Abstract
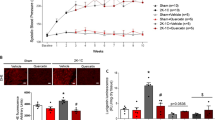
Angiotensin II induced increase in hypertension enhances oxidative stress and compromises insulin action and pancreatic function. Quercetin-rich foods are beneficial for hypertensive and diabetic animals owing to their antioxidant function. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant effects of quercetin in hypertensive rats on insulin action, signaling, and secretion. Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups: sham, hypertensive rats (H), and hypertensive rats supplemented with quercetin (HQ). After three months of initial hypertension, quercetin was administered at 50 mg/kg/day for 30 days. Our results indicate that hypertension and serum lipid peroxidation levels were reduced by quercetin supplementation. We observed increased insulin sensitivity in adipose tissue, corroborating the insulin tolerance test, HOMA index, and improvements in lipid profile. Despite normal insulin secretion at 2.8 and 20 mM of glucose, animals treated with quercetin exhibited increased number of islets per section; increased protein expression of muscarinic receptor type 3, VEGF, and catalase in islets; and hepatic mRNA levels of Ide were normalized. In conclusion, supplementation with quercetin improved insulin action and prevented pancreatic and metabolic dysfunction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Hay SO, Kang D, McBride M, Li L, Zhao J, Leissring MA. Deletion of insulin-degrading enzyme elicits antipodal, age-dependent effects on glucose and insulin tolerance. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20818. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020818.
Ali AM, Gabbar MA, Abdel-Twab SM, Fahmy EM, Ebaid H, Alhazza IM, Ahmed OM. Antidiabetic potency, antioxidant effects, and mode of actions of Citrus reticulata fruit Peel Hydroethanolic extract, hesperidin, and quercetin in nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-induced Wistar diabetic rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1730492. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1730492.
Aprotosoaie AC, Miron A, Trifan A, Luca VS, Costache II. The cardiovascular effects of cocoa polyphenols-an overview. Diseases. 2016;4(4) https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4040039.
Bardy G, Virsolvy A, Quignard JF, Ravier MA, Bertrand G, Dalle S, Cros G, Magous R, Richard S, Oiry C. Quercetin induces insulin secretion by direct activation of L-type calcium channels in pancreatic beta cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;169(5):1102–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12194.
Basso N, Terragno NA. History about the discovery of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension. 2001;38(6):1246–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/hy1201.101214.
Bhattacharya S, Oksbjerg N, Young JF, Jeppesen PB. Caffeic acid, naringenin and quercetin enhance glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and glucose sensitivity in INS-1E cells. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16(7):602–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12236.
Bonora E, Moghetti P, Zancanaro C, Cigolini M, Querena M, Cacciatori V, Corgnati A, Muggeo M. Estimates of in vivo insulin action in man: comparison of insulin tolerance tests with euglycemic and hyperglycemic glucose clamp studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989;68(2):374–8. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-68-2-374.
Brissova M, Aamodt K, Brahmachary P, Prasad N, Hong JY, Dai C, Mellati M, Shostak A, Poffenberger G, Aramandla R, Levy SE, Powers AC. Islet microenvironment, modulated by vascular endothelial growth factor-a signaling, promotes beta cell regeneration. Cell Metab. 2014;19(3):498–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.02.001.
Brull V, Burak C, Stoffel-Wagner B, Wolffram S, Nickenig G, Muller C, Langguth P, Alteheld B, Fimmers R, Naaf S, Zimmermann BF, Stehle P, Egert S. Effects of a quercetin-rich onion skin extract on 24 h ambulatory blood pressure and endothelial function in overweight-to-obese patients with (pre-)hypertension: a randomised double-blinded placebo-controlled cross-over trial. Br J Nutr. 2015;114(8):1263–77. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515002950.
Bule M, Abdurahman A, Nikfar S, Abdollahi M, Amini M. Antidiabetic effect of quercetin: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019;125:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.01.037.
Chan YC, Leung PS. The renin-angiotensin system and reactive oxygen species: implications in pancreatitis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(10):2743–55. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2011.4071.
Dhanya R, Arya AD, Nisha P, Jayamurthy P. Quercetin, a Lead compound against type 2 diabetes ameliorates glucose uptake via AMPK pathway in skeletal muscle cell line. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:336. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00336.
Edwards RL, Lyon T, Litwin SE, Rabovsky A, Symons JD, Jalili T. Quercetin reduces blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. J Nutr. 2007;137(11):2405–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/137.11.2405.
Egert S, Bosy-Westphal A, Seiberl J, Kurbitz C, Settler U, Plachta-Danielzik S, Wagner AE, Frank J, Schrezenmeir J, Rimbach G, Wolffram S, Muller MJ. Quercetin reduces systolic blood pressure and plasma oxidised low-density lipoprotein concentrations in overweight subjects with a high-cardiovascular disease risk phenotype: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled cross-over study. Br J Nutr. 2009;102(7):1065–74. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114509359127.
Eid HM, Haddad PS. The antidiabetic potential of quercetin: underlying mechanisms. Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(4):355–64. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666160909153707.
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH. Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:407–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(90)86134-h.
Faselis C, Doumas M, Papademetriou V. Common secondary causes of resistant hypertension and rational for treatment. Int J Hypertens. 2011;2011:236239. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/236239.
Fernandez-Cabezudo MJ, George JA, Bashir G, Mohamed YA, Al-Mansori A, Qureshi MM, Lorke DE, Petroianu G, Al-Ramadi BK. Involvement of acetylcholine receptors in cholinergic pathway-mediated protection against autoimmune diabetes. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1038. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01038.
Fullerton MD, Galic S, Marcinko K, Sikkema S, Pulinilkunnil T, Chen ZP, O'Neill HM, Ford RJ, Palanivel R, O'Brien M, Hardie DG, Macaulay SL, Schertzer JD, Dyck JR, van Denderen BJ, Kemp BE, Steinberg GR. Single phosphorylation sites in Acc1 and Acc2 regulate lipid homeostasis and the insulin-sensitizing effects of metformin. Nat Med. 2013;19(12):1649–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3372.
Gautam D, Ruiz de Azua I, Li JH, Guettier JM, Heard T, Cui Y, Lu H, Jou W, Gavrilova O, Zawalich WS, Wess J. Beneficial metabolic effects caused by persistent activation of beta-cell M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in transgenic mice. Endocrinology. 2010;151(11):5185–94. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2010-0519.
Ghorbani A, Rashidi R, Shafiee-Nick R. Flavonoids for preserving pancreatic beta cell survival and function: a mechanistic review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;111:947–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.127.
Gilon P, Henquin JC. Mechanisms and physiological significance of the cholinergic control of pancreatic beta-cell function. Endocr Rev. 2001;22(5):565–604. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.22.5.0440.
Goldblatt H, Lynch J, Hanzal RF, Summerville WW. Studies on experimental hypertension : I. the production of persistent elevation of systolic blood pressure by means of renal ischemia. J Exp Med. 1934;59(3):347–79. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.59.3.347.
Gormaz JG, Quintremil S, Rodrigo R. Cardiovascular disease: a target for the pharmacological effects of quercetin. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015;15(17):1735–42. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026615666150427124357.
Herrmann SM, Textor SC. Renovascular Hypertension. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2019;48(4):765–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2019.08.007.
Ihoriya C, Satoh M, Kuwabara A, Sasaki T, Kashihara N. Angiotensin II regulates islet microcirculation and insulin secretion in mice. Microcirculation. 2014;21(2):112–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/micc.12094.
Ikewuchi JC, Ikewuchi CC, Ifeanacho MO, Igboh NM, Ijeh II. Moderation of hematological and plasma biochemical indices of sub-chronic salt-loaded rats by aqueous extract of the sclerotia of Pleurotus tuberregium (Fr) Sing's: implications for the reduction of cardiovascular risk. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;150(2):466–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.002.
Ito Y, Kaji M, Sakamoto E, Terauchi Y. The beneficial effects of a muscarinic agonist on pancreatic beta-cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):16180. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52691-8.
Jiang H, Yamashita Y, Nakamura A, Croft K, Ashida H. Quercetin and its metabolite isorhamnetin promote glucose uptake through different signalling pathways in myotubes. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2690. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38711-7.
Jing F, Mogi M, Horiuchi M. Role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in adipose tissue dysfunction. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;378(1–2):23–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2012.03.005.
Kang GG, Francis N, Hill R, Waters D, Blanchard C, Santhakumar AB. Dietary polyphenols and gene expression in molecular pathways associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010140.
Kim KH. Regulation of mammalian acetyl-coenzyme a carboxylase. Annu Rev Nutr. 1997;17:77–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.17.1.77.
Kittl M, Beyreis M, Tumurkhuu M, Furst J, Helm K, Pitschmann A, Gaisberger M, Glasl S, Ritter M, Jakab M. Quercetin stimulates insulin secretion and reduces the viability of rat INS-1 Beta-cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):278–93. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445623.
Koistinen HA, Galuska D, Chibalin AV, Yang J, Zierath JR, Holman GD, Wallberg-Henriksson H. 5-amino-imidazole carboxamide riboside increases glucose transport and cell-surface GLUT4 content in skeletal muscle from subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52(5):1066–72. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.5.1066.
Lacraz G, Figeac F, Movassat J, Kassis N, Coulaud J, Galinier A, Leloup C, Bailbe D, Homo-Delarche F, Portha B. Diabetic beta-cells can achieve self-protection against oxidative stress through an adaptive up-regulation of their antioxidant defenses. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6500. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006500.
Lo S, Russell JC, Taylor AW. Determination of glycogen in small tissue samples. J Appl Physiol. 1970;28(2):234–6. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1970.28.2.234.
Maianti JP, McFedries A, Foda ZH, Kleiner RE, Du XQ, Leissring MA, Tang WJ, Charron MJ, Seeliger MA, Saghatelian A, Liu DR. Anti-diabetic activity of insulin-degrading enzyme inhibitors mediated by multiple hormones. Nature. 2014;511(7507):94–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13297.
Marunaka Y, Marunaka R, Sun H, Yamamoto T, Kanamura N, Inui T, Taruno A. Actions of quercetin, a polyphenol, on blood pressure. Molecules. 2017;22(2) https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020209.
Moulle VS, Tremblay C, Castell AL, Vivot K, Ethier M, Fergusson G, Alquier T, Ghislain J, Poitout V. The autonomic nervous system regulates pancreatic beta-cell proliferation in adult male rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019;317(2):E234–43. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00385.2018.
Msauko Koboria YT, Akimotoa Y, SakuraiaIzumi M, Haruno M, KatsunariIppoushia N, Oikea H, Ohnishi-Kameyamaa M. Chronic high intake of quercetin reduces oxidative stress and induces expression of the antioxidant enzymes in the liver and visceral adipose tissues in mice. J Funct Foods. 2015;15 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.04.006.
Najjar SM, Perdomo G. Hepatic insulin clearance: mechanism and physiology. Physiology (Bethesda). 2019;34(3):198–215. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00048.2018.
Navar LG, Zou L, Von Thun A, Tarng Wang C, Imig JD, Mitchell KD. Unraveling the mystery of Goldblatt hypertension. News Physiol Sci. 1998;13:170–6. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiologyonline.1998.13.4.170.
Rahal A, Kumar A, Singh V, Yadav B, Tiwari R, Chakraborty S, Dhama K. Oxidative stress, prooxidants, and antioxidants: the interplay. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:761264. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/761264.
Ritchie J, Green D, Chrysochou C, Chalmers N, Foley RN, Kalra PA. High-risk clinical presentations in atherosclerotic renovascular disease: prognosis and response to renal artery revascularization. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(2):186–97. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.07.020.
Sabrane K, Kruse MN, Fabritz L, Zetsche B, Mitko D, Skryabin BV, Zwiener M, Baba HA, Yanagisawa M, Kuhn M. Vascular endothelium is critically involved in the hypotensive and hypovolemic actions of atrial natriuretic peptide. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(6):1666–74. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI23360.
Salehi B, Machin L, Monzote L, Sharifi-Rad J, Ezzat SM, Salem MA, Merghany RM, El Mahdy NM, Kilic CS, Sytar O, Sharifi-Rad M, Sharopov F, Martins N, Martorell M, Cho WC. Therapeutic potential of quercetin: new insights and perspectives for human health. ACS Omega. 2020;5(20):11849–72. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01818.
Serban MC, Sahebkar A, Zanchetti A, Mikhailidis DP, Howard G, Antal D, Andrica F, Ahmed A, Aronow WS, Muntner P, Lip GY, Graham I, Wong N, Rysz J, Banach M, Lipid, Blood Pressure Meta-analysis Collaboration G. Effects of quercetin on blood pressure: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5(7) https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.115.002713.
Sowers JR. Hypertension, angiotensin II, and oxidative stress. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(25):1999–2001. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMe020054.
Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286(5):H1597–602. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00026.2004.
Szkudelska K, Deniziak M, Hertig I, Wojciechowicz T, Tyczewska M, Jaroszewska M, Szkudelski T. Effects of resveratrol in Goto-Kakizaki rat, a model of type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. 2019;11(10) https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102488.
Tang WJ. Targeting insulin-degrading enzyme to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016;27(1):24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2015.11.003.
Tikellis C, Wookey PJ, Candido R, Andrikopoulos S, Thomas MC, Cooper ME. Improved islet morphology after blockade of the renin- angiotensin system in the ZDF rat. Diabetes. 2004;53(4):989–97. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.53.4.989.
Vessal M, Hemmati M, Vasei M. Antidiabetic effects of quercetin in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2003;135C(3):357–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1532-0456(03)00140-6.
World Health Organization (2020a) Hypertension.
World Health Organization (2020b) Improving hypertension control in 3 million people: country experiences of programme development and implementation.
Xiao JB, Hogger P. Dietary polyphenols and type 2 diabetes: current insights and future perspectives. Curr Med Chem. 2015;22(1):23–38. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666140706130807.
Xu D, Hu MJ, Wang YQ, Cui YL. Antioxidant activities of quercetin and its complexes for medicinal application. Molecules. 2019;24(6) https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061123.
Youl E, Bardy G, Magous R, Cros G, Sejalon F, Virsolvy A, Richard S, Quignard JF, Gross R, Petit P, Bataille D, Oiry C. Quercetin potentiates insulin secretion and protects INS-1 pancreatic beta-cells against oxidative damage via the ERK1/2 pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;161(4):799–814. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00910.x.
Youl E, Magous R, Cros G, Oiry C. MAP kinase cross talks in oxidative stress-induced impairment of insulin secretion. Involvement in the protective activity of quercetin. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2014;28(6):608–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12078.
Zhao Y, Chen B, Shen J, Wan L, Zhu Y, Yi T, Xiao Z. The beneficial effects of quercetin, curcumin, and resveratrol in obesity. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:1459497. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1459497.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Bruno Alves Cia, BSc, Sr Mateus Eduardo Bortolanza da Silva, Sra Ana Cristina Pires Menegheti, Renata Barbieri, and Lucas Eduardo Orzari for their excellent technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Herminio Ometto Foundation.
C. A. Serra was the recipient of a graduate fellowship grant from the Biomedical Sciences Graduate Program, FHO.
C. S. Bueno and S. A. R. de Souza were the recipients of undergraduate fellowships from the Programa Institucional de Bolsas de Iniciação Científica e Apoio à Pesquisa of Hermínio Ometto Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors performed all the experiments. B. Calsa and Maria Esméria Corezola do Amaral analyzed the results and revised the manuscript; Maria Esméria Corezola do Amaral designed the study and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that this research was performed without any conflicts of interest or commercial or financial gains.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Cristiane Alves Serra and Alexandre Freire dos Reis are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serra, C.A., dos Reis, A.F., Calsa, B. et al. Quercetin prevents insulin dysfunction in hypertensive animals. J Diabetes Metab Disord 21, 407–417 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-022-00987-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-022-00987-4