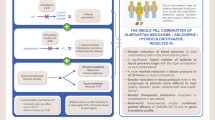
Abstract
The triple-component fixed-dose combination of olmesartan medoxomil (OLM)/amlodipine (AML)/hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) is a rational choice for patients who require treatment with three or more antihypertensives. The three drugs in the FDC have complementary mechanisms of action, with OLM, AML and HCT being an angiotensin II receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker and diuretic, respectively. Once-daily OLM/AML/HCT 20 mg/5 mg/12.5 mg reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure, thereby enabling patients to achieve blood pressure goals, and was generally well tolerated in clinical trials. Moreover, the use of a fixed-dose combination comprising three antihypertensive components reduces pill burden, which may improve patient adherence to treatment and, ultimately, clinical outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 June 2018
Page 2, column 2, section “What is the clinical efficacy of OLM/AMT/HCT 20 mg/5 mg/12.5 mg?”, paragraph 1, lines 5–8: The following text, which previously read.
References
ESH/ESC Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. 2013 practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC): ESH/ESC Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2013;31(10):1925–8.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289(19):2560–72.
Volpe M, Tocci G. Rationale for triple fixed-dose combination therapy with an angiotensin II receptor blocker, a calcium channel blocker, and a thiazide diuretic. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012;8:371–80.
Chrysant SG. Single-pill triple-combination therapy: an alternative to multiple-drug treatment of hypertension. Postgrad Med. 2011;123(6):21–31.
Wang YR, Alexander GC, Stafford RS. Outpatient hypertension treatment, treatment intensification, and control in Western Europe and the United States. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(2):141–7.
Erdine S. How do compliance, convenience, and tolerability affect blood pressure goal rates? Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012;12(5):295–302.
Düsing R, Waeber B, Destro M, et al. Triple-combination therapy in the treatment of hypertension: a review of the evidence. J Hum Hypertens. 2017;31(8):501–10.
Volpe M, Santolamazza C, Mastromarino V, et al. Triple combination therapies based on olmesartan: a personalized therapeutic approach to improve blood pressure control. High Blood Press. 2017;24(3):255–63.
Neutel JM. Prescribing patterns in hypertension: the emerging role of fixed-dose combinations for attaining BP goals in hypertensive patients. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24(8):2389–401.
Xie L, Frech-Tamas F, Marrett E, et al. A medication adherence and persistence comparison of hypertensive patients treated with single-, double- and triple-pill combination therapy. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014;30(12):2415–22.
Zolnor HCT (olmesartan medoxomil 20 mg + amlodipine 5 mg + hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg) film-coated tablets: summary of product characteristics [in Portuguese]. Paço de Arcos: A. Menarini Portugal—Farmacêutica, S.A.; 2014.
Agata J, Ura N, Yoshida H, et al. Olmesartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker with an inhibitory effect on angiotensin-converting enzyme. Hypertens Res. 2006;29:865–74.
Fliser D, Buchholz K, Haller H. EUropean Trial on Olmesartan and Pravastatin in Inflammation and Atherosclerosis (EUTOPIA) Investigators. Antiinflammatory effects of angiotensin II subtype 1 receptor blockade in hypertensive patients with microinflammation. Circulation. 2004;110(9):1103–7.
Hirohata A, Yamamoto K, Miyoshi T, et al. Impact of olmesartan on progression of coronary atherosclerosis a serial volumetric intravascular ultrasound analysis from the OLIVUS (impact of OLmesarten on progression of coronary atherosclerosis: evaluation by intravascular ultrasound) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(10):976–82.
Hirohata A, Yamamoto K, Miyoshi T, et al. Four-year clinical outcomes of the OLIVUS-Ex (impact of Olmesartan on progression of coronary atherosclerosis: evaluation by intravascular ultrasound) extension trial. Atherosclerosis. 2012;220(1):134–8.
Scott LJ, McCormack PL. Olmesartan medoxomil: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs. 2008;68(9):1239–72.
Wang L, Zhao JW, Liu B, et al. Antihypertensive effects of olmesartan compared with other angiotensin receptor blockers. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012;12(5):335–44.
Olmetec Plus (olmesartan medoxomil + hydrochlorothiazide) film-coated tablets: UK summary of product characteristics. Gerrards Cross; Daiichi Sankyo UK Limited; 2017.
Sohn IS, Kim C-J, Oh B-H, et al. Efficacy and safety study of olmesartan medoxomil, amlodipine, and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in patients with hypertension not controlled with olmesartan medoxomil and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy: results of a randomized, double-blind, multicenter trial. [Erratum appears in Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2016;16(2):139]. Am J Cardiovasc. 2016;16(2):129–38.
Volpe M, Rump L, Ammentorp B, et al. Efficacy and safety of triple antihypertensive therapy with the olmesartan/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide combination. Clin Drug Investig. 2012;32(10):649–64.
Oparil S, Melino M, Lee J, et al. Triple therapy with olmesartan medoxomil, amlodipine besylate, and hydrochlorothiazide in adult patients with hypertension: the TRINITY multicenter, randomized, double-blind, 12-week, parallel-group study. Clin Ther. 2010;32(7):1252–69.
Volpe M, de la Sierra A, Ammentorp B, et al. Open-label study assessing the long-term efficacy and safety of triple olmesartan/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy for hypertension. Adv Ther. 2014;31(5):561–74.
da Silva M, Haag U, Guest JF, et al. Health-related quality of life impact of a triple combination of olmesartan medoxomil, amlodipine besylate and hydrochlorothiazide in subjects with hypertension. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015;13:24.
Chrysant SG, Germino FW, Neutel JM. Olmesartan medoxomil-based antihypertensive therapy evaluated by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: efficacy in high-risk patient subgroups. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012;12(6):375–89.
Bramlage P, Fronk EM, Wolf WP, et al. Safety and effectiveness of a fixed-dose combination of olmesartan, amlodipine, and hydrochlorothiazide in clinical practice. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014;11:1–8.
Bramlage P, Ketelhut R, Fronk EM, et al. Clinical impact of patient adherence to a fixed-dose combination of olmesartan, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide. Clin Drug Investig. 2014;34(6):403–11.
Epstein BJ, Vogel K, Palmer BF. Dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists in the management of hypertension. Drugs. 2007;67(9):1309–27.
Mizuno M, Sada T, Ikeda M, et al. Pharmacology of CS-866, a novel nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;285(2):181–8.
Acknowledgements
The article was reviewed by: A. Battistoni, Division of Cardiology, Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Psychology, University of Rome Sapienza, Sant’Andrea Hospital, Rome, Italy; IS. Sohn, Department of Cardiology, Cardiovascular Center, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Republic of Korea. During the peer review process, the Portuguese Marketing Authorization Holder of OLM/AML/HCT 20 mg/5 mg/12.5 mg was also offered an opportunity to review this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Conflict of interest
K.A. Lyseng-Williamson is a salaried employee of Adis/Springer, is responsible for the article content and declares no relevant conflicts of interest.
Additional information about this Adis Drug Review may be found here http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/44DCF0602F86BFFF.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyseng-Williamson, K.A. Olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide 20 mg/5 mg/12.5 mg fixed-dose combination in hypertension: a profile of its use. Drugs Ther Perspect 34, 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-017-0465-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-017-0465-z