Panigarhi, P. K.: Efficient quantum algorithm for solving the travelling salesman problem: an IBM quantum experience. arXiv:1805.10928
Shenoy, K.S., Sheth, D.Y., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Demonstration of measurement based adaption based protocol with quantum reinforce learning on IBM Q experience platform. Quant. Inf. Process. 19, 161 (2020)
Rajiuddin, S.K., Baishya, A., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental realization of quantum teleportation of an arbitrary two-qubit state using a four-qubit cluster state. Quant. Inf. Process. 19, 87 (2020)
O’Malley, P.J.J., et al.: Scalable quantum simulation of molecular energies. Phys. Rev. X 6, 031007 (2016)
Shen, Y., et al.: Quantum implementation of the unitary coupled cluster for simulating molecular electronic structure. Phys. Rev. A 95, 020501 (2017)
Dumitrescu, E.F., et al.: Cloud quantum computing of an atomic nucleus. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 210501 (2018)
Kandala, A., et al.: Hardware-efficient variational quantum eigensolver for small molecules and quantum magnets. Nature 549, 242–246 (2017)
Yordanov, Y.S., Arvidsson-Shukur, D.R.M., Barnes, C.H.W.: Efficient quantum circuits for quantum computational chemistry. Phys. Rev. A 102, 062612 (2020)
Briegel, H.J., Raussendorf, R.: Persistent entanglement in arrays of interacting particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 910 (2001)
Raussendorf, R., Briegel, H.J.: A one-way quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5188 (2001)
Hein, M., Dur, W., Eisert, J., Raussendorf, R., Van den Nest, M., Briegel, H.-J.: Entanglement in graph states and its applications. arXiv:quant-ph/0602096
Cervera-Lierta, A., Lattore, J.I., Goyeneche, D.: Quantum circuits for maximally entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 100, 022342 (2019)
McKay, D.C., Sheldon, S., Smolin, J.A., Chow, J.M., Gambetta, J.M.: Three-qubit randomized benchmarking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 200502 (2019)
Tannu, S. S., Qureshi, M. K.: Not all qubits are created equal: a case for variability-aware policies for NISQ-era quantum computers. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems. (987-999) (2019)
Makhlin, Y.: Nonlocal properties of two-qubit gates and mixed states, and the optimization of quantum computations. Quant. Inf. Process. 4, 243 (2002)
Shende, V.V., Markov, I.L., Bullock, S.S.: Minimal universal two-qubit controlled-NOT-based circuits. Phys. Rev. A 69, 062321 (2004)
Ozaeta, A., MacMahon, P.L.: Decohrence of upto 8-qubit entangled states in a 16-qubit superconducting quantum processor. Quant. Sci. Technol. 4, 2 (2019)
Preskill, J.: Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2, 79 (2018)
Peruzzo, A., et al.: A variational eigenvalue solver on a photonic quantum processor. Nat. Commun. 5, 4213 (2014)
Acknowledgements
JR would like to thank the University Grant Commission, New Delhi for providing the financial assistance Junior Research Fellowship vide Ref. No. 20/12/2015(ii)EU-V and IBM Quantum experience for giving access to its various quantum processors. We are also thankful to Pankaj Kumar who helped us in plots and figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ram, J., Dutt, D., Dhiman, S.K. et al. Entanglement concentration of multi-qubit entangled states: an IBM quantum experience. Quantum Stud.: Math. Found. 10, 329–342 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40509-023-00298-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40509-023-00298-0