Abstract
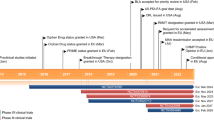
Fidanacogene elaparvovec (PrBEQVEZ™) is an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector-based gene therapy developed by Spark Therapeutics (a subsidiary of Roche) and Pfizer (under a license from Spark Therapeutics) for the treatment of haemophilia B. In December 2023, fidanacogene elaparvovec received its first approval for the treatment of adults (aged ≥ 18 years) with moderately severe to severe haemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency) who are negative for neutralizing antibodies to variant AAV serotype Rh74 (AAVRh74var). Fidanacogene elaparvovec is under regulatory review in the USA and the European Union and clinical studies are ongoing in multiple countries. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of fidanacogene elaparvovec leading to this first approval for moderately severe to severe (factor IX activity ≤ 2%) haemophilia B who are negative for neutralizing antibodies to AAVRh74var.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller CH. The clinical genetics of hemophilia B (factor IX deficiency). Appl Clin Genet. 2021;14:445–54.
Samelson-Jones BJ, George LA. Adeno-associated virus gene therapy for hemophilia. Annu Rev Med. 2023;74:231–47.
Srivastava A, Santagostino E, Dougall A, et al. WFH Guidelines for the Management of Hemophilia, 3rd edition. Haemophilia. 2020;26(Suppl 6):1–158.
George LA, Sullivan SK, Giermasz A, et al. Hemophilia B gene therapy with a high-specific-activity factor IX variant. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(23):2215–27.
Manno CS, Pierce GF, Arruda VR, et al. Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat Med. 2006;12(3):342–7.
Monahan P, Walsh C, Powell J, et al. Update on a phase 1/2 open-label trial of BAX335, an adeno-associated virus 8 (AAV8) vector-based gene therapy program for hemophilia B [abstract no. LB010]. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(Suppl 2):010.
Nathwani AC, Reiss UM, Tuddenham EG, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of factor IX gene therapy in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(21):1994–2004.
Crudele JM, Finn JD, Siner JI, et al. AAV liver expression of FIX-Padua prevents and eradicates FIX inhibitor without increasing thrombogenicity in hemophilia B dogs and mice. Blood. 2015;125(10):1553–61.
Pfizer Canada ULC. PrBEQVEZTM (fidanacogene elaparvovec): Canadian prescribing information 2023. https://health-products.canada.ca/dpd-bdpp/info?lang=eng&code=103268. Accessed 8 Jan 2024.
Spark Therapeutics. Spark Therapeutics Launched with $50 Million in Financing to Advance Late- and Mid-Stage Gene Therapy Programs with Clinical Proof of Concept [media release]. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/spark-therapeutics-launched-with-50-million-in-financing-to-advance-late--and-mid-stage-gene-therapy-programs-with-clinical-proof-of-concept-228752221.html. Accessed 22 Oct 2013.
Spark Therapeutics. Amedment to form S-1. 2015. https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1609351/000119312515013888/d776249ds1a.htm. Accessed 28 Jan 2024.
Pfizer. Spark Therapeutics and Pfizer announce that SPK-9001, an investigational hemophilia B Medicine, has been granted access to the PRIority MEdicines (PRIME) program by the European Medicines Agency [media release]. https://sparktx.com/press_releases/spark-therapeutics-and-pfizer-amend-license-agreement-for-investigational-spk-9001-in-hemophilia-b/. Accessed 1 Mar 2017.
Spark Therapeutics. Spark Therapeutics reports 2017 financial results and recent business progress. 2018. https://sparktx.com/press_releases/spark-therapeutics-reports-2017-financial-results-and-recent-business-progress/. Accessed 28 Jan 2024.
Roche. Roche concludes acquisition of Spark Therapeutics, Inc. to strengthen presence in gene therapy [media release]. https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2019-12-17b. Accessed 17 Dec 2019.
George LA, Sullivan SK, Rasko JEJ, et al. Efficacy and safety in 15 hemophilia B patients treated with the AAV gene therapy vector fidanacogene elaparvovec and followed for at least 1 year [abstract no. 3347]. Blood. 2019;134(Suppl 1):3347.
Frenzel L, Alzahrani H, Cuker A, et al. Vector clearance following administration of fidanacogene elaparvovec gene therapy in adults with haemophilia B [abstract no. PO132]. Haemophilia. 2024;30(Suppl 1):124–5.
Cuker A, Alzahrani H, Astermark J, et al. Efficacy and safety of fidanacogene elaparvovec in adults with moderately severe or svere hemophilia B: results from the phase 3 BENEGENE-2 gene therapy trial [abstract no. OC 52.3]. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023;7(Suppl 2):124–5.
Frenzel L, Kavakli K, Klamroth R, et al. Characterizing a cohort of patients with hemophilia B treated with fidanacogene elaparvovec from the phase 3 BENEGENE-2 study who returned to factor IX prophylaxis. Blood. 2023;142(Suppl 1):2257.
von Mackensen S, Bagot CN, Lienhart A, et al. Health-related quality of life in adults with haemophilia B after gene therapy with fidanacogene elaparvovec in the BENEGENE-2 trial [abstract no. PO116]. Haemophilia. 2024;30(Suppl 1):92.
Rasko JEJ, Chhabra A, Ducore JM, et al. Patterns of joint bleeds in patients with hemophilia B following fidanacogene elaparvovec adeno-associated virus gene therapy. Haemophilia. 2023;29(Suppl 1):113–4.
Samelson-Jones BJ, Sullivan SK, Rasko JEJ, et al. Follow-up of more than 5 years in a cohort of patients with hemophilia B treated with fidanacogene elaparvovec adeno-associated virus gene therapy. Blood. 2021;138(Suppl 1):3975.
von Mackensen S, Ducore JM, George LA, et al. Health-related quality of life in adults with hemophilia B after receiving gene therapy with fidanacogene elaparvovec. Blood. 2023;142(Suppl 1):3628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and Conflict of interest
During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Sohita Dhillon is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to this article and are responsible for its content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dhillon, S. Fidanacogene Elaparvovec: First Approval. Drugs (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-024-02017-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-024-02017-4