Abstract
Background: Cytokines may alter metabolic pathways and contribute to malnutrition among human immunodefiency virus (HIV)-positive individuals.
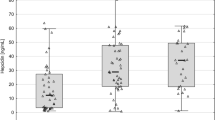
Patients and Methods: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), soluble IL-2 receptors (sIL-2R), β2-microglobulin serum levels and plasma viral load of 45 HIV-positive patients were determined and correlated to nutritinal status impairment. Patients were grouped by CD4 counts into categories I (< 200/μl), II (200–499/μl), III (≥ 500/μl). There were 15 healthy controls. A nutritional grading system, based on anthropometric and laboratory data, was devised. Scores ranged from 0 to 5 (eutrophic to malnutrition).
Results: AIDS patients' cytokines and immune marker levels were significantly higher than those of the controls, but not always higher than those of other categories. AIDS patients had higher nutritional deficit grades than category III (p < 0.05) or the controls (p < 0.02) which, except for viral load, correlated with the parameters studied.
Conclusion: Nutritional status impairments in HIV-positive individuals were associated with immune activation but not with viral load.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: June 27, 2000 · Revision accepted: June 30, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galhardo, M., de Carvalho, M., Georg, I. et al. Nutritional Status Impairments in HIV-Infected Patients Are Associated with Increased TNF-α and IL-6 Serum Levels but Not with Viral Load. Infection 29, 257–261 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-001-1074-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-001-1074-1