Abstract
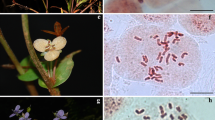
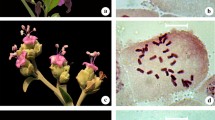
In order to explore the karyotype and evolutionary trend of Clematis and provide taxonomically useful data, the chromosome number, the number and position of satellites, the karyotype formulae, the karyotype, arm ratio, relative length centromeric index, and the index of the karyotype asymmetry of 11 species of the genus Clematis were studied. All the analyzed species showed the same stable chromosome number (2n = 2x = 16) and basic chromosome number 8. Clematis karyotypes are composed by metacentric, submetacentric, and terminal centromeric chromosomes. Clematis lanuginosa, C. otophora, C. lasiandra, C. shenlungchiaensis, C. florida var. plena, C. fusca var. violacea, C. crispa, and C. viticella belong to Type 2A, a very symmetric and plesiomorphic type. Clematis henryi, C. integrifolia, and C. japonaca belong to Type 2B, which is apomorphic relative to the other group. The 11 species of Clematis are different in karyotype parameters providing data for the taxonomy of the genus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawson MI (1993) Contributions to a chromosome atlas of the New Zealand flora—31 Clematis (Ranunculaceae). NZ J Bot 31:91–96
Dennis WM (1976) Chromosome morphology of Clematis, subsection Viornae (Ranunculaceae). Can J Bot 54:1135–1139
Desal N, Kawalkar H, Dixit G (2012) Biosystematics and evolutionary studies in Indian Drimia species. J Syst Evol 50:512–518
Ebrahim F, Pakniyat H, Arzani A, Rahimmalek M (2012) Karyotype analysis and new chromosome number reports in Achillea species. Biologia 67:284–288
Gong WZ, Long YY, Li MX (1985) Karyotype studies on clematis from Beijing China. J Wuhan Bot Res 3:371–379
Grey-Wilson C (2000) Clematis the genus. Oregon Timber Press, Portland
Langlet O (1927) Beiträge zur Zytologie der Ranunculaceen. Sv Bot Tids 21:1
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg A (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–210
Li MX, Chen RY (1985) A suggestion on the standardization of karyotype analysis in plants. J Wuhan Bot Res 3:297–302
Liu HM, Cheng YJ, Lu GE, Li L, Wu FZ (2010) Karyotype features of 17 species of Spiraea and karyotype parameters analysis. Acta Hortic Sin 27:1456–1462
Meurman O, Therman E (1939) Studies in the chromosome morphology and structural hybridity in genus Clematis. Cytologia 10:1–2
Stebbins GL (1971) Chromosomal evolution in higher plants. Edward Arnold, London, pp 87–89
Tamura M (1987) A classification of genus Clematis. Acta Phytotaxon Geobot 38:33–44
Tamura M (1995) Archiclematis and Clematis. In: Hiepko P (ed) DieNatürlichen Pflanzenfamilien. Zwei. Aufl. 17a (4). Duncker and Humblot, Berlin, pp 366–387
Wang WT, Bartholomew B (2001) Clematis. In: Wu Z-Y and Raven P (eds) Flora of China, vol 6. Beijing: Science Press, St. Louis, p 97–165
Wang WT, Li LQ (2005) A new system of classification of the genus Clematis (Ranunculaceae). Acta Phytotaxon Sin 43:431–488
Xie L, Wen J, Li LQ (2011) Phylogenetic analyses of Clematis (Ranunculaceae) based on sequences of nuclear ribosomal ITS and three plastid regions. Systematic Botany 36:907–921 (15)
Yang QE (1998) Does Actaea asiatica have the most symmetric and primitive karyotype in the Ranunculaccae? Acta Phytotax Sin 36:490–495
Zhang YL, He SY (1990) Chromosome studies on 6 species of Clematis in China. J Wuhan Bot Res 8:115–121
Zhang YL, He SY (1991) Chromosome studies on 7 species of Clematis in China. J Wuhan Bot Res 9:107–113
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Wang LP who provided technical assistance and Wu DD who gave us helpful suggestions. This study was supported by A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, L., Ji, K. & Yu, L. Karyotype analysis on 11 species of the genus Clematis . Braz. J. Bot 37, 601–608 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-014-0099-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-014-0099-5