Abstract
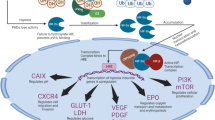
Von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) is an autosomal dominant disease that predisposes individuals to various types of malignancies, including renal cell carcinoma, systemic hemangioblastomas, pheochromocytomas, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, and endolymphatic sac tumors, with renal cell carcinoma being the most prevalent. The disease is caused by a mutation in the VHL gene on chromosome 3. One function of the VHL gene is to suppress the expression of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF). HIF promotes cellular proliferation and angiogenesis under hypoxic conditions. In VHL, mutations allow HIF to promote cellular propagation unchecked, leading to neoplastic proliferation. Medications currently used for the treatment of Von Hippel Lindau associated renal cell carcinoma are tyrosine kinas inhibitors, which are enzymes downstream from HIF. These medications have been shown to have limited efficacy and an unfavorable side effect profile. Bezutifan (Welireg™) is the first drug approved by the FDA that inhibits HIF, specifically HIF2a, and has been promising for treatment of VHL-associated renal cell carcinoma. The present investigation summarizes the findings of studies conducted on the use of Belzutifan for VHL-associated renal cell carcinoma. The results to date indicate that Belzutifan is a well-tolerated and efficacious drug for VHL-associated renal cell carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chittiboina P, Lonser RR. Von Hippel–Lindau disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2015;132:139–56.
Hudler P, Urbancic M. The role of VHL in the development of von Hippel–Lindau disease and erythrocytosis. Genes. 2022;13(2):362.
Zhou J, Gong K. Belzutifan: a novel therapy for von Hippel–Lindau disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022;18(4):205–6.
Visweswaran V, Pavithran K. Belzutifan: a narrative drug review. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2022;14(2):88–95.
Deeks ED. Belzutifan: first approval. Drugs. 2021;81(16):1921–7.
Kim H, Shim BY, Lee S-J, et al. Loss of von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressorgene function: VHL-HIF pathway and advances in treatments for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(18):9795.
Rosellini M, Marchetti A, Mollica V, et al. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol. 2023;20(3):133–57.
Binderup MLM, Smerdel M, Borgwadt L, et al. Von Hippel–Lindau disease: updated guideline for diagnosis and surveillance. Eur J Med Genet. 2022;65(8): 104538.
Zhang JJ, Zhang Q. VHL and hypoxia signaling: beyond HIF in cancer. Biomedicines. 2018;6(1):35.
Kaelin WG, Maher ER. The VHL tumour-suppressor gene paradigm. Trends Genet TIG. 1998;14(10):423–6.
Gallou C, Joly D, Mejean A, et al. Mutations of the VHL gene in sporadic renal cell carcinoma: definition of a risk factor for VHL patients to develop an RCC. Hum Mutat. 1999;13(6):464–75.
Park KC, Lee DC, Yeom YI. NDRG3-mediated lactate signaling in hypoxia. BMB Rep. 2015;48(6):301–2.
An J, Rettig MB. Mechanism of von Hippel–Lindau protein-mediated suppression of nuclear factor kappa B activity. Mol Cell Biol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.25.17.7546-7556.2005.
Cowman SJ, Koh MY. Revisiting the HIF switch in the tumor and its immune microenvironment. Trends Cancer. 2022;8(1):28–42.
Choueiri TK, Bauer TM, Papadopoulos KP, et al. Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in renal cell carcinoma with belzutifan: a phase 1 trial and biomarker analysis. Nat Med. 2021;27(5):802–5.
Fallah J, Brave MH, Weinstock C, et al. FDA approval summary: belzutifan for von Hippel–Lindau disease-associated tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(22):4843–8.
US Food and Drug Administration, Welireg™ (belzutifan) tablets, for oral use. 2021 [Online]. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215383s000lbl.pdf. Accessed Apr 29, 2023.
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, An open-label, randomized phase 3 study of MK-6482 versus everolimus in participants with advanced renal cell carcinoma that has progressed after prior PD-1/L1 and VEGF-targeted therapies (NCT04195750); 2022 [Online]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04195750. Accessed Apr 27, 2023.
Arevalo A, Patel N, Muraki P, et al. Understanding the impact of belzutifan on treatment strategies for patients with VHL. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 2022;9(3):41–6.
Méndez-Vidal MJ, Molina A, Anido U, et al. Pazopanib: evidence review and clinical practice in the management of advanced renal cell carcinoma. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018;19:77.
Jonasch E, McCutcheon IE, Gombos DS, et al. Single-arm nonrandomized phase II study of pazopanib in patients with von Hippel–Lindau disease. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(10):1351–9.
Iacovelli R, Massari F, Albigas L, et al. Evidence and clinical relevance of tumor flare in patients who discontinue tyrosine kinase inhibitors for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2015;68(1):154–60.
Hasinoff BB, Wu X, Nitiss JL, et al. The anticancer multi-kinase inhibitor dovitinib also targets topoisomerase I and topoisomerase II. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84(12):1617–26.
Jonasch E, Donskov F, Iliopoulos O, et al. Belzutifan for renal cell carcinoma in von Hippel–Lindau disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(22):2036–46.
“Votrient (pazopanib) FDA Approval History,” Drugs.com [Online]. https://www.drugs.com/history/votrient.html. Accessed Oct 21, 2023.
“Dovitinib: what is it and is it FDA approved?—Drugs.com” [Online]. https://www.drugs.com/history/dovitinib.html. Accessed Oct 21, 2023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethics approval
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
None.
Author contributions
All authors listed have made a direct and intellectual contribution to the work and approved for publication.
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Availability of data and material
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Schwartz, A.M., Fakhre, W., Jin, K. et al. The role of belzutifan, an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor, for renal cell carcinoma in adults with Von Hippel–Lindau disease: a review. Drugs Ther Perspect 39, 388–392 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-023-01031-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-023-01031-y