Abstract
Background:
Norovirus is increasingly being recognized as a leading cause of foodborne disease. Nevertheless, welldocumented foodborne outbreaks due to norovirus are rarely found in the literature.
Material and Methods:
A retrospective cohort study was conducted for identifying the source of a gastroenteritis outbreak. A total of 325 persons were identified as the atrisk group.
Results:
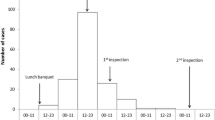
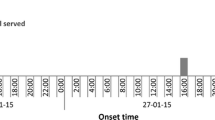
The overall attack rate was 56% (182/325). Of the four working days of possible foodborne exposure to norovirus (Monday till Thursday), Wednesday (risk ratio [RR]: 18.82; 95%CI 11.82–29.96) and Thursday (RR 2.14; 95%CI 1.65–2.79) turned out to be the most likely days on which infections with norovirus occurred. The day-by-day food specific cohort analyses yielded consumption of salad on Wednesday (adjusted RR 2.82; 95%CI 1.0–7.94) to be associated with highest risk of illness. The most likely source of food contamination is a kitchen assistant having prepared salad manually. She fell ill with symptoms of gastroenteritis on Wednesday during the early working hours and continued working. Human stool samples obtained from five out of six outbreak cases, including the sick kitchen assistant, were RT-PCR positive for norovirus genotype GGII.7 (Leeds-like).
Conclusion:
This foodborne norovirus outbreak underlines the drastic consequences of neglecting the rules of basic kitchen hygiene. Food handlers working despite manifest diarrhea or vomiting – often in fear of job loss – are a common cause of foodborne norovirus outbreaks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmid, D., Stüger, H.P., Lederer, I. et al. A Foodborne Norovirus Outbreak Due To Manually Prepared Salad, Austria 2006. Infection 35, 232–239 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-6327-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-6327-1