Abstract
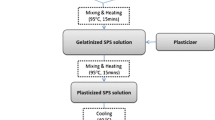
The feasibility of potato-based bioplastics as food or fresh produce packaging materials was investigated using glycerol and sorbitol plasticizers at three different concentrations (30, 50, and 70%). The effects of plasticizers on the tensile strength, water vapour transmission rate, water absorption, and contact angle of the plasticized bioplastic were compared to the pure potato starch-based bioplastic. At same concentration, glycerol-plasticized bioplastic films were more flexible and stickier than sorbitol-plasticized bioplastic films. At all concentrations, however, the tensile strength and elongation at break were consistently lower than the latter. The experimental results revealed that glycerol with a higher hydrophilicity produced bioplastic films with higher water vapour transmission (63.68–80.91%), water absorption (252.65–432.71%), and lower contact angle (36.669°–50.506°) in comparison with sorbitol-plasticized bioplastics. In Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, the major absorption bands characteristics of all bioplastics, with or without the presence of plasticizers, were found to be identical. A weight loss test on strawberries stored at different temperatures was used to investigate the feasibility of plasticized potato starch-based bioplastics for use as food and fresh produce packaging materials. Increase in the concentration of both plasticizers from 30 to 70% reduced the weight loss of strawberries kept at 4 °C and room temperature, with no significant difference in weight loss observed at the same concentration of the plasticizers. It was also found that when strawberries were wrapped in plasticized bioplastics and kept at 4 °C, water loss was reduced by 4 to 6.8 fold compared to room temperature.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdullah ZW, Dong Y (2019) Biodegradable and water resistant poly(vinyl) alcohol (PVA)/Starch (ST)/glycerol (GL)/halloysite nanotube (HNT) nanocomposite films for sustainable food packaging. Front Mater 6:58. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2019.00058
Abdullah AHD, Pudjirahar S, Karina M, Dwi Putri O, Fauziyyah RH (2018) Fabrication and characterization of sweet potato starch-based bioplastics plasticized with glycerol. J Biol Sci 19(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2019.57.64
Aguirre A, Borneo R, León AE (2013) Properties of triticale protein films and their relation to plasticizing-antiplasticizing effects of glycerol and sorbitol. Ind Crops Prod 50:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.07.043
Ahimbisibwe M, Banadda N, Seay J, Nabuuma B, Atwijukire E, Wembabazi E, Nuwamanya E (2019) Influence of weather and purity of plasticizer on degradation of cassava starch bioplastics in natural environmental conditions. J Agric Food Chem Environ 8(4):237–250. https://doi.org/10.4236/jacen.2019.84018
Ayala-Zavala J, Wang SY, Wang CY, González-Aguilar GA (2004) Effect of storage temperatures on antioxidant capacity and aroma compounds in strawberry fruit. LWT Food Sci Technol 37(7):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2004.03.002
Azmin SNHM, Hayat NABM, Nor MSM (2020) Development and characterization of food packaging bioplastic film from cocoa pod husk cellulose incorporated with sugarcane bagasse fibre. J Bioresour Bioprod 5(4):248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2020.10.003
Ballesteros-Mártinez L, Pérez-Cervera C, Andrade-Pizarro R (2020) Effect of glycerol and sorbitol concentrations on mechanical, optical, and barrier properties of sweet potato starch film. NFS J 20:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.002
Bangar SP, Purewal SS, Trif M, Maqsood S, Kumar M, Manjunatha V, Rusu AV (2021) Functionality and applicability of starch-based films: an eco- friendly approach. Foods 10(9):2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092181
Bartz J, Madruga KM, Klein B, Pinto VZ, Dias LRG (2012) Pasting properties of native and acetylated rice starches. Braz J Food Technol. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1981-67232012005000040
Basiak E, Lenart A, Debeaufort F (2018) How glycerol and water contents affect the structural and functional properties of starch-based edible films. Polymers 10(4):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040412
Bilck AP, Müller CMO, Olivato JB, Mali S, Grossmann MVE, Yamashita F (2015) Using glycerol produced from biodiesel as a plasticiser in extruded biodegradable films. Polímeros 25(4):331–335. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-1428.1803
Borah A, Balasubramanian S, Kaur A, Kaur J, Sukhija S, Balasubramanian S (2019) Thermal and microbial characteristics of barley pasta as affected by moisture content. Our Heritage 67(7):300–314
Chamas A, Moon H, Zheng J, Qiu Y, Tabassum T, Jang JH, Abu-Omar M, Scott SL, Suh S (2020) Degradation rates of plastics in the environment. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 8(9):3494–3511. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06635
Chen Y, Wei X, Chang G, Fu T, Cui L, Li J (2017) Study of bagasse/tapioca starch film preparation and characterization. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 69:012053. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/69/1/012053
Ciriminna R, Pagliaro M (2019) Biodegradable and compostable plastics: a critical perspective on the dawn of their global adoption. ChemistryOpen 9(1):8–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/open.201900272
Dawam Abdullah AH, Pudjirahar S, Karina M, Dwi Putri O, Fauziyyah RH (2018) Fabrication and characterization of sweet potato starch-based bioplastics plasticized with glycerol. Sci J Biol Sci 19(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2019.57.64
Dehghani S, Hosseini SV, Regenstein JM (2018) Edible films and coatings in seafood preservation: a review. Food Chem 240:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.034
Geleta TT, Habtegebreil SA, Tolesa GN (2020) Physical, mechanical, and optical properties of enset starch from bulla films influenced by different glycerol concentrations and temperatures. J Food Process Preserv 44(8):e14586. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14586
Geyer R, Jambeck JR, Law KL (2017) Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv 3(7):e1700782. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Ghasemlou M, Aliheidari N, Fahmi R, Shojaee-Aliabadi S, Keshavarz B, Cran MJ, Khaksar R (2013) Physical, mechanical and barrier properties of corn starch films incorporated with plant essential oils. Carbohydr Polym 98(1):1117–1126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.07.026
Halden RU (2010) Plastics and health risks. Annu Rev Public Health 31(1):179–194. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.012809.103714
Harnkarnsujarit N, Wongphan P, Chatkitanan T, Laorenza Y, Srisa A (2021) Chapter 7 - Bioplastic for Sustainable Food Packaging. In: Galanakis CM (ed) Sustainable Food Processing and Engineering Challenges. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 203–277
Hazrati KZ, Sapuan SM, Zuhri MYM, Jumaidin R (2021) Preparation and characterization of starch-based biocomposite films reinforced by Dioscorea hispida Fibers. J Mater Res Technol 15:1342–1355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.003
Heydari A, Alemzadeh I, Vossoughi M (2013) Functional properties of biodegradable corn starch nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Mater Des 50:954–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.084
Hossain S, Rahman MA, Chowdhury AM, Mohonta KS (2020) Plastic pollution in bangladesh: a review on current status emphasizing the impacts on environment and public health. Environ Eng Res 26(6):200535. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.535
Ibrahim MIJ, Sapuan SM, Zainudin ES, Zuhri MYM (2019) Physical, thermal, morphological, and tensile properties of cornstarch-based films as affected by different plasticizers. Int J Food Prop 22(1):925–941. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2019.1618324
Ikegaya A, Ohba S, Nakajima T, Toyoizumi T, Ito S, Arai E (2020) Practical long-term storage of strawberries in refrigerated containers at ice temperature. Food Sci Nutr 8(9):5138–5148. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1817
Isotton F, Bernardo G, Baldasso C, Rosa L, Zeni M (2015) The plasticizer effect on preparation and properties of etherified corn starchs films. Ind Crops Prod 76:717–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.04.005
Jafarzadeh S, Alias AK, Ariffin F, Mahmud S (2018) Physico-mechanical and microstructural properties of semolina flour films as influenced by different sorbitol/glycerol concentrations. Int J Food Prop 21(1):983–995. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2018.1474056
Jafarzadeh S, Jafari SM, Salehabadi A, Nafchi AM, Kumar USU, Abdul Khalil HPS (2020) Biodegradable green packaging with antimicrobial functions based on the bioactive compounds from tropical plants and their by-products. Trends Food Sci Technol 100:262–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.04.017
Jost V, Kobsik K, Schmid M, Noller K (2014) Influence of plasticiser on the barrier, mechanical and grease resistance properties of alginate cast films. Carbohydr Polym 110:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.03.096
Kumar PS, Sagar VR (2012) Drying kinetics and physico-chemical characteristics of osmo-dehydrated mango, guava and aonla under different drying conditions. J Food Sci Technol 51(8):1540–1546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0658-3
Laohakunjit N, Noomhorm A (2004) Effect of plasticizers on mechanical and barrier properties of rice starch film. Starch 56:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.200300249
Li Y, Ceylan M, Shrestha B, Wang H, Lu QR, Asmatulu R, Yao L (2013) Nanofibers support oligodendrocyte precursor cell growth and function as a neuron-free model for myelination study. Biomacromol 15(1):319–326. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm401558c
Lim R, Kiew PL, Lam MK, Yeoh WM, Ho MY (2021) Corn starch/PVA bioplastics—the properties and biodegradability study using Chlorella vulgaris cultivation. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 16(3):e2622. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.2622
López OV, Castillo LA, García MA, Villar MA, Barbosa SE (2015) Food packaging bags based on thermoplastic corn starch reinforced with talc nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll 43:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.04.021
Lusiana SW, Putri D, Nurazizah IZ, Bahruddin, (2019) Bioplastic properties of sago-PVA starch with glycerol and sorbitol plasticizers. J Phys Conf Ser 1351:012102. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1351/1/012102
Mali S, Grossmann MVE, García MA, Martino MN, Zaritzky NE (2006) Effects of controlled storage on thermal, mechanical and barrier properties of plasticized films from different starch sources. J Food Eng 75(4):453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.04.031
Maraei RW, Elsawy KM (2017) Chemical quality and nutrient composition of strawberry fruits treated by γ-irradiation. J Radiat Res Appl 10(1):80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2016.12.004
Maulida KT, Harahap MB, Ginting MHS (2018) Utilization of mango seed starch in manufacture of bioplastic reinforced with microparticle clay using glycerol as plasticizer. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 309:012068. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/309/1/012068
Muscat D, Adhikari B, Adhikari R, Chaudhary D (2012) Comparative study of film forming behaviour of low and high amylose starches using glycerol and xylitol as plasticizers. J Food Eng 109(2):189–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.10.019
Nasir NN, Othman SA (2021) The physical and mechanical properties of corn-based bioplastic films with different starch and glycerol content. J Phys Sci 32(3):89–101
Ng JS, Kiew PL, Lam MK, Yeoh WM, Ho MY (2022) Preliminary evaluation of the properties and biodegradability of glycerol- and sorbitol-plasticized potato-based bioplastics. Int J Environ Sci Technol 19(3):1545–1554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03213-5
Nordin N, Othman SH, Rashid SA, Basha RK (2020) Effects of Glycerol and Thymol on Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Corn Starch Films. Food Hydrocoll 106:105884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105884
North EJ, Halden RU (2013) Plastics and environmental health: the road ahead. Rev Environ Health 28(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2012-0030
Nouraddini M, Esmaiili M, Mohtarami F (2018) Development and characterization of edible films based on eggplant flour and corn starch. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1639–1645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.126
Ooi ZX, Ismail H, Bakar AA, Aziz NAA (2012) The Comparison effect of sorbitol and glycerol as plasticizing agents on the properties of biodegradable polyvinyl alcohol/rambutan skin waste flour blends. Polym Plast Technol Eng 51(4):432–437. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2011.639827
Paluch M, Ostrowska J, Tyński P, Sadurski W, Konkol M (2022) Structural and thermal properties of starch plasticized with glycerol/urea mixture. J Polym Environ 30:728–740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02235-x
Phil C R (2019) Plastics in the Environment. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335338250_Plastics_in_the_Environment. Accessed 28 September 2021.
Plastic Oceans International (2021) Plastic Pollution Facts. https://plasticoceans.org/the-facts/. Accessed 1 March 1 2021.
Prata JC, Silva ALP, da Costa JP, Mouneyrac C, Walker TR, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos T (2019) Solutions and integrated strategies for the control and mitigation of plastic and microplastic pollution. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(13):2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132411
Proshad R, Kormoker T, Islam MS, Haque MA, Rahman MM, Mithu MMR (2017) Toxic effects of plastic on human health and environment: a consequences of health risk assessment in bangladesh. Int J Health 6(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijh.v6i1.8655
Rahman MM, Moniruzzaman M, Ahmad MR, Sarker B, Khurshid Alam M (2016) Maturity stages affect the postharvest quality and shelf-life of fruits of strawberry genotypes growing in subtropical regions. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 15(1):28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2014.05.002
Sam ST, Nuradibah MA, Chin KM, Hani N (2016) Current Application and Challenges on Packaging Industry Based On Natural Polymer Blending. In: Olatunji O (ed) Natural Polymers-Industry Techniques and Applications. Springer, London, pp 163–184
Sanyang ML, Sapuan SM, Jawaid M, Ishak MR, Sahari J (2015) Effect of plasticizer type and concentration on dynamic mechanical properties of sugar palm starch–based films. Int J Polym Anal Charact 20(7):627–636. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023666X.2015.1054107
Sanyang ML, Sapuan SM, Jawaid M, Ishak MR, Sahari J (2016) Effect of plasticizer type and concentration on physical properties of biodegradable films based On Sugar Palm (Arenga pinnata) starch for food packaging. J Food Sci Technol 53(1):326–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2009-7
Siracusa V, Rocculi P, Romani S, Rosa MD (2008) Biodegradable Polymers for Food Packaging: A Review. Trends Food Sci Technol 19(12):634–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2008.07.003
Sofiah Y, Aznury M, Melianti, (2019) Mechanical Properties of Bioplastics Product from Musa Paradisica Formatypica Concentrate with Plasticizer Variables. J Phys Conf Ser 1167:012048. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1167/1/012048
Suman TY, Li WG, Alif S, Faris VRP, Amarnath DJ, Ma JG, Pei DS (2020) Characterization of Petroleum-based Plastics and Their Absorbed Trace Metals from the Sediments of the Marina Beach in Chennai. Environ Sci Eur, India. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-00388-5
Talja RA, Helén H, Roos YH, Jouppila K (2007) Effect of various polyols and polyol contents on physical and mechanical properties of potato starch-based films. Carbohydr Polym 67(3):288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.05.019
Tapia-Blácido DR, Sobral PJDA, Menegalli FC (2013) Effect of drying conditions and plasticizer type on some physical and mechanical properties of amaranth flour films. LWT Food Sci Technol 50:392–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.09.008
Vieira MGA, da Silva MA, dos Santos LO, Beppu MM (2011) Natural-based plasticizers and biopolymer films: a review. Eur Polym J 47(3):254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2010.12.01
Walker TR, Xanthos D (2018) A call for canada to move toward zero plastic waste by reducing and recycling single-use plastics. Resour Conserv Recycl 133:99–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.02.014
Zavareze EDR, Pinto VZ, Klein B, El Halal SLM, Elias MC, Prentice-Hernández C, Dias ARG (2012) Development of oxidised and heat-moisture treated potato starch film. Food Chem 132(1):344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.10.090
Zhang M, Xiao G, Peng J, Salokhe V (2003) Effects of modified atmosphere package on preservation of strawberries. Int Agrophysics 17(3):143–148
Zhou H (2016) Physio-Chemical Properties of Bioplastics and Its Application for Fresh-Cut Fruits Packaging. Hokkaido University. http://hdl.handle.net/2115/61802. Accessed 18 September 2021.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, UTM Encouragement Research (UTMER) with reference No. PY/2021/01231/Q.K130000.3843.20J90.
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, UTM Encouragement Research (UTMER) with reference No. PY/2021/01231/Q.K130000.3843.20J90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: Lau Hou Yip and Kiew Peck Loo were involved in the paper conception and design; Tan Lian See and Lau Hou Yip contributed to the literature review and data collection; Lam Man Kee and Yeoh Wei Ming assisted in the characterization of bioplastic. Lau Hou Yip and Kiew Peck Loo prepared the draft manuscript. All authors reviewed the write-up and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
This paper has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere. All authors have been agreed to submit this paper to International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.
Consent for publication
This paper has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere. All authors have been agreed to submit this paper to International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, H.Y., Kiew, P.L., Tan, L.S. et al. Deciphering the effects of plasticizers in potato-based bioplastic for food and fresh produce packaging. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 13703–13716 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04936-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04936-3