Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to evaluate the status of scientific research output of omics in regards to human diseases with more attention shifted toward endocrine and metabolism disorders in Iran, in order to find scientific gaps and also to design future plans for further investigations in this field.
Methods
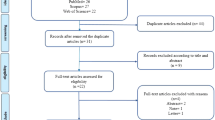
Extensive search was performed in the electronic databases of Scopus and PubMed, and documents published by Iranian authors up to 27 December 2020 were extracted. Articles related to human diseases were included and categorized based on their types and topics.
Results
A total of 904 publications were found. Followed by checking their titles and abstracts, 327 studies were included. The trend of publication has been increasing during the past years. Regarding this subject, the highest number of publications was in the field of malignant disorders with 82 publications followed by reproductive system diseases and infectious diseases with 33 publications in each subject. Only 12 articles were found in the field of endocrinology and metabolism. The most popular techniques used in those reports were two-dimensional electrophoresis coupled with mass spectrometry (34.4 %) followed by NMR (22.6 %), LC/MS/MS (15 %).
Conclusions
Omics studies in Iran are a relatively new approach and the number of original articles regarding endocrine disorders in humans is limited. Providing appropriate infrastructures including lab facilities with high technology instruments can improve the quality and quantity of basic and clinical researches in this field.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is available and can be accessed by contacting the Corresponding Author.
References
Arjmand B, Abdollahi M, Larijani B. Precision medicine: A new revolution in healthcare system. Iran Biomed J. 2017;21(5):282–3.
Agharezaee N, Hashemi M, Shahani M, Gilany K. Male infertility, precision medicine and systems proteomics. J Reprod Infant Psychol. 2018;19(4):185–92.
Adamski J. Key elements of metabolomics in the study of biomarkers of diabetes. Diabetologia. 2016;59(12):2497–502.
Zhang A, Sun H, Wang P, Han Y, Wang X. Modern analytical techniques in metabolomics analysis. Analyst. 2012;137(2):293–300.
Chashmniam S, Madani NH, Ghoochani BFNM, Safari-Alighiarloo N, Khamseh ME. The metabolome profiling of obese and non-obese individuals: Metabolically healthy obese and unhealthy non-obese paradox. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020;23(2):186.
Bagheri M, Djazayery A, Farzadfar F, Qi L, Yekaninejad MS, Aslibekyan S, et al. Plasma metabolomic profiling of amino acids and polar lipids in Iranian obese adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):1–9.
Bagheri M, Farzadfar F, Qi L, Yekaninejad MS, Chamari M, Zeleznik OA, et al. Obesity-related metabolomic profiles and discrimination of metabolically unhealthy obesity. J Proteome Res. 2018;17(4):1452–62.
Bagheri M, Djazayery A, Qi L, Yekaninejad MS, Chamari M, Naderi M, et al. Effectiveness of vitamin D therapy in improving metabolomic biomarkers in obesity phenotypes: Two randomized clinical trials. Int J Obes. 2018;42(10):1782–96.
Rahimi N, Razi F, Nasli-Esfahani E, Qorbani M, Shirzad N, Larijani B. Amino acid profiling in the gestational diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2017;16(1):13.
Kazemi Khoo N, Iravani A, Arjmand M, Vahabi F, Lajevardi M, Akrami SM, et al. A metabolomic study on the effect of intravascular laser blood irradiation on type 2 diabetic patients. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28(6):1527–32.
Naderi N, Zaefizadeh M. Expression of growth factors in re-epithelialization of diabetic foot ulcers after treatment with non-thermal plasma radiation. Biomed Res. 2017;28(8):3402–7.
Maleki A, Ramazani A, Foroutan M, Biglari A, Ranjzad P, Mellati AA. Comparative proteomics study of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats kidneys transfected with adenovirus-mediated fibromodulin gene. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2014;6(2):104–12.
Abooshahab R, Hooshmand K, Razavi SA, Gholami M, Sanoie M, Hedayati M. Plasma metabolic profiling of human thyroid nodules by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based untargeted metabolomics. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:385.
Yekta RF, Oskouie AA, Tavirani MR, Mohajeri-Tehrani MR, Soroush AR. Decreased apolipoprotein A4 and increased complement component 3 as potential markers for papillary thyroid carcinoma: A proteomic study. Int J Biol Markers. 2018;33(4):455–62.
Yekta RF, Tavirani MR, Oskouie AA, Mohajeri-Tehrani MR, Soroush AR, Baghban AA. Serum-based metabolic alterations in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma unveiled by non-targeted 1H-NMR metabolomics approach. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018;21(11):1140–7.
Abooshahab R, Gholami M, Sanoie M, Azizi F, Hedayati M. Advances in metabolomics of thyroid cancer diagnosis and metabolic regulation. Endocrine. 2019;65(1):1–14.
Khatami F, Payab M, Sarvari M, Gilany K, Larijani B, Arjmand B, et al. Oncometabolites as biomarkers in thyroid cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:1829–41.
Farrokhi Yekta R, Rezaie Tavirani M, Arefi Oskouie A, Mohajeri-Tehrani MR, Soroush AR. The metabolomics and lipidomics window into thyroid cancer research. Biomarkers. 2017;22(7):595–603.
Gilany K, Minai-Tehrani A, Savadi-Shiraz E, Rezadoost H, Lakpour N. Exploring the human seminal plasma proteome: An unexplored gold mine of biomarker for male Infertility and male reproduction disorder. J Reprod Infertil. 2015;16(2):61–71.
Mehrparavar B, Minai-Tehrani A, Arjmand B, Gilany K. Metabolomics of male infertility: A new tool for diagnostic tests. J Reprod Infertil. 2019;20(2):64–9.
Gilany K, Mani-Varnosfaderani A, Minai-Tehrani A, Mirzajani F, Ghassempour A, Sadeghi MR, et al. Untargeted metabolomic profiling of seminal plasma in nonobstructive azoospermia men: A noninvasive detection of spermatogenesis. Biomed Chromatogr. 2017;31(8):e3931.
Gilany K, Jafarzadeh N, Mani-Varnosfaderani A, Minai-Tehrani A, Sadeghi MR, Darbandi M, et al. Metabolic fingerprinting of seminal plasma from non-obstructive azoospermia patients: Positive versus negative sperm retrieval. J Reprod Infertil. 2018;19(2):109–14.
Hashemitabar M, Sabbagh S, Orazizadeh M, Ghadiri A, Bahmanzadeh M. A proteomic analysis on human sperm tail: Comparison between normozoospermia and asthenozoospermia. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32(6):853–63.
Vakilian H, Mirzaei M, Sharifi Tabar M, Pooyan P, Habibi Rezaee L, Parker L, et al. DDX3Y, a male-specific region of y chromosome gene, may modulate neuronal differentiation. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(9):3474–83.
Larijani B, Goodarzi P, Payab M, Alavi-Moghadam S, Rahim F, Bana N, et al. Metabolomics and cell therapy in diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Cell Med (IJMCM). 2019;8(2):0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated and approved the paper prior to submission. Hossein Aazami led survey implementation. Shaghayegh Hosseinkhani and Niloufar Najjar led data collection, data analysis, and preparation of the manuscript. Nastaran Hadizadeh contributed to the preparation of the manuscript and participated in critical review. Parvin Pasalar1 and Farideh Razi played key roles in the planning, implementation, and management of the study. Babak Arjmand and Fatemeh Bandarian participated in the study design, helped to refine data-collection tools, and assisted in managing data collection.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Endocrinology and Metabolism Molecular-Cellular Sciences Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinkhani, S., Arjmand, B., Bandarian, F. et al. Omics experiments in Iran, a review in endocrine and metabolism disorders studies. J Diabetes Metab Disord (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00727-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00727-0