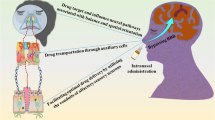
Abstract
Background
Tight junctions and efflux transporters are two chief bodyguards of the blood–brain barrier that protect the brain and create challenges for the treatment of neurological disorders by hampering the systemic delivery of conventional therapeutics to the brain. Approaches involving drug delivery across the brain are either invasive which require disruption of barrier integrity, leading to develop the risk of neurological changes and brain abscess, or non-invasive patient friendly approach like intranasal delivery. Several investigations have strongly confirmed the direct connection between nose and brain via olfactory and trigeminal pathway which deliver neurotherapeutics directly to the brain bypassing obstructive barriers.
Area covered
Since last two decades, extensive researches are ongoing for intranasal delivery of drugs in the form of different novel colloidal carriers wherein, microemulsion with their unique composition and small globule size (< 100 nm) have shown higher efficacy in-vivo and revealed their great potential to treat severe brain disorders where rapid onset of action is needed. In this discussion, why intranasal delivery of microemulsion seems to be promising for brain targeting is the foremost focus while, the importance of delivery device for efficient brain targeting is also covered.
Expert opinion
Considering the translation of positive in-vivo outcomes further into clinical studies and humans, future direction should be aimed at evaluating the suitability of microemulsion with an efficient intranasal delivery device capable of delivering formulation into upper nasal segment. Limitations associated to intranasal delivery of microemulsion such as performing brain distribution studies in most appropriate model resembling humans, impact of diseased condition on the drug absorption and toxicity related to prolonged use, etc. must be addressed in the near future to establish a strong bench to bedside platform.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelbary G, Fahmy RH (2009) Diazepam-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: design and characterization. AAPS PharmSciTech 10(1):211–219
Ahmad E, Feng Y, Qi J, Fan W, Ma Y, He H, Xia F, Dong X, Zhao W, Lu Y, Wu W (2017) Evidence of nose-to-brain delivery of nanoemulsions: cargoes but not vehicles. Nanoscale 9(3):1174–1183
Ahmad N, Ahmad R, Naqvi AA, Alam MA, Ashafaq M, Abdur Rub R, Ahmad FJ (2018) Intranasal delivery of quercetin-loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsion for treatment of cerebral ischaemia. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(4):717–729
Alexander A, Saraf S (2018) Nose-to-brain drug delivery approach: A key to easily accessing the brain for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res 13(12):2102–2104
Asmari AKA, Ullah Z, Tariq M, Fatani A (2016) Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of intranasally administered liposomal formulation of donepezil. Drug Des Devel Ther 10:205–215
Balin BJ, Broadwell RD, Salcman M, el-Kalliny M (1986) Avenues for entry of peripherally administered protein to the central nervous system in mouse, rat, and squirrel monkey. J Comp Neurol 251(2):260–280
Baltzley S, Mohammad A, Malkawi AH, Al-Ghananeem AM (2014) Intranasal drug delivery of olanzapine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 15(6):1598–1602
Barta CA, Sachs-Barrable K, Feng F, Wasan KM (2008) Effects of monoglycerides on P-glycoprotein: modulation of the activity and expression in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Mol Pharm 5(5):863–875
Bourganis V, Kammona O, Alexopoulos A, Kiparissides C (2018) Recent advances in carrier mediated nose-to-brain delivery of pharmaceutics. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 128:337–362
Brambilla M, Manenti R, de Girolamo G, Adenzato M, Bocchio-Chiavetto L, Cotelli M (2016) Effects of Intranasal Oxytocin on Long-Term Memory in Healthy Humans: A Systematic Review. Drug Dev Res 77(8):479–488
Brioschi AM, Calderoni S, Zara GP, Priano L, RosaGasco M, Mauro A (2009) Solid lipid nanoparticles for brain tumors therapy: State of the art and novel challenges. S H.S. Elsevier 180:193–223
Bruinsmann FA, Vaz GR, de Cristo Soares Alves A, Aguirre T, Raffin Pohlmann A, Staniscuaski Guterres S, Sonvico F (2019) Nasal Drug Delivery of Anticancer Drugs for the Treatment of Glioblastoma: Preclinical and Clinical Trials. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234312
Bshara H, Osman R, Mansour S, El-Shamy Ael H (2014) Chitosan and cyclodextrin in intranasal microemulsion for improved brain buspirone hydrochloride pharmacokinetics in rats. Carbohydr Polym 99:297–305
Casettari L, Illum L (2014) Chitosan in nasal delivery systems for therapeutic drugs. J Control Release 190:189–200
Chang J, Jallouli Y, Barras A, Dupont N, Betbeder D (2009) Chapter 1–Drug delivery to the brain using colloidal carriers. Prog Brain Res 180:2–17
Chatterjee B, Gorain B, Mohananaidu K, Sengupta P, Mandal UK, Choudhury H (2019) Targeted drug delivery to the brain via intranasal nanoemulsion: Available proof of concept and existing challenges. Int J Pharm 565:258–268
Chauhan MB, Chauhan NB (2015) Brain Uptake of Neurotherapeutics after Intranasal versus Intraperitoneal Delivery in Mice. J Neurol Neurosurg 2(1):009
Collaborators GN (2019) Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet Neurology 18(5):459–480
Costantino L, Boraschi D (2012) Is there a clinical future for polymeric nanoparticles as brain-targeting drug delivery agents? Drug Discov Today 17(7–8):367–378
Crowe TP, Greenlee MHW, Kanthasamy AG, Hsu WH (2018) Mechanism of intranasal drug delivery directly to the brain. Life Sci 195:44–52
Deli MA (2009) Potential use of tight junction modulators to reversibly open membranous barriers and improve drug delivery. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788(4):892–910
Dey S, Mahanti B, Mazumder B, Dasgupta S (2011) nasal drug delivery: an approach of drug delivery through nasal route. Der Pharmacia Sinica 2(3):94–106
Djupesland PG, Skretting A, Winderen M, Holand T (2004) Bi-directional nasal delivery of aerosols can prevent lung deposition. J Aerosol Med 17(3):249–259
Djupesland PG, Skretting A, Winderen M, Holand T (2006) Breath actuated device improves delivery to target sites beyond the nasal valve. Laryngoscope 116(3):466–472
Djupesland PG, Messina JC, Mahmoud RA (2014) The nasal approach to delivering treatment for brain diseases: an anatomic, physiologic, and delivery technology overview. Ther Deliv 5(6):709–733
Dong X, Ke X, Liao Z (2011) The microstructure characterization of meloxicam microemulsion and its influence on the solubilization capacity. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 37(8):894–900
Dora CL, Silva LF, Costa T, Mónika P, Silva S, Antonio M, Senna L, Elenara, (2011) Formulation study of quercetin-loaded lipid-based nanocarriers obtained by hot solvent diffusion method. Lat Am J Pharm 30(2):289–296
Erdo F, Bors LA, Farkas D, Bajza A, Gizurarson S (2018) Evaluation of intranasal delivery route of drug administration for brain targeting. Brain Res Bull 143:155–170
Espinoza LC, Vacacela M, Clares B, Garcia ML, Fabrega MJ, Calpena AC (2018) Development of a Nasal Donepezil-loaded Microemulsion for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: in vitro and ex vivo Characterization. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 17(1):43–53
Fanun M (2009) Oil type effect on diclofenac solubilization in mixed nonionic surfactants microemulsions. Colloids Surf, A 343(1–3):75–82
Fanun M (2012) Microemulsions as delivery systems. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 17(5):306–313
Fazil M, Md S, Haque S, Kumar M, Baboota S, Sahni JK, Ali J (2012) Development and evaluation of rivastigmine loaded chitosan nanoparticles for brain targeting. Eur J Pharm Sci 47(1):6–15
Florence K, Manisha L, Kumar BA, Ankur K, Kumar MA, Ambikanandan M (2011) Intranasal clobazam delivery in the treatment of status epilepticus. J Pharm Sci 100(2):692–703
WH Frey 1997 Methods of administering neurologic agents to the brain United states Ramsey foundation US 5 624 898
Furlanetto S, Cirri M, Piepel G, Mennini N, Mura P (2011) Mixture experiment methods in the development and optimization of microemulsion formulations. J Pharm Biomed Anal 55(4):610–617
Gadhave D, Gorain B, Tagalpallewar A, Kokare C (2019) Intranasal teriflunomide microemulsion: An improved chemotherapeutic approach in glioblastoma. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 51:276–289
Ganger S, Schindowski K (2018) Tailoring Formulations for Intranasal Nose-to-Brain Delivery: A Review on Architecture, Physico-Chemical Characteristics and Mucociliary Clearance of the Nasal Olfactory Mucosa. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030116
Gartziandia O, Egusquiaguirre SP, Bianco J, Pedraz JL, Igartua M, Hernandez RM, Preat V, Beloqui A (2016) Nanoparticle transport across in vitro olfactory cell monolayers. Int J Pharm 499(1–2):81–89
Ge X, Wei M, He S, Yuan WE (2019) Advances of Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) and Their Application in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020055
Graff CL, Pollack GM (2003) P-Glycoprotein attenuates brain uptake of substrates after nasal instillation. Pharm Res 20(8):1225–1230
Graff CL, Pollack GM (2005a) Nasal drug administration: potential for targeted central nervous system delivery. J Pharm Sci 94(6):1187–1195
Graff CL, Pollack GM (2005b) Functional evidence for P-glycoprotein at the nose-brain barrier. Pharm Res 22(1):86–93
Harush-Frenkel O, Rozentur E, Benita S, Altschuler Y (2008) Surface charge of nanoparticles determines their endocytic and transcytotic pathway in polarized MDCK cells. Biomacromol 9(2):435–443
He CX, He ZG, Gao JQ (2010) Microemulsions as drug delivery systems to improve the solubility and the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7(4):445–460
Hellweg T (2002) Phase structures of microemulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 7(1–2):50–56
Hetal P, Thakkar AAP, Chauhan NP (2014) Intranasal mucoadhesive microemulsion of mirtazapine: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies. Asian journal of pharmaceutics 7(1):36–42
Hoekman JD, Ho RJ (2011) Enhanced analgesic responses after preferential delivery of morphine and fentanyl to the olfactory epithelium in rats. Anesth Analg 113(3):641–651
Hoekman J BA, Hite M (2013) "SPECT imaging of direct nose‐to‐brain transfer of MAG‐3 in man." American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists Annual Meeting.
Hu L, Wu H, Niu F, Yan C, Yang X, Jia Y (2011) Design of fenofibrate microemulsion for improved bioavailability. Int J Pharm 420(2):251–255
Illum L (2000) Transport of drugs from the nasal cavity to the central nervous system. Eur J Pharm Sci 11(1):1–18
Illum L (2004) Is nose-to-brain transport of drugs in man a reality? J Pharm Pharmacol 56(1):3–17
Illum L (2012) Nasal drug delivery - recent developments and future prospects. J Control Release 161(2):254–263
Jadhav KR, Gambhire MN, Shaikh IM, Vilarsrao K, Pisal SS (2007) Nasal Drug Delivery System-Factors Affecting and Applications. Current Drug Therapy 2(1):27–38
Jain A, Jain S (2019) Formulations and evaluations of Intranasal Nose to Brain Delivery of Curcumin with resveratrol Nanoparticle for treatment of Parkisonism. International Congress Movement Disorder. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27795
Joseph E, Reddi S, Rinwa V, Balwani G, Saha R (2017) Design and in vivo evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticulate systems of Olanzapine for acute phase schizophrenia treatment: Investigations on antipsychotic potential and adverse effects. Eur J Pharm Sci 104:315–325
Kang YJ, Cutler EG, Cho H (2018) Therapeutic nanoplatforms and delivery strategies for neurological disorders. Nano Converg 5(1):35
Karasulu HY (2008) Microemulsions as novel drug carriers: the formation, stability, applications and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 5(1):119–135
Khan AR, Liu M, Khan MW, Zhai G (2017) Progress in brain targeting drug delivery system by nasal route. J Control Release 268:364–389
Khunt D, Shah B, Misra M (2017) Role of butter oil in brain targeted delivery of Quetiapine fumarate microemulsion via intranasal route. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 40:11–20
Kogan A, Aserin A, Garti N (2007) Improved solubilization of carbamazepine and structural transitions in nonionic microemulsions upon aqueous phase dilution. J Colloid Interface Sci 315(2):637–647
Kokare C, Koli D, Gadhave D, Mote C, Khandekar G (2020) Efavirenz-loaded intranasal microemulsion for crossing blood-CNS interfaces in neuronal-AIDS: pharmacokinetic and in vivo safety evaluation. Pharm Dev Technol 25(1):28–39
Krishan M, Gudelsky GA, Desai PB, Genter MB (2014) Manipulation of olfactory tight junctions using papaverine to enhance intranasal delivery of gemcitabine to the brain. Drug Deliv 21(1):8–16
Kumar M, Misra A, Babbar AK, Mishra AK, Mishra P, Pathak K (2008a) Intranasal nanoemulsion based brain targeting drug delivery system of risperidone. Int J Pharm 358(1–2):285–291
Kumar M, Misra A, Mishra AK, Mishra P, Pathak K (2008b) Mucoadhesive nanoemulsion-based intranasal drug delivery system of olanzapine for brain targeting. J Drug Target 16(10):806–814
Kumar M, Pathak K, Misra A (2009) Formulation and characterization of nanoemulsion-based drug delivery system of risperidone. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 35(4):387–395
Lee VHL, Yamamoto A (1989) Penetration and enzymatic barriers to peptide and protein absorption. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 4(2):171–207
Li L, Nandi I, Kim KH (2002) Development of an ethyl laurate-based microemulsion for rapid-onset intranasal delivery of diazepam. Int J Pharm 237(1–2):77–85
Li JC, Zhang WJ, Zhu JX, Zhu N, Zhang HM, Wang X, Zhang J, Wang QQ (2015) Preparation and brain delivery of nasal solid lipid nanoparticles of quetiapine fumarate in situ gel in rat model of schizophrenia. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(10):17590–17600
Lin H, Gebhardt M, Bian S, Kwon KA, Shim CK, Chung SJ, Kim DD (2007) Enhancing effect of surfactants on fexofenadine.HCl transport across the human nasal epithelial cell monolayer. Int J Pharm 330(1–2):23–31
Liwarska-Bizukojc E, Miksch K, Malachowska-Jutsz A, Kalka J (2005) Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of five selected anionic and nonionic surfactants. Chemosphere 58(9):1249–1253
Lochhead JJ, Thorne RG (2012) Intranasal delivery of biologics to the central nervous system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(7):614–628
Lochhead JJ, Wolak DJ, Pizzo ME, Thorne RG (2015) Rapid transport within cerebral perivascular spaces underlies widespread tracer distribution in the brain after intranasal administration. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35(3):371–381
Lopes LB (2014) Overcoming the cutaneous barrier with microemulsions. Pharmaceutics 6(1):52–77
Madane RG, Mahajan HS (2016) Curcumin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for nasal administration: design, characterization, and in vivo study. Drug Deliv 23(4):1326–1334
Mahajan HS, Mahajan MS, Nerkar PP, Agrawal A (2014) Nanoemulsion-based intranasal drug delivery system of saquinavir mesylate for brain targeting. Drug Deliv 21(2):148–154
Mandal S, Mandal SD, Chuttani K, Sawant KK, Subudhi BB (2016) Design and evaluation of mucoadhesive microemulsion for neuroprotective effect of ibuprofen following intranasal route in the MPTP mice model. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 42(8):1340–1350
Mather M, Jacobsen la, Jarosz B, Kilduff l, Lee A, Pollard Km, Scommegna p and Vanorman A (2019). "America’s Changing Population." Population Bulletin.
McMartin C, Hutchinson LE, Hyde R, Peters GE (1987) Analysis of structural requirements for the absorption of drugs and macromolecules from the nasal cavity. J Pharm Sci 76(7):535–540
Mehta AK, Yadav KS, Sawant KK (2007) Nimodipine loaded PLGA nanoparticles: formulation optimization using factorial design, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Curr Drug Deliv 4(3):185–193
Mena-Hernandez J, Jung-Cook H, Llaguno-Munive M, Garcia-Lopez P, Ganem-Rondero A, Lopez-Ramirez S, Barragan-Aroche F, Rivera-Huerta M, Mayet-Cruz L (2020) Preparation and Evaluation of Mebendazole Microemulsion for Intranasal Delivery: an Alternative Approach for Glioblastoma Treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 21(7):264
Mistry A, Stolnik S, Illum L (2009) Nanoparticles for direct nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. Int J Pharm 379(1):146–157
Mittal D, Ali A, Md S, Baboota S, Sahni JK, Ali J (2014) Insights into direct nose to brain delivery: current status and future perspective. Drug Deliv 21(2):75–86
Miyamoto M, Natsume H, Satoh I, Ohtake K, Yamaguchi M, Kobayashi D, Sugibayashi K, Morimoto Y (2001) Effect of poly-L-arginine on the nasal absorption of FITC-dextran of different molecular weights and recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) in rats. Int J Pharm 226(1–2):127–138
Moran DT, Rowley JC 3rd, Jafek BW, Lovell MA (1982) The fine structure of the olfactory mucosa in man. J Neurocytol 11(5):721–746
Mustafa G, Baboota S, Ahuja A, Ali J (2012) Formulation Development of Chitosan Coated Intra Nasal Ropinirole Nanoemulsion for Better Management Option of Parkinson: An In Vitro Ex Vivo Evaluation. Curr Nanosci 8(3):348–360
Narayan R, Singh M, Ranjan O, Nayak Y, Garg S, Shavi GV, Nayak UY (2016) Development of risperidone liposomes for brain targeting through intranasal route. Life Sci 163:38–45
Negi LM, Tariq M, Talegaonkar S (2013) Nano scale self-emulsifying oil based carrier system for improved oral bioavailability of camptothecin derivative by P-Glycoprotein modulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 111:346–353
Neuropharma I. (2013). "Impel NeuroPharma, Inc. SPECT Imaging of Direct Nose-to-Brain Transfer of MAG-3 in Man."
NeuroPharma I. (2018). "Impel NeuroPharma Announces FDA Clearance of IND for Pivotal Phase 3 Study of INP104 for Acute Treatment of Migraine." from https://impelnp.com/2018/06/22/impel-neuropharma-announces-fda-clearance-of-ind-for-pivotal-phase-3-study-of-inp104-for-acute-treatment-of-migraine/.
NeuroPharma I. (2018). "Impel NeuroPharma Announces First Patient Dosed in Phase 3 Trial Evaluating INP104 for the Treatment of Acute Migraine Headache." from https://impelnp.com/2018/08/22/impel-neuropharma-announces-first-patient-dosed-in-phase-3-trial-evaluating-inp104-for-the-treatment-of-acute-migraine-headache/.
Pandey V, Gadeval A, Asati S, Jain P, Jain N, Roy RK, Soni V, Tekade RK (2020) Formulation strategies for nose-to- brain delivery of therapeutic molecules. In: Tekade RK (ed) Drug Delivery Systems Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development and Research. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 291–332
Pardeshi CV, Belgamwar VS (2013) Direct nose to brain drug delivery via integrated nerve pathways bypassing the blood-brain barrier: an excellent platform for brain targeting. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 10(7):957–972
Pardeshi CV, Rajput PV, Belgamwar VS, Tekade AR, Surana SJ (2013) Novel surface modified solid lipid nanoparticles as intranasal carriers for ropinirole hydrochloride: application of factorial design approach. Drug Deliv 20(1):47–56
Pardridge WM (2007) Blood-brain barrier delivery. Drug Discov Today 12(1–2):54–61
Pasha S, Gupta K (2010) Various drug delivery approaches to the central nervous system. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7(1):113–135
Patel S, Chavhan S, Soni H, Babbar AK, Mathur R, Mishra AK, Sawant K (2011) Brain targeting of risperidone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles by intranasal route. J Drug Target 19(6):468–474
Patel RB, Patel MR, Bhatt KK, Patel BG, Gaikwad RV (2016) Microemulsion-based drug delivery system for transnasal delivery of Carbamazepine: preliminary brain-targeting study. Drug Deliv 23(1):207–213
Patel RB, Patel MR, Bhatt KK, Patel BG, Gaikwad RV (2016) Evaluation of brain targeting efficiency of intranasal microemulsion containing olanzapine: pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic consideration. Drug Deliv 23(1):307–315
Patil G, Surana SJ (2013) Fabrication and statistical optimization of surface engineered PLGA nanoparticles for naso-brain delivery of ropinirole hydrochloride: in-vitro-ex-vivo studies. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 24(15):1740–1756
Piao HM, Balakrishnan P, Cho HJ, Kim H, Kim YS, Chung SJ, Shim CK, Kim DD (2010) Preparation and evaluation of fexofenadine microemulsion for intranasal delivery. Int J Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.05.041
Pires A, Fortuna A, Alves G, Falcao A (2009) Intranasal drug delivery: how, why and what for? J Pharm Pharm Sci 12(3):288–311
Pollard J, Rajabi-Siahboomi A, Badhan RKS, Mohammed AR, Perrie Y (2019) High-throughput screening of excipients with a biological effect: a kinetic study on the effects of surfactants on efflux-mediated transport. J Pharm Pharmacol 71(6):889–897
Pouton CW (1997) Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 25(1):47–58
Praveen Kumar PR (2011) Nonionic surfactant vesicular systems for effective drug delivery—An overview. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 1(4):208–219
Ramreddy S, Janapareddi K (2019) Brain targeting of chitosan-based diazepam mucoadhesive microemulsions via nasal route: formulation optimization, characterization, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 45(1):147–158
Rejman J, Oberle V, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstra D (2004) Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J 377(Pt 1):159–169
Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K, Dizaj SM (2019) Applications of nanotechnology in drug delivery to the central nervous system. Biomed Pharmacother 111:666–675
Salama HA, Mahmoud AA, Kamel AO, Abdel Hady M, Awad GA (2012) Brain delivery of olanzapine by intranasal administration of transfersomal vesicles. J Liposome Res 22(4):336–345
Samudre S, Tekade A, Thorve K, Jamodkar A, Parashar G (2016) Xanthan Gum Coated Mucoadhesive Liposomes for Efficient Nose to Brain Delivery of Curcumin. Drug Delivery Letter 5(3):201–207
Schaefer ML, Bottger B, Silver WL, Finger TE (2002) Trigeminal collaterals in the nasal epithelium and olfactory bulb: a potential route for direct modulation of olfactory information by trigeminal stimuli. J Comp Neurol 444(3):221–226
Shadab Md, Ali Mushir, Bhatnagar Aseem, Baboota Sanjula, Sahni Jasjeet, Kaur; Ali, Javed, (2014) Design, Development, Optimization and Characterization of Donepezil Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles for Brain Targeting to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Science of Advanced Materials 6(4):720–735
Shadab M, Subrat KB, Farrukh Z, Naiyer S, Md A, VenkataSrikanth M (2018) Nano-carrier enabled drug delivery systems for nose to brain targeting for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 43:295–310
Shafir Botner AF, Sintov AC (2012) Direct Delivery of Intranasal Insulin to the Brain via Microemulsion as a Putative Treatment of CNS Functioning Disorders. Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology 3:1–6
Shah BM, Misra M, Shishoo CJ, Padh H (2015) Nose to brain microemulsion-based drug delivery system of rivastigmine: formulation and ex-vivo characterization. Drug Deliv 22(7):918–930
Shah B, Khunt D, Bhatt H, Misra M, Padh H (2015) Application of quality by design approach for intranasal delivery of rivastigmine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Effect on formulation and characterization parameters. Eur J Pharm Sci 78:54–66
Shah BM, Khunt D, Bhatt H, Misra M, Padh H (2016) Intranasal delivery of venlafaxine loaded nanostructured lipid carrier: Risk assessment and QbD based optimization. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 33:37–50
Shah B, Khunt D, Misra M, Padh H (2016) Non-invasive intranasal delivery of quetiapine fumarate loaded microemulsion for brain targeting: Formulation, physicochemical and pharmacokinetic consideration. Eur J Pharm Sci 91:196–207
Shah B, Khunt D, Misra M, Padh H (2016) "Application of Box-Behnken design for optimization and development of quetiapine fumarate loaded chitosan nanoparticles for brain delivery via intranasal route* ". Int J Biol Macromol 89:206–218
Shah B, Khunt D, Misra M, Padh H (2018) Formulation and In-vivo Pharmacokinetic Consideration of Intranasal Microemulsion and Mucoadhesive Microemulsion of Rivastigmine for Brain Targeting. Pharm Res 35(1):8
Shah B, Khunt D, Misra M (2021) Comparative evaluation of intranasally delivered quetiapine loaded mucoadhesive microemulsion and polymeric nanoparticles for brain targeting: pharmacokinetic and gamma scintigraphy studies. Futur J Pharm Sci 7(6):1–12
Sharma D, Sharma RK, Sharma N, Gabrani R, Sharma SK, Ali J, Dang S (2015) Nose-To-Brain Delivery of PLGA-Diazepam Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 16(5):1108–1121
Shinde RL, Devarajan PV (2017) Docosahexaenoic acid-mediated, targeted and sustained brain delivery of curcumin microemulsion. Drug Deliv 24(1):152–161
Shinde RL, Jindal AB, Devarajan PV (2011) Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions for Targeted Drug Delivery to the Brain. Curr Nanosci 7(1):119–133
Shinde RL, Bharkad GP, Devarajan PV (2015) Intranasal microemulsion for targeted nose to brain delivery in neurocysticercosis: Role of docosahexaenoic acid. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 96:363–379
Sindhu P, Kumar S, Iqbal B, Ali J, Baboota S (2018) Duloxetine loaded-microemulsion system to improve behavioral activities by upregulating serotonin and norepinephrine in brain for the treatment of depression. J Psychiatr Res 99:83–95
Singh S, Muthu MS (2007) Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles containing an atypical antipsychotic agent. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2(2):233–240
Talegaonkar S, Azeem A, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK, Pathan SA, Khan ZI (2008) Microemulsions: a novel approach to enhanced drug delivery. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul 2(3):238–257
Thorne RG, Pronk GJ, Padmanabhan V, Frey WH 2nd (2004) Delivery of insulin-like growth factor-I to the rat brain and spinal cord along olfactory and trigeminal pathways following intranasal administration. Neuroscience 127(2):481–496
Touitou E, Illum L (2013) Nasal drug delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res 3(1):1–3
Trows S, Wuchner K, Spycher R, Steckel H (2014) Analytical challenges and regulatory requirements for nasal drug products in europe and the u.s. Pharmaceutics 6(2):195–219
Upadhyay P, Trivedi J, Pundarikakshudu K, Sheth N (2016) Comparative study between simple and optimized liposomal dispersion of quetiapine fumarate for diffusion through nasal route. Drug Deliv 23(4):1214–1221
Vyas TK, Babbar AK, Sharma RK, Misra A (2005) Intranasal mucoadhesive microemulsions of zolmitriptan: preliminary studies on brain-targeting. J Drug Target 13(5):317–324
Vyas TK, Babbar AK, Sharma RK, Singh S, Misra A (2006) Intranasal mucoadhesive microemulsions of clonazepam: preliminary studies on brain targeting. J Pharm Sci 95(3):570–580
Vyas TK, Babbar AK, Sharma RK, Singh S, Misra A (2006) Preliminary brain-targeting studies on intranasal mucoadhesive microemulsions of sumatriptan. AAPS PharmSciTech 7(1):E49–E57
Vyas TK, Shahiwala A, Amiji MM (2008) Improved oral bioavailability and brain transport of Saquinavir upon administration in novel nanoemulsion formulations. Int J Pharm 347(1–2):93–101
Washington N, Steele RJ, Jackson SJ, Bush D, Mason J, Gill DA, Pitt K, Rawlins DA (2000) Determination of baseline human nasal pH and the effect of intranasally administered buffers. Int J Pharm 198(2):139–146
Wavikar PR, Vavia PR (2015) Rivastigmine-loaded in situ gelling nanostructured lipid carriers for nose to brain delivery. J Liposome Res 25(2):141–149
Yang ZZ, Zhang YQ, Wang ZZ, Wu K, Lou JN, Qi XR (2013) Enhanced brain distribution and pharmacodynamics of rivastigmine by liposomes following intranasal administration. Int J Pharm 452(1–2):344–354
Yasir M, Sara UVS, Chauhan I, Gaur PK, Singh AP, Puri D, Ameeduzzafar, (2018) Solid lipid nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery of donepezil: formulation, optimization by Box-Behnken design, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 46(8):1838–1851
Yeh TH, Hsu LW, Tseng MT, Lee PL, Sonjae K, Ho YC, Sung HW (2011) Mechanism and consequence of chitosan-mediated reversible epithelial tight junction opening. Biomaterials 32(26):6164–6173
Yuan Y, Lee TR (2013) Contact Angle and Wetting Properties. Springer, Berlin
Zhang SSY (2016) Medical Big Data: Neurological Diseases Diagnosis Through Medical Data Analysis. Data Science and Engineering 1:54–64
Zhang Q, Jiang X, Jiang W, Lu W, Su L, Shi Z (2004) Preparation of nimodipine-loaded microemulsion for intranasal delivery and evaluation on the targeting efficiency to the brain. Int J Pharm 275(1–2):85–96
Zhao C, Zhang J, Hu H, Qiao M, Chen D, Zhao X, Yang C (2018) Design of lactoferrin modified lipid nano-carriers for efficient brain-targeted delivery of nimodipine. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 92:1031–1040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author (B. Shah) report no conflict of interest. The author alone are responsible for the content and writing of paper.
Statement of animal rights and ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, B. Microemulsion as a promising carrier for nose to brain delivery: journey since last decade. J. Pharm. Investig. 51, 611–634 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00528-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00528-w