Abstract
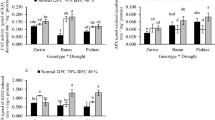
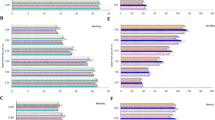
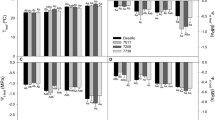
Drought is a common abiotic stress that considerably limits crop production. The objective of this study is to explore the influence of water deficiency on the yield, physiologic and metabolomic attributes in upland cotton cultivars (Gossypium hirsutum L). Cotton cultivars, 'Ishonch' and 'Tashkent-6' were selected to study the relationships among their physiologic, metabolomic and yield attributes during water deficiency. Deficit irrigation was designed by modifying the traditional watering protocol to reduce water use. Results indicate that cotton cultivars respond differently to water deficit stress. Water deficit significantly influenced plant height, the number of internodes, and sympodial branches in both cultivars. However, yield components such as the number of bolls, boll seed, lint mass, and individual plant yield were significantly reduced only in 'Tashkent-6'. The leaf area decreased and the specific leaf weight increased in 'Ishonch' under deficit irrigation conditions. However, 'Tashkent-6' demonstrated significant water loss compared to 'Ishonch', and both cultivars showed reduced transpiration rates. Untargeted metabolite profiles of leaves showed clear separation in 'Ishonch', but not in 'Tashkent-6' under deficit irrigation compared to full irrigation. The individual metabolites such as proline and galactinol showed strong association with yield under water deficit stress. Moreover, this study indicates that leaf area and transpiration intensity influence yield during water deficiency. In summary, the correlation among morpho-physiologic, metabolic, and yield components significantly varied between the two cultivars under water deficiency. The flowering stage was sensitive to water stress for both cultivars. The direct relationship between physiology, metabolism, and yield may be a useful selection criterion for determining candidate parents for cotton drought tolerance breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbdelGadir A H, Dougherty M, Fulton J P, et al. 2012. Effect of different deficit-irrigation capabilities on cotton yield in the tennessee valley. Irrigation & Drainage Systems Engineering, 1(1): 102, doi: 10.4172/2168-9768.1000102.
Abouziena H, Amin A A, Abd El-Kader A A, et al. 2016. Effects of benzoic acid and thiourea on growth and productivity of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Plants. Ponte Academic Journal, 72(4): 132–149, doi: 10.21506/j.ponte.2016.4.26.
Agrawala S, Barlow M, Cullen H, et al. 2001. The drought and humanitarian crisis in central and southwest asia: a climate perspective. IRI Special Report 01-11. Palisades: International Research Institute for Climate Prediction.
Alves A C A, Setter T L. 2004. Response of cassava leaf area expansion to water deficit: cell proliferation, cell expansion and delayed development. Annals of Botany, 94(4): 605–613.
Amid B T, Mirhosseini H, Poorazarang H, et al. 2013. Implications of partial conjugation of whey protein isolate to durian seed gum through maillard reactions: foaming properties, water holding capacity and interfacial activity. Molecules, 18(12): 15110–15125.
Baboev S K, Buranov A K, Bozorov T A, et al. 2017. Biological and agronomical assessment of wheat landraces cultivated in mountain areas of Uzbekistan. Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Biologiya, 52(3): 553–560, doi: 10.15389/agrobiology.2017.3.553eng.
Basal H, Dagdelen N, Unay A, et al. 2009. Effects of deficit drip irrigation ratios on cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield and fibre quality. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 195(1): 19–29.
Benavides-Mendoza A, Burgos-Limón D, Ramírez H, et al. 2012. Benzoic acid effect in the growth and yield of tomato in calcareous soil. In: Prioceedings of the 28th International Horticultural Congress on Science and Horticulture for People (IHC2010): International Symposium on Environmental, Edaphic, and Genetic Factors Affecting Plants, Seeds and Turfgrass. Lisboa, Portugal: ISHS, 938: 251–256.
Bohnert H J, Nelson D E, Jensen R G. 1995. Adaptations to environmental stresses. The Plant Cell, 7(7): 1099–1111.
Borsani O, Valpuesta V, Botella M A. 2001. Evidence for a role of salicylic acid in the oxidative damage generated by NaCl and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Physiology, 126(3): 1024–1030.
Boyer J S. 1982. Plant productivity and environment. Science, 218(4571): 443–448.
Bozorov T A, Usmanov R M, Nabiev S, et al. 2016. Metabolome profiling during water deficiency in medium-fiber cotton varieties of Gossypium hirsutum L. species. Problems of Modern Science and Education, 33(75): 10–12.
Bray E A. 1997. Plant responses to water deficit. Trends in Plant Science, 2(2): 48–54.
Burke J J. 2002. Moisture sensitivity of cotton pollen: an emasculation tool for hybrid production. Agronomy Journal, 94(4): 883–888.
Chen Y, Liu Z H, Feng L, et al. 2013. Genome-wide functional analysis of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) in response to drought. PLoS ONE, 8(11): e80879.
Dai A G. 2011. Drought under global warming: a review. WIREs Climate Change, 2(1): 45–65.
De Fátima Fumis T, Pedras J F. 2002. Proline, diamine and polyamines accumulation in wheat cultivars submitted to water deficits. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 37(4): 449–453.
Dhanda S S, Sethi G S. 1998. Inheritance of excised-leaf water loss and relative water content in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). Euphytica, 104(1): 39–47.
Duan L X, Chen T L, Li M, et al. 2012. Use of the metabolomics approach to characterize Chinese medicinal material Huangqi. Molecular Plant, 5(2): 376–386.
Garnier E, Shipley B, Roumet C, et al. 2011. A Standardized protocol for the determination of specific leaf area and leaf dry matter content. Functional Ecology, 15(5): 688–695.
Gerik T J, Faver K L, Thaxton P M, et al. 1996. Late season water stress in cotton: I. plant growth, water use, and yield. Crop Science, 36(4): 914–921.
Grimes D W, Dickens W L, Anderson W D. 1969. Functions for cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) production from irrigation and nitrogen fertilization variables: II. yield components and quality characteristics. Agronomy Journal, 61(5): 773–776.
Guimarães E R, Mutton M A, Mutton M J R, et al. 2008. Free proline accumulation in sugarcane under water restriction and spittlebug infestation. Scientia Agricola, 65(6): 628–633.
Jaleel C A, Manivannan P, Wahid A, et al. 2009. Drought stress in plants: a review on morphological characteristics and pigments composition. International Journal of Agriculture & Biology, 11(1): 100–105.
Keinänen M, Oldham N J, Baldwin I T. 2001. Rapid HPLC screening of jasmonate-induced increases in tobacco alkaloids, phenolics, and diterpene glycosides in Nicotiana attenuata. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(8): 3553–3558.
Kirda C. 2002. Deficit irrigation scheduling based on plant growth stages showing water stress tolerance. In: Deficit Irrigation Practices. Rome: FAO, 22: 1–3.
Kulmatov R. 2014. Problems of sustainable use and management of water and land resources in Uzbekistan. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 6(1): 35–42.
Laffray D, Louguet P. 1990. Stomatal responses and drought resistance. Bulletin de la Société Botanique de France. Actualités Botaniques, 137(1): 47–60.
Leidi E O, López J M, López M, et al. 1993. Searching for tolerance to water stress in cotton genotypes: photosynthesis, stomatal conductance and transpiration. Photosynthetica, 28(3): 383–390.
Levi A, Paterson A H, Cakmak I, et al. 2011. Metabolite and mineral analyses of cotton near-isogenic lines introgressed with QTLs for productivity and drought-related traits. Physiologia Plantarum, 141(3): 265–275.
Loka D A, Oosterhuis D M, Pilon C. 2015. Endogenous levels of polyamines under water-deficit stress during cotton’s reproductive development. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 6(2): 344–354.
Lu X K, Wang X G, Chen X G, et al. 2017. Single-base resolution methylomes of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) reveal epigenome modifications in response to drought stress. BMC Genomics, 18: 297.
Mammadova A, Aliyev R, Babayeva S, et al. 2015. Adaptive reaction of cotton accessions of G. hirsutum L. and G. barbadense L. species to drought stress. Genetika, 47(2): 617–626.
Maniou F, Chorianopoulou S N, Bouranis D L. 2014. New insights into trophic aerenchyma formation strategy in maize (Zea mays L.) organs during sulfate deprivation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5: 581.
McGarry R C, Prewitt S F, Culpepper S, et al. 2016. Monopodial and sympodial branching architecture in cotton is differentially regulated by the Gossypium hirsutum single flower truss and self-pruning orthologs. The New Phytologist, 212(1): 244–258.
McMichael B L, Jordan W R, Powell R D. 1973. Abscission processes in cotton: induction by plant water deficit. Agronomy Journal, 65(2): 202–204.
McMichael B L, Elmore C D. 1977. Proline accumulation in water stressed cotton leaves. Crop Science, 17(6): 905–908.
McMichael B L, Hesketh J D. 1982. Field investigations of the response of cotton to water deficits. Field Crops Research, 5: 319–333.
Meyer E, Aspinwall M J, Lowry D B, et al. 2014. Integrating transcriptional, metabolomic, and physiological responses to drought stress and recovery in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). BMC Genomics, 15: 527.
Nepomuceno A L, Oosterhuis D M, Stewart J M. 1998. Physiological responses of cotton leaves and roots to water deficit induced by polyethylene glycol. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 40(1): 29–41.
Nishizawa A, Yabuta Y, Shigeoka S. 2008. Galactinol and raffinose constitute a novel function to protect plants from oxidative damage. Plant Physiology, 147(3): 1251–1263.
Obata T, Fernie A R. 2012. The use of metabolomics to dissect plant responses to abiotic stresses. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 69(19): 3225–3243.
Obata T, Witt S, Lisec J, et al. 2015. Metabolite profiles of maize leaves in drought, heat, and combined stress field trials reveal the relationship between metabolism and grain yield. Plant Physiology, 169(4): 2665–2683.
Onder D, Akiscan Y, Onder S, et al. 2009. Effect of different irrigation water level on cotton yield and yield components. African Journal of Biotechnology, 8(8): 1536–1544.
Orgaz F, Mateos L, Fereres E. 1992. Season length and cultivar determine the optimum evapotranspiration deficit in cotton. Agronomy Journal, 84(4): 700–706.
Pace P F, Cralle H T, El-Halawany S H M, et al. 1999. Drought-induced changes in shoot and root growth of young cotton plants. Journal of Cotton Science, 3(4): 183–187.
Patil M D, Biradar D P, Patil V C, et al. 2011. Response of cotton genotypes to drought mitigation practices. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural & Environmental, 11(3): 360–364.
Peel M F, Finlayson B L, McMahon B T. 2007. Updated world map of the Köppen–Geiger climate classification. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions, 4: 439–473.
Pettigrew W T. 2004. Moisture deficit effects on cotton lint yield, yield components, and boll distribution. Agronomy Journal, 96(2): 377–383.
Plaut Z, Ben-Hur M, Meiri A. 1992. Yield and vegetative growth as related to plant water potential of cotton irrigated with a moving sprinkler system at different frequencies and wetting depths. Irrigation Science, 13(1): 39–44.
Pucholt P, Sjödin P, Weih M, et al. 2015. Genome-wide transcriptional and physiological responses to drought stress in leaves and roots of two willow genotypes. BMC Plant Biology, 15: 244.
Radin J W, Reaves L L, Mauney J R, et al. 1992. Yield enhancement in cotton by frequent irrigations during fruiting. Agronomy Journal, 84(4): 551–557.
Saini H S, Lalonde S. 1997. Injuries to reproductive development under water stress, and their consequences for crop productivity. Journal of Crop Production, 1(1): 223–248.
Sampathkumar T, Pandian B J, Rangaswamy M V, et al. 2013. Influence of deficit irrigation on growth, yield and yield parameters of cotton–maize cropping sequence. Agricultural Water Management, 130: 90–102.
Sawada H, Shim I S, Usui K. 2006. Induction of benzoic acid 2-hydroxylase and salicylic acid biosynthesis—Modulation by salt stress in rice seedlings. Plant Science, 171(2): 263–270.
Saxena A, Cramer C S. 2013. Metabolomics: a potential tool for breeding nutraceutical vegetables. Advances in Crop Science and Technology, 1: 106.
Smart R E, Bingham G E. 1974. Rapid estimates of relative water content. Plant Physiology, 53(2): 258–260.
Snider J L, Oosterhuis D M, Loka D A, et al. 2011. High temperature limits in vivo pollen tube growth rates by altering diurnal carbohydrate balance in field-grown Gossypium hirsutum pistils. Journal of Plant Physiology, 168(11): 1168–1175.
Snowden C, Ritchie G, Thompson T. 2013. Water use efficiency and irrigation response of cotton cultivars on subsurface drip in west texas. The Journal of Cotton Science, 17(1): 1–9.
Soomro M H, Markhand G S, Soomro B A. 2011. Screening pakistani cotton for drought tolerance. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 44(1): 383–388.
Tahara M, Carver B F, Johnson R C, et al. 1990. Relationship between relative water content during reproductive development and winter wheat grain yield. Euphytica, 49(3): 255–262.
Taji T, Ohsumi C, Iuchi S, et al. 2002. Important roles of drought- and cold-inducible genes for galactinol synthase in stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 29(4): 417–426.
Tiwari R S, Picchioni G A, Steiner R L, et al. 2013. Genetic variation in salt tolerance during seed germination in a backcross inbred line population and advanced breeding lines derived from Upland cotton×Pima cotton. Crop Science, 53(5): 1974–1982.
Trolinder N L, McMichael B L, Upchurch D R. 1993. Water relations of cotton flower petals and fruit. Plant, Cell & Environment, 16(6): 755–760.
Ullah A, Sun H, Yang X Y, et al. 2017. Drought coping strategies in cotton: increased crop per drop. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 15(3): 271–284.
Ullah I, Mehboob-ur-Rahman, Ashraf M, et al. 2008. Genotypic variation for drought tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.): leaf gas exchange and productivity. Flora–Morphology, Distribution, Functional Ecology of Plants, 203(2): 105–115.
Witt S, Galicia L, Lisec J, et al. 2012. Metabolic and phenotypic responses of greenhouse-grown maize hybrids to experimentally controlled drought stress. Molecular Plant, 5(2): 401–417.
Xu Z Z, Zhou G S. 2008. Responses of leaf stomatal density to water status and its relationship with photosynthesis in a grass. Journal of Experimental Botany, 59(12): 3317–3325.
Zhang H Y, Ni Z Y, Chen Q J, et al. 2016. Proteomic responses of drought-tolerant and drought-sensitive cotton varieties to drought stress. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 291(3): 1293–1303.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Committee of Science and Technology of Uzbekistan (F5-T025), CAS PIFI fellowships (2017PB0051, 2017VBA0017) and the High Technology Research and Development Program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (201411104). We would like to show our gratitude to the employees of Zangi-Ata Experimental Field Station for growing and maintaining cotton plants and Dr. Andrew J WOOD for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozorov, T.A., Usmanov, R.M., Yang, H. et al. Effect of water deficiency on relationships between metabolism, physiology, biomass, and yield of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). J. Arid Land 10, 441–456 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-018-0009-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-018-0009-y