Abstract
Background
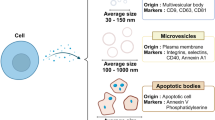
Exosomes, nano-sized vesicles ranging between 30 and 150 nm secreted by human cells, play a pivotal role in long-range intercellular communication and have attracted significant attention in the field of regenerative medicine. Nevertheless, their limited productivity and cost-effectiveness pose challenges for clinical applications. These issues have recently been addressed by cell-derived nanovesicles (CDNs), which are physically synthesized exosome-mimetic nanovesicles from parent cells, as a promising alternative to exosomes. CDNs exhibit structural, physical, and biological properties similar to exosomes, containing intracellular protein and genetic components encapsulated by the cell plasma membrane. These characteristics allow CDNs to be used as regenerative medicine and therapeutics on their own, or as a drug delivery system.
Methods
The paper reviews diverse methods for CDN synthesis, current analysis techniques, and presents engineering strategies to improve lesion targeting efficiency and/or therapeutic efficacy.
Results
CDNs, with their properties similar to those of exosomes, offer a cost-effective and highly productive alternative due to their non-living biomaterial nature, nano-size, and readiness for use, allowing them to overcome several limitations of conventional cell therapy methods.
Conclusion
Ongoing research and enhancement of CDNs engineering, along with comprehensive safety assessments and stability analysis, exhibit vast potential to advance regenerative medicine by enabling the development of efficient therapeutic interventions.



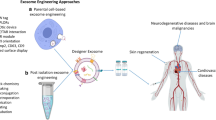
© 2015 PLOS), NTA, DLS, and AFM (Reprinted with permission from Ridolfi et al. [86], Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society)

© 2020 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. B CDNs were synthesized from IONP-treated hMSCs resulting in enhanced growth factor release. Magnetic attraction was employed to recruit CDNs to the spinal cord injury site. Reprinted with permission from Kim et al. [65], Copyright © 2018 American Chemical Society. C C6 cell membrane fragments were extruded with tumor targeting (T7c) peptides to synthesize T7c-incorporating CDNs. Anti-miRNA-21 oligonucleotide, modified with cholesterol, was sequentially loaded through hydrophobic interaction. Reprinted with permission from Lee et al. [109], Copyright © 2022 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. D CDNs were extruded from HEK293 cells engineered to express an EGFR-binding domain for cancer targeting. The CDNs were fused with photosensitizer-loaded liposomes for cancer therapy. Reprinted with permission from Shin et al. [110], Copyright © 2023 The Korean Society of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Jang SC, Kim SR, Yoon YJ, Park KS, Kim JH, Lee J, et al. In vivo kinetic biodistribution of nano-sized outer membrane vesicles derived from bacteria. Small. 2015;11:456–61.
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367:eaau6977.
Yeo RWY, Lai RC, Tan KH, Lim SK. Exosome: a novel and safer therapeutic refinement of mesenchymal stem cell. Exosomes Microvesicles. 2013;1:7.
Yoon JK, Kim DH, Kang ML, Jang HK, Park HJ, Lee JB, et al. Anti-atherogenic effect of stem cell nanovesicles targeting disturbed flow sites. Small. 2020;16:e2000012.
Heo JS, Kim S, Yang CE, Choi Y, Song SY, Kim HO. Human adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: a key player in wound healing. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18:537–48.
Choi H, Choi Y, Yim HY, Mirzaaghasi A, Yoo JK, Choi C. Biodistribution of exosomes and engineering strategies for targeted delivery of therapeutic exosomes. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18:499–511.
Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:581–93.
van Niel G, Porto-Carreiro I, Simoes S, Raposo G. Exosomes: a common pathway for a specialized function. J Biochem. 2006;140:13–21.
Wang W, Zhu N, Yan T, Shi YN, Chen J, Zhang CJ, et al. The crosstalk: exosomes and lipid metabolism. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18:119.
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200:373–83.
Raimondo F, Morosi L, Chinello C, Magni F, Pitto M. Advances in membranous vesicle and exosome proteomics improving biological understanding and biomarker discovery. Proteomics. 2011;11:709–20.
Hood JL. Post isolation modification of exosomes for nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine. 2016;11:1745–56.
Ankrum JA, Ong JF, Karp JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:252–60.
Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Peng N, Liu Q, Qiu D, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with ischemic rat heart extracts promote angiogenesis via the delivery of DMBT1. Cell Transplant. 2022;31:9636897221102898.
Greening DW, Xu R, Ji H, Tauro BJ, Simpson RJ. A protocol for exosome isolation and characterization: evaluation of ultracentrifugation, density-gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1295:179–209.
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–9.
Ratajczak J, Miekus K, Kucia M, Zhang J, Reca R, Dvorak P, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia. 2006;20:847–56.
Gong M, Yu B, Wang J, Wang Y, Liu M, Paul C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:45200–12.
Kim JY, Rhim WK, Seo HJ, Lee JY, Park CG, Han DK. Comparative analysis of MSC-derived exosomes depending on cell culture media for regenerative bioactivity. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18:355–67.
Park CO, Kim HL, Park JW. Microneedle transdermal drug delivery systems for allergen-specific immunotherapy, skin disease treatment, and vaccine development. Yonsei Med J. 2022;63:881–91.
Sun Y, Hao G, Zhuang M, Lv H, Liu C, Su K. MEG3 LncRNA from exosomes released from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances cisplatin chemoresistance in SCLC via a MiR-15a-5p/CCNE1 axis. Yonsei Med J. 2022;63:229–40.
Zhao X, Ren Y, Cui N, Wang X, Cui Y. Identification of key microRNAs and their targets in exosomes of pancreatic cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Medicine. 2018;97:e12632.
Park HJ, Kelly JM, Hoffman JR, Takaesu F, Schwartzman W, Ulziibayar A, et al. Computational analysis of serum-derived extracellular vesicle miRNAs in juvenile sheep model of single stage Fontan procedure. Extracell Vesicle. 2022;1:100013.
Katsuda T, Tsuchiya R, Kosaka N, Yoshioka Y, Takagaki K, Oki K, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1197.
Jang SC, Kim OY, Yoon CM, Choi DS, Roh TY, Park J, et al. Bioinspired exosome-mimetic nanovesicles for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics to malignant tumors. ACS Nano. 2013;7:7698–710.
Jo W, Kim J, Yoon J, Jeong D, Cho S, Jeong H, et al. Large-scale generation of cell-derived nanovesicles. Nanoscale. 2014;6:12056–64.
Todorova D, Simoncini S, Lacroix R, Sabatier F, Dignat-George F. Extracellular vesicles in angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2017;120:1658–73.
Minciacchi VR, Freeman MR, Di Vizio D. Extracellular vesicles in cancer: exosomes, microvesicles and the emerging role of large oncosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:41–51.
Sato K, Meng F, Glaser S, Alpini G. Exosomes in liver pathology. J Hepatol. 2016;65:213–21.
Malm T, Loppi S, Kanninen KM. Exosomes in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int. 2016;97:193–9.
Zhang Y, Hu YW, Zheng L, Wang Q. Characteristics and roles of exosomes in cardiovascular disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36:202–11.
Zhong Y, Li H, Li P, Chen Y, Zhang M, Yuan Z, et al. Exosomes: a new pathway for cancer drug resistance. Front Oncol. 2021;11:743556.
Wang J, Chen D, Ho EA. Challenges in the development and establishment of exosome-based drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2021;329:894–906.
Cheng L, Zhang K, Wu S, Cui M, Xu T. Focus on mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: opportunities and challenges in cell-free therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:6305295.
Varderidou-Minasian S, Lorenowicz MJ. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in tissue repair: challenges and opportunities. Theranostics. 2020;10:5979–97.
Li MY, Liu LZ, Dong M. Progress on pivotal role and application of exosome in lung cancer carcinogenesis, diagnosis, therapy and prognosis. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:22.
Zabeo D, Cvjetkovic A, Lässer C, Schorb M, Lötvall J, Höög JL. Exosomes purified from a single cell type have diverse morphology. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017;6:1329476.
Kahlert C, Melo SA, Protopopov A, Tang J, Seth S, Koch M, et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer*. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:3869–75.
van der Pol E, Böing AN, Harrison P, Sturk A, Nieuwland R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64:676–705.
Kogure T, Lin WL, Yan IK, Braconi C, Patel T. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: a mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology. 2011;54:1237–48.
Bryniarski K, Ptak W, Jayakumar A, Püllmann K, Caplan MJ, Chairoungdua A, et al. Antigen-specific, antibody-coated, exosome-like nanovesicles deliver suppressor T-cell microRNA-150 to effector T cells to inhibit contact sensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:170–81.
Jo W, Jeong D, Kim J, Cho S, Jang SC, Han C, et al. Microfluidic fabrication of cell-derived nanovesicles as endogenous RNA carriers. Lab Chip. 2014;14:1261–9.
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;3:3–22.
Peterson MF, Otoc N, Sethi JK, Gupta A, Antes TJ. Integrated systems for exosome investigation. Methods. 2015;87:31–45.
Sidhom K, Obi PO, Saleem A. A review of exosomal isolation methods: is size exclusion chromatography the best option? Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6466.
Li P, Kaslan M, Lee SH, Yao J, Gao Z. Progress in exosome isolation techniques. Theranostics. 2017;7:789–804.
Livshits MA, Khomyakova E, Evtushenko EG, Lazarev VN, Kulemin NA, Semina SE, et al. Isolation of exosomes by differential centrifugation: theoretical analysis of a commonly used protocol. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17319.
Gurunathan S, Kang MH, Jeyaraj M, Qasim M, Kim JH. Review of the isolation, characterization, biological function, and multifarious therapeutic approaches of exosomes. Cells. 2019;8:307.
Zhang Y, Bi J, Huang J, Tang Y, Du S, Li P. Exosome: a review of its classification, isolation techniques, storage, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:6917–34.
Konoshenko MY, Lekchnov EA, Vlassov AV, Laktionov PP. Isolation of extracellular vesicles: general methodologies and latest trends. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8545347.
Contreras-Naranjo JC, Wu HJ, Ugaz VM. Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab Chip. 2017;17:3558–77.
Wu M, Mao Z, Chen K, Bachman H, Chen Y, Rufo J, et al. Acoustic separation of nanoparticles in continuous flow. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27:1606039.
Wu M, Ouyang Y, Wang Z, Zhang R, Huang PH, Chen C, et al. Isolation of exosomes from whole blood by integrating acoustics and microfluidics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114:10584–9.
Davies RT, Kim J, Jang SC, Choi EJ, Gho YS, Park J. Microfluidic filtration system to isolate extracellular vesicles from blood. Lab Chip. 2012;12:5202–10.
Cho S, Jo W, Heo Y, Kang JY, Kwak R, Park J. Isolation of extracellular vesicle from blood plasma using electrophoretic migration through porous membrane. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2016;233:289–97.
Shi L, Kuhnell D, Borra VJ, Langevin SM, Nakamura T, Esfandiari L. Rapid and label-free isolation of small extracellular vesicles from biofluids utilizing a novel insulator based dielectrophoretic device. Lab Chip. 2019;19:3726–34.
Song Z, Mao J, Barrero RA, Wang P, Zhang F, Wang T. Development of a CD63 aptamer for efficient cancer immunochemistry and immunoaffinity-based exosome isolation. Molecules. 2020;25:5585.
Li A, Zhang T, Zheng M, Liu Y, Chen Z. Exosomal proteins as potential markers of tumor diagnosis. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:175.
Yi K, Rong Y, Huang L, Tang X, Zhang Q, Wang W, et al. Aptamer-exosomes for tumor theranostics. ACS Sens. 2021;6:1418–29.
Sancho-Albero M, Sebastian V, Sese J, Pazo-Cid R, Mendoza G, Arruebo M, et al. Isolation of exosomes from whole blood by a new microfluidic device: proof of concept application in the diagnosis and monitoring of pancreatic cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. 2020;18:150.
Xu H, Liao C, Zuo P, Liu Z, Ye BC. Magnetic-based microfluidic device for on-chip isolation and detection of tumor-derived exosomes. Anal Chem. 2018;90:13451–8.
Tang J, Jia X, Li Q, Cui Z, Liang A, Ke B, et al. A DNA-based hydrogel for exosome separation and biomedical applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120:e2303822120.
Goh WJ, Zou S, Ong WY, Torta F, Alexandra AF, Schiffelers RM, et al. Bioinspired cell-derived nanovesicles versus exosomes as drug delivery systems: a cost-effective alternative. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14322.
Kim HY, Kim TJ, Kang L, Kim YJ, Kang MK, Kim J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived magnetic extracellular nanovesicles for targeting and treatment of ischemic stroke. Biomaterials. 2020;243:119942.
Kim HY, Kumar H, Jo MJ, Kim J, Yoon JK, Lee JR, et al. Therapeutic efficacy-potentiated and diseased organ-targeting nanovesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells for spinal cord injury treatment. Nano Lett. 2018;18:4965–75.
Lee JR, Park BW, Kim J, Choo YW, Kim HY, Yoon JK, et al. Nanovesicles derived from iron oxide nanoparticles–incorporated mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac repair. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eeaz0952.
Guo RM, Cao N, Zhang F, Wang YR, Wen XH, Shen J, et al. Controllable labelling of stem cells with a novel superparamagnetic iron oxide–loaded cationic nanovesicle for MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:2328–37.
Kang S, Bhang SH, Hwang S, Yoon JK, Song J, Jang HK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells aggregate and deliver gold nanoparticles to tumors for photothermal therapy. ACS Nano. 2015;9:9678–90.
Li X, Wang Y, Shi L, Li B, Li J, Wei Z, et al. Magnetic targeting enhances the cutaneous wound healing effects of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived iron oxide exosomes. J Nanobiotechnol. 2020;18:113.
Tivony R, Fletcher M, Al Nahas K, Keyser UF. A microfluidic platform for sequential assembly and separation of synthetic cell models. ACS Synth Biol. 2021;10:3105–16.
Yoon J, Jo W, Jeong D, Kim J, Jeong H, Park J. Generation of nanovesicles with sliced cellular membrane fragments for exogenous material delivery. Biomaterials. 2015;59:12–20.
Go G, Lee J, Choi DS, Kim SS, Gho YS. Extracellular vesicle-mimetic ghost nanovesicles for delivering anti-inflammatory drugs to mitigate gram-negative bacterial outer membrane vesicle-induced systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8:1801082.
Wang L, Abhange KK, Wen Y, Chen Y, Xue F, Wang G, et al. Preparation of engineered extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with ultrasonication for skin rejuvenation. ACS Omega. 2019;4:22638–45.
Gao J, Wang S, Wang Z. High yield, scalable and remotely drug-loaded neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) for anti-inflammation therapy. Biomaterials. 2017;135:62–73.
Ishida T, Ichihara M, Wang X, Yamamoto K, Kimura J, Majima E, et al. Injection of PEGylated liposomes in rats elicits PEG-specific IgM, which is responsible for rapid elimination of a second dose of PEGylated liposomes. J Controll Release. 2006;112:15–25.
Griffin JI, Wang G, Smith WJ, Vu VP, Scheinman R, Stitch D, et al. Revealing dynamics of accumulation of systemically injected liposomes in the skin by intravital microscopy. ACS Nano. 2017;11:11584–93.
Bordanaba-Florit G, Royo F, Kruglik SG, Falcon-Perez JM. Using single-vesicle technologies to unravel the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. Nat Protoc. 2021;16:3163–85.
Ong SG, Chitneni M, Lee KS, Ming LC, Yuen KH. Evaluation of extrusion technique for nanosizing liposomes. Pharmaceutics. 2016;8:36.
Rayamajhi S, Nguyen TDT, Marasini R, Aryal S. Macrophage-derived exosome-mimetic hybrid vesicles for tumor targeted drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2019;94:482–94.
Hartner WC, Verma DD, Levchenko TS, Bernstein EA, Torchilin VP. ATP-loaded liposomes for treatment of myocardial ischemia. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2009;1:530–9.
Piffoux M, Silva AKA, Wilhelm C, Gazeau F, Tareste D. Modification of extracellular vesicles by fusion with liposomes for the design of personalized biogenic drug delivery systems. ACS Nano. 2018;12:6830–42.
Antimisiaris SG, Mourtas S, Marazioti A. Exosomes and exosome-inspired vesicles for targeted drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10:218.
Khatun Z, Bhat A, Sharma S, Sharma A. Elucidating diversity of exosomes: biophysical and molecular characterization methods. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016;11:2359–77.
Lee H, Cha H, Park JH. Derivation of cell-engineered nanovesicles from human induced pluripotent stem cells and their protective effect on the senescence of dermal fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:343.
Enderle D, Spiel A, Coticchia CM, Berghoff E, Mueller R, Schlumpberger M, et al. Characterization of RNA from exosomes and other extracellular vesicles isolated by a novel spin column-based method. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0136133.
Ridolfi A, Brucale M, Montis C, Caselli L, Paolini L, Borup A, et al. AFM-based high-throughput nanomechanical screening of single extracellular vesicles. Anal Chem. 2020;92:10274–82.
Hartjes TA, Mytnyk S, Jenster GW, van Steijn V, van Royen ME. Extracellular vesicle quantification and characterization: common methods and emerging approaches. Bioengineering. 2019;6:7.
Liu A, Yang G, Liu Y, Liu T. Research progress in membrane fusion-based hybrid exosomes for drug delivery systems. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:939441.
Hassellov M, Readman JW, Ranville JF, Tiede K. Nanoparticle analysis and characterization methodologies in environmental risk assessment of engineered nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology. 2008;17:344–61.
Franken LE, Boekema EJ, Stuart MCA. Transmission electron microscopy as a tool for the characterization of soft materials: application and interpretation. Adv Sci. 2017;4:1600476.
Dragovic RA, Gardiner C, Brooks AS, Tannetta DS, Ferguson DJ, Hole P, et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using nanoparticle tracking analysis. Nanomedicine. 2011;7:780–8.
Cavallaro S, Pevere F, Stridfeldt F, Görgens A, Paba C, Sahu SS, et al. Multiparametric profiling of single nanoscale extracellular vesicles by combined atomic force and fluorescence microscopy: correlation and heterogeneity in their molecular and biophysical features. Small. 2021;17:2008155.
Boriachek K, Islam MN, Möller A, Salomon C, Nguyen N-T, Hossain MSA, et al. Biological functions and current advances in isolation and detection strategies for exosome nanovesicles. Small. 2018;14:1702153.
Ramasubramanian L, Jyothi H, Goldbloom-Helzner L, Light BM, Kumar P, Carney RP, et al. Development and characterization of bioinspired lipid raft nanovesicles for therapeutic applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14:54458–77.
Donoso-Quezada J, Ayala-Mar S, González-Valdez J. The role of lipids in exosome biology and intercellular communication: function, analytics and applications. Traffic. 2021;22:204–20.
Lobasso S, Tanzarella P, Mannavola F, Tucci M, Silvestris F, Felici C, et al. A lipidomic approach to identify potential biomarkers in exosomes from melanoma cells with different metastatic potential. Front Physiol. 2021;12:748895.
Zhu Q, Li H, Ao Z, Xu H, Luo J, Kaurich C, et al. Lipidomic identification of urinary extracellular vesicles for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis diagnosis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2022;20:349.
Sancho-Albero M, Jarne C, Savirón M, Martín-Duque P, Membrado L, Cebolla VL, et al. High-performance thin-layer chromatography-densitometry-tandem ESI-MS to evaluate phospholipid content in exosomes of cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:1150.
Zhang M, Ma Z, Li R, Guo S, Qiu Y, Gao X. Proteomic analysis reveals proteins and pathways associated with lactation in bovine mammary epithelial cell-derived exosomes. J Proteome Res. 2020;19:3211–9.
Guyon J, Novion M, Fulda V, Ducint D, Molimard M, Couzi L, et al. A UPLC-MS/MS method for plasma biological monitoring of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection and application to a case. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2022;33:1975–81.
Cha M, Jeong SH, Bae S, Park JH, Baeg Y, Han DW, et al. Efficient labeling of vesicles with lipophilic fluorescent dyes via the salt-change method. Anal Chem. 2023;95:5843–9.
Mahgoub EO, Razmara E, Bitaraf A, Norouzi FS, Montazeri M, Behzadi-Andouhjerdi R, et al. Advances of exosome isolation techniques in lung cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47:7229–51.
Jakobsen KR, Paulsen BS, Bæk R, Varming K, Sorensen BS, Jørgensen MM. Exosomal proteins as potential diagnostic markers in advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26659.
Neupane KR, McCorkle JR, Kopper TJ, Lakes JE, Aryal SP, Abdullah M, et al. Macrophage-engineered vesicles for therapeutic delivery and bidirectional reprogramming of immune cell polarization. ACS Omega. 2021;6:3847–57.
Casadei L, Sarchet P, de Faria FCC, Calore F, Nigita G, Tahara S, et al. In situ hybridization to detect DNA amplification in extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11: e12251.
Cui C, Shu W, Li P. Fluorescence in situ hybridization: cell-based genetic diagnostic and research applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:89.
de Voogt WS, Tanenbaum ME, Vader P. Illuminating RNA trafficking and functional delivery by extracellular vesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;174:250–64.
Patel VR, Salinas AM, Qi D, Gupta S, Sidote DJ, Goldschen-Ohm MP. Single-molecule imaging with cell-derived nanovesicles reveals early binding dynamics at a cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel. Nat Commun. 2021;12:6459.
Lee Y, Kim M, Ha J, Lee M. Brain-targeted exosome-mimetic cell membrane nanovesicles with therapeutic oligonucleotides elicit anti-tumor effects in glioblastoma animal models. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;8:e10426.
Eun Shin H, Wook OS, Park W. Hybrid nanovesicle of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered cell-derived vesicle and drug-encapsulated liposome for effective cancer treatment. J Ind Eng Chem. 2023;122:127–37.
Lee CS, Fan J, Hwang HS, Kim S, Chen C, Kang M, et al. Bone-targeting exosome mimetics engineered by bioorthogonal surface functionalization for bone tissue engineering. Nano Lett. 2023;23:1202–10.
Li B, Yang T, Liu J, Yu X, Li X, Qin F, et al. Genetically engineered PD-1 displaying nanovesicles for synergistic checkpoint blockades and chemo-metabolic therapy against non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Biomater. 2023;161:184–200.
Lu X, Xu G, Lin Z, Zou F, Liu S, Zhang Y, et al. Engineered exosomes enriched in netrin-1 modRNA promote axonal growth in spinal cord injury by attenuating inflammation and pyroptosis. Biomater Res. 2023;27:3.
Lee JR, Sim WS, Park HJ, Park BW, Joung YK. Targeted delivery of apoptotic cell-derived nanovesicles prevents cardiac remodeling and attenuates cardiac function exacerbation. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33:2210864.
Choo YW, Kang M, Kim HY, Han J, Kang S, Lee JR, et al. M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. ACS Nano. 2018;12:8977–93.
Hong J, Jung M, Kim C, Kang M, Go S, Sohn H, et al. Senescent cancer cell-derived nanovesicle as a personalized therapeutic cancer vaccine. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55:541–54.
Kuen DS, Hong J, Lee S, Koh CH, Kwak M, Kim BS, et al. A personalized cancer vaccine that induces synergistic innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv Mater. 2023;35:2303080.
Hong J, Kang M, Jung M, Lee YY, Cho Y, Kim C, et al. T-cell-derived nanovesicles for cancer immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 2021;33: e2101110.
Go G, Lee J, Choi DS, Kim SS, Gho YS. Extracellular vesicle-mimetic ghost nanovesicles for delivering anti-inflammatory drugs to mitigate gram-negative bacterial outer membrane vesicle-induced systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8:e1801082.
Tao SC, Rui BY, Wang QY, Zhou D, Zhang Y, Guo SC. Extracellular vesicle-mimetic nanovesicles transport LncRNA-H19 as competing endogenous RNA for the treatment of diabetic wounds. Drug Deliv. 2018;25:241–55.
Jin Y, Lee JS, Min S, Park HJ, Kang TJ, Cho SW. Bioengineered extracellular membranous nanovesicles for efficient small-interfering RNA delivery: versatile platforms for stem cell engineering and in vivo delivery. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26:5804–17.
Tang J, Su T, Huang K, Dinh PU, Wang Z, Vandergriff A, et al. Targeted repair of heart injury by stem cells fused with platelet nanovesicles. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018;2:17–26.
Jung M, Kang M, Kim BS, Hong J, Kim C, Koh CH, et al. Nanovesicle-mediated targeted delivery of immune checkpoint blockades to potentiate therapeutic efficacy and prevent side effects. Adv Mater. 2022;34:e2106516.
Yu Y, Li Y, Tian Y, Hu Q, Li X, Tu J, et al. Boosting B cell and macrophage-mediated humoral immunity with fusion nanovesicles for triple-negative breast cancer combined therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12:2202209.
Lv Q, Cheng L, Lu Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, Deng J, et al. Thermosensitive exosome-liposome hybrid nanoparticle-mediated chemoimmunotherapy for improved treatment of metastatic peritoneal cancer. Adv Sci. 2020;7:2000515.
Sato YT, Umezaki K, Sawada S, Mukai SA, Sasaki Y, Harada N, et al. Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21933.
Sun L, Fan M, Huang D, Li B, Xu R, Gao F, et al. Clodronate-loaded liposomal and fibroblast-derived exosomal hybrid system for enhanced drug delivery to pulmonary fibrosis. Biomaterials. 2021;271: 120761.
Jhan YY, Prasca-Chamorro D, Palou Zuniga G, Moore DM, Arun Kumar S, Gaharwar AK, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles with synthetic lipids via membrane fusion to establish efficient gene delivery. Int J Pharm. 2020;573:118802.
Lee JR, Kyung JW, Kumar H, Kwon SP, Song SY, Han IB, et al. Targeted delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-derived nanovesicles for spinal cord injury treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:4185.
Li Q, Song Y, Wang Q, Chen J, Gao J, Tan H, et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles with platelet membranes fusion enhanced targeted therapeutic angiogenesis in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia reperfusion. Theranostics. 2021;11:3916–31.
Acknowledgements
This study received funding from (i) the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (2021R1C1C1011015, 2021K1A3A1A74099704, and RS-2023-00213691); (ii) the Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for the Department of Biological Science of Sookmyung Women’s University; (iii) Sookmyung Women’s University Research Grants (1-2103-2002 and 1-2203-2025); and National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2021R1C1C1011015, 2021K1A3A1A74099704, RS-2023–00213691).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical statement
There are no animal experiments carried out for this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, HJ., Shim, KS., Lee, J. et al. Engineering of Cell Derived-Nanovesicle as an Alternative to Exosome Therapy. Tissue Eng Regen Med 21, 1–19 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-023-00610-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-023-00610-4