Abstract
Background and Objective
177Lu-Dotatate is a radio-labeled analog of somatostatin used in the treatment of somatostatin receptor-positive gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. In order to prevent nephrotoxic effects of 177Lu-Dotatate a co-infusion of amino acids (AA) is administered, resulting in a decrease in tubular renal reabsorption of 177Lu-Dotatate. This study aimed to quantify the impact of AA co-infusion on the pharmacokinetics of 177Lu-Dotatate in cancer patients and to evaluate its relationship with toxicity during the first treatment cycle (C1).
Methods
7.4 GBq of 177Lu-Dotatate was administered to 42 patients over a 30-min intravenous infusion. Infusion of AA started 2 h before and continued for 6 h after the infusion of 177Lu-Dotatate. Radioactivity–time data (n = 346) were analyzed using NONMEM® (version 7.2.0).
Results
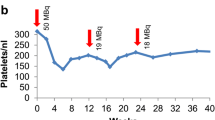
177Lu-Dotatate pharmacokinetics was best described by a three-compartment model with first-order elimination. AA co-infusion had a significant effect (‘fixed effect’) on 177Lu-Dotatate pharmacokinetics, with a mean value of 1.5-fold (95% confidence interval 1.03–1.97) increase in the elimination rate constant (k10) from 0.204 to 0.306 h−1, but this AA co-infusion effect was associated with a large inter-individual variability (IIV) of 104%. The individual k10 values increased during concomitant AA infusion by a factor ranging from 1.01 to 21.3 for 27 patients, whereas the opposite effect was observed in 15 patients (range 0.36–0.99) of whom seven had a k10 value lower than 0.85. This variability in AA effect contributed to the variability in 177Lu-Dotatate plasma exposure (area under the concentration–time curve from time zero to Day 15 for C1 [AUCDay15]) that correlated with lymphopenia observed at Day 15 (p = 0.004).
Conclusions
A substantial effect of AA co-infusion on 177Lu-Dotatate pharmacokinetics was shown but was associated with high IIV, contributing to IIV in hematological toxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kwekkeboom DJ, de Herder WW, Kam BL, van Eijck CH, van Essen M, Kooij PP, et al. Treatment with the radiolabeled somatostatin analog [177 Lu-DOTA 0, Tyr3]octreotate: toxicity, efficacy, and survival. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2124–30.
Strosberg J, El-Haddad G, Wolin E, Hendifar A, Yao J, Chasen B, et al. NETTER-1 Trial Investigators. Phase 3 trial of (177)Lu-Dotatate for midgut neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:125–35.
Hammond P, Wade A, Gwilliam M, Peters A, Myers M, Gilbey S, et al. Amino acid infusion blocks renal tubular uptake of an indium-labelled somatostatin analogue. Br J Cancer. 1993;67:1437–9.
Rolleman EJ, Krenning EP, Bernard BF, de Visser M, Bijster M, Visser TJ, et al. Long-term toxicity of [(177)Lu-DOTA (0), Tyr (3)]octreotate in rats. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34:219–27.
Sabet A, Ezziddin K, Pape U-F, Reichman K, Haslerud T, Ahmadzadehfar H, et al. Accurate assessment of long-term nephrotoxicity after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with (177)Lu-octreotate. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:505–10.
Sabet A, Ezziddin K, Pape U-F, Ahmadzadehfar H, Mayer K, Pöppel T, et al. Long-term hematotoxicity after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-octreotate. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:1857–61.
Bergstrand M, Hooker AC, Wallin JE, Karlsson MO. Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J. 2011;13(2):143–51.
Yeo TW, Rooslamiati I, Gitawati R, Tjitra E, Lampah DA, Kenangalem E, et al. Pharmacokinetics of l-arginine in adults with moderately severe malaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:4381–7.
Melis M, Krenning EP, Bernard BF, Barone R, Visser TJ, de Jong M. Localisation and mechanism of renal retention of radiolabelled somatostatin analogues. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:1136–43.
Kantarci S, Al-Gazali L, Hill RS, Donnai D, Black GCM, Bieth E, et al. Mutations in LRP2, which encodes the multiligand receptor megalin, cause Donnai-Barrow and facio-oculo-acoustico-renal syndromes. Nat Genet. 2007;39:957–9.
Chasman DI, Fuchsberger C, Pattaro C, Teumer A, Böger CA, Endlich K, et al. Integration of genome-wide association studies with biological knowledge identifies six novel genes related to kidney function. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:5329–43.
Lutathera. Highlights of prescribing information. https://www.adacap.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/Lutathera_lutetium_Lu_-177_dotatate_PI_2018_01.pdf. Accessed 18 Apr 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was conducted in compliance with ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
Alicja Puszkiel, Mathilde Bauriaud-Mallet, Roxane Bourgeois, Lawrence Dierickx, Frédéric Courbon, and Etienne Chatelut declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
No specific funding was received for either carrying out the study or preparing the manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puszkiel, A., Bauriaud-Mallet, M., Bourgeois, R. et al. Evaluation of the Interaction of Amino Acid Infusion on 177Lu-Dotatate Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin Pharmacokinet 58, 213–222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-018-0674-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-018-0674-1