Abstract
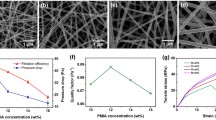
This study aims to investigate the effects of gelatin concentration, air pressure, and an electric voltage on the average fiber diameter (AFD) and average droplet area (ADA) of nanofibrous webs to obtain filters with high filtration capacity. Most of the researched synthetic polymer-based air filters cause secondary pollution to the environment when their service period is over. Thus, replacing synthetic filters with nanofiber filters fabricated from biodegradable organic waste gelatin biopolymer is the novelty of this study. Nanofibers were spun from gelatin solution using a novel method: electrically assisted solution blow spinning (ESBS). According to test results, nanofibrous webs having a large area of droplets were noticed in samples having a lower gelatin-concentrated solution. Fibers with mean diameters in the range of 93.86 ± 1.32 to 250.13 ± 3.55 nm were produced via ESBS. On the other hand, Taguchi’s ANOVA exhibited that gelatin concentration had a significant contribution of 98.27% to the variation of AFD of nanofibrous webs. It has also a notable effect of about 56.26% on the ADA of filter webs. Furthermore, an air filtration test revealed that a filtration efficiency of 90.5% for 0.3-µm particle size at the expense of 225-Pa pressure drop was noticed on G-12120. Therefore, the quality factor of the optimized nanofibrous web was 0.0105 Pa−1. According to EN 1822 filter standards, the G-12120 nanofiber filter web was categorized under E10. Finally, G-12120 nanofiber filter media are effective to be applied in air filtration applications as an alternative to commercially available synthetic-based filters.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Attabi R, Dumée LF, Kong L et al (2018) High efficiency poly (acrylonitrile) electrospun nanofiber membranes for airborne nanomaterials filtration. Adv Eng Mater 20:1700572. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201700572
Arican F, Uzuner-Demir A, Polat O et al (2022) Fabrication of gelatin nanofiber webs via centrifugal spinning for N95 respiratory filters. Bull Mater Sci 45:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-022-02668-7
Bian Y, Wang S, Zhang L, Chen C (2020) Influence of fiber diameter, filter thickness, and packing density on PM2. 5 removal efficiency of electrospun nanofiber air filters for indoor applications. Build Environ 170:106628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106628
Bonfim DP, Cruz FG, Bretas RE et al (2021) A sustainable recycling alternative: electrospun PET-membranes for air nanofiltration. Polymers 13:1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071166
Bui TT, Shin MK, Jee SY et al (2022) Ferroelectric PVDF nanofiber membrane for high-efficiency PM0. 3 air filtration with low air flow resistance. Colloids Surf a: Physicochem Eng Aspects 640:128418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128418
Buivydiene D, Todea AM, Asbach C et al (2021) Composite micro/nano fibrous air filter by simultaneous melt and solution electrospinning. J Aerosol Sci 154:105754. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAEROSCI.2021.105754
Chen R, Zhang H, Wang M et al (2020) Thermoplastic polyurethane nanofiber membrane based air filters for efficient removal of ultrafine particulate matter PM0. 1. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02484
de Almeida DS, Martins LD, Muniz EC et al (2020) Biodegradable CA/CPB electrospun nanofibers for efficient retention of airborne nanoparticles. Process Saf Environ Prot 144:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.07.024
Dehghan SF, GolbabaeiMaddah FB et al (2015) Experimental Investigations on electrospun mat production: for use in high-performance air filters. Int J Occup Hyg 7:110–118
Dehghan SF, Golbabaei F, Maddah B et al (2016) Optimization of electrospinning parameters for polyacrylonitrile-MgO nanofibers applied in air filtration. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 66:912–921. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2016.1162228
Deng Y, Lu T, Cui J et al (2022) Morphology engineering processed nanofibrous membranes with secondary structure for high-performance air filtration. Sep Purif Technol 294:121093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121093
Deshmukh K, Ahamed MB, Deshmukh RR et al (2017) Biopolymer composites with high dielectric performance: interface engineering. In: Biopolymer composites in electronics. Elsevier, pp 27–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809261-3.00003-6
Doğan C, Doğan N, Gungor M et al (2022a) Novel active food packaging based on centrifugally spun nanofibers containing lavender essential oil: Rapid fabrication, characterization, and application to preserve of minced lamb meat. Food Packag Shelf Life 34:100942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.100942
Doğan N, Doğan C, Eticha AK et al (2022b) Centrifugally spun micro-nanofibers based on lemon peel oil/gelatin as novel edible active food packaging: fabrication, characterization, and application to prevent foodborne pathogens E. coli and S. aureus in cheese. Food Control 139:109081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109081
Ehrmann A (2021) Non-toxic crosslinking of electrospun gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering and biomedicine—a review. Polymers 13:1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121973
Erencia M, Cano F, Tornero JA et al (2015) Electrospinning of gelatin fibers using solutions with low acetic acid concentration: Effect of solvent composition on both diameter of electrospun fibers and cytotoxicity. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42115
Etxabide A, Akbarinejad A, Chan EW et al (2022) Effect of gelatin concentration, ribose and glycerol additions on the electrospinning process and physicochemical properties of gelatin nanofibers. Eur Polymer J 180:111597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111597
Gao Y, Zhang J, Su Y et al (2021) Recent progress and challenges in solution blow spinning. Mater Horiz 8:426–446. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01096K
Gough CR, Callaway K, Spencer E et al (2021) Biopolymer-based filtration materials. ACS Omega 6:11804–11812. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00791
Gundogdu NS, Akgul Y, Kilic A (2018) Optimization of centrifugally spun thermoplastic polyurethane nanofibers for air filtration applications. Aerosol Sci Technol 52:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2018.1433813
Gungor M, Toptas A, Calisir MD, Kilic A (2021) Aerosol filtration performance of nanofibrous mats produced via electrically assisted industrial-scale solution blowing. Polym Eng Sci 61:2557–2566. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25780
Han M-C, He H-W, Kong W-K et al (2022) High-performance electret and antibacterial polypropylene meltblown nonwoven materials doped with boehmite and ZnO nanoparticles for air filtration. Fibers Polym 23:1947–1955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4786-8
He J, Lian Y, Zhang X et al (2014) Mass preparation of nanofibers by high pressure air-jet split electrospinning: Effect of electric field. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 52:993–1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.23519
Horuz Tİ, Belibağlı KB (2017) Production of electrospun gelatin nanofibers: an optimization study by using Taguchi’s methodology. Mater Res Exp 4:015023. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa57ea
Kadam V, Truong YB, Easton C et al (2018) Electrospun polyacrylonitrile/β-cyclodextrin composite membranes for simultaneous air filtration and adsorption of volatile organic compounds. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1:4268–4277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b01056
Kadam V, Truong YB, Schutz J et al (2021) Gelatin/β–Cyclodextrin Bio-Nanofibers as respiratory filter media for filtration of aerosols and volatile organic compounds at low air resistance. J Hazard Mater 403:123841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123841
Kanu NJ, Gupta E, Vates UK, Singh GK (2020) Electrospinning process parameters optimization for biofunctional curcumin/gelatin nanofibers. Mater Res Exp 7:035022. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab7f60
Khansari S, Sinha-Ray S, Yarin AL, Pourdeyhimi B (2013) Biopolymer-based nanofiber mats and their mechanical characterization. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:15104–15113. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie402246x
Kim HB, Lee WJ, Choi SC et al (2021) Filter quality factors of fibrous filters with different fiber diameter. Aerosol Sci Technol 55:154–166. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2020.1829535
Kwak HW, Park J, Yun H et al (2021) Effect of crosslinkable sugar molecules on the physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of fish gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocolloids 111:106259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106259
Li L, Kang W, Zhuang X et al (2015) A comparative study of alumina fibers prepared by electro-blown spinning (EBS) and solution blowing spinning (SBS). Mater Lett 160:533–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.016
Li W, Shen S, Li H (2016a) Study and optimization of the filtration performance of multi–fiber filter. Adv Powder Technol 27:638–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.02.018
Li Z, Kang W, Zhao H et al (2016b) Fabrication of a polyvinylidene fluoride tree-like nanofiber web for ultra high performance air filtration. RSC Adv 6:91243–91249. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA17097H
Liguori A, Uranga J, Panzavolta S et al (2019) Electrospinning of fish gelatin solution containing citric acid: An environmentally friendly approach to prepare crosslinked gelatin fibers. Materials 12:2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172808
Liu F, Türker Saricaoglu F, Avena-Bustillos RJ et al (2018) Preparation of fish skin gelatin-based nanofibers incorporating cinnamaldehyde by solution blow spinning. Int J Mol Sci 19:618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020618
Liu Y, Jia C, Zhang H et al (2021) Free-Standing ultrafine nanofiber papers with high PM0. 3 Mechanical filtration efficiency by scalable blow and electro-blow spinning. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:34773–34781. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c04253
Lu S, Li C, Liu R, Lv A (2021) PVP-assisted shellac nanofiber membrane as highly efficient, eco-friendly. Translucent Air Filter Appl Sci 11:11094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311094
Mostofi Sarkari N, Rasoulzadeh Y, Musavi S et al (2022) Electrospun polyurethane/β-cyclodextrin composite membranes for aerosol filtration and adsorption of volatile organic compounds from the air. J Environ Health Sustain Dev 7:1684–1697
Mukherjee S, Kumar S, Sahu RK, Nayar S (2020) PVA-graphene-hydroxyapatite electrospun fibres as air-filters. Mater Res Exp 6:125366. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6ac9
Naragund VS, Panda PK (2021) Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membranes for air filtration application. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03705-4
Polat Y, Calisir M, Gungor M et al (2019) Solution blown nanofibrous air filters modified with glass microparticles. J Ind Text. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083719888674
Quan Z, Zu Y, Wang Y et al (2021) Slip effect based bimodal nanofibrous membrane for high-efficiency and low-resistance air purification. Sep Purif Technol 275:119258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119258
Rathod NB, Bangar SP, Šimat V, Ozogul F (2022) Chitosan and gelatine biopolymer-based active/biodegradable packaging for the preservation of fish and fishery products. Int J Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.16038
Sarac Z, Kilic A, Tasdelen-Yucedag C (2023) Optimization of electro-blown polysulfone nanofiber mats for air filtration applications. Polym Eng Sci 63:723–737. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.26236
Shen C, Cao Y, Rao J et al (2021) Application of solution blow spinning to rapidly fabricate natamycin-loaded gelatin/zein/polyurethane antimicrobial nanofibers for food packaging. Food Packag Shelf Life 29:100721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100721
Song J, Liu Z, Li Z, Wu H (2020) Continuous production and properties of mutil-level nanofiber air filters by blow spinning. RSC Adv 10:19615–19620. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA01656J
Souzandeh H, Wang Y, Zhong W-H (2016) “Green” nano-filters: fine nanofibers of natural protein for high efficiency filtration of particulate pollutants and toxic gases. RSC Adv 6:105948–105956. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA24512A
Souzandeh H, Molki B, Zheng M et al (2017) Cross-linked protein nanofilter with antibacterial properties for multifunctional air filtration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:22846–22855. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b05796
Stojanovska E, Canbay E, Pampal ES et al (2016) A review on non-electro nanofibre spinning techniques. RSC Adv 6:83783–83801. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA16986D
Ulpatek (2021) Home Page. In: Ulpatek. https://www.ulpatek.com/. Accessed 30 May 2023
Vilches JL, Souza Filho MD, Rosa MD, Sanches AO, Malmonge JA (2019) Fabrication of fish gelatin microfibrous mats by solution blow spinning. Mater Res. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2019-0158
Vinh ND, Kim H-M (2016) Electrospinning fabrication and performance evaluation of polyacrylonitrile nanofiber for air filter applications. Appl Sci 6:235. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090235
Wang S, Zhao X, Yin X et al (2016) Electret polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers hybridized by polytetrafluoroethylene nanoparticles for high-efficiency air filtration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:23985–23994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b08262
Xiao Y, Wen E, Sakib N et al (2020) Performance of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibrous membrane in air filtration. Autex Res J 20:552–559. https://doi.org/10.2478/aut-2019-0043
Yang Y, Xie B, Liu Q et al (2020) Fabrication and characterization of a novel polysaccharide based composite nanofiber films with tunable physical properties. Carbohyd Polym 236:116054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116054
Yang B, Wang J, Kang L et al (2022) Antibacterial, efficient and sustainable CS/PVA/GA electrospun nanofiber membrane for air filtration. Mater Res Exp 9:125002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aca74a
Yikar E, Demir D, Bölgen N (2021) Electrospinning of gelatin nanofibers: effect of gelatin concentration on chemical, morphological and degradation characteristics. Turkish J Eng. 5:171–176. https://doi.org/10.31127/tuje.704573
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Karabuk University Iron and Steel Institute and ITU TEMAG laboratory for their support for the analysis. Also, we would like to thank Halavet Gıda LLC, Türkiye, for their gelatin supply.
Funding
This article was supported by the Scientific Research Projects (Grant No: KBUBAP-21-ABP-031) of Karabuk University in Türkiye.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: U.W. Tang.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material:
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eticha, A.K., Akgul, Y. Optimization of gelatin nanofibrous webs fabricated via electrically assisted solution blow spinning for air filtration applications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 7135–7152 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05482-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05482-2