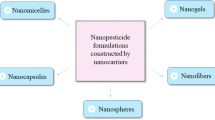
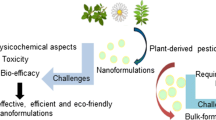
Abstract
Increasing global population demands modernization in agricultural production to achieve sustainable food security. The frequent pest infestation causes a significant economic loss and deleterious impact on agriculture production. While, the traditional application of conventional pesticides leads to loss of soil biodiversity, decline in pollinator population, and negative impacts on non-target organisms. In recent years, nanotechnology has gained much interest in agricultural application. Various studies have demonstrated the beneficial effect of engineered nanomaterials as an active ingredients or the nanoformulations in insect pest control and plant protection. Nanopesticides have shown more advantages over conventional pesticides in terms of high adsorption, reduced volatilization, improved tissue permeation, controlled release, etc. However, studies are also highlighting the potential toxicity of nanopesticides in non-target organism and their environmental risk. The goal of this review is to provide a comprehensive information on recent developments in nanopesticides and its consequences in the environment. This review highlights various aspects of nanopesticides including, preparation methods, types, characterization techniques, importance in pest control, toxicity in plant and animal models, environmental risk, and current approaches in risk assessment and regulatory strategies.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Aziz HMM, Hasaneen MNA, Omer AM (2019) Impact of engineered nanomaterials either alone or loaded with NPK on growth and productivity of French bean plants: seed priming vs foliar application. S Afr J Bot 125:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.07.005
Abdelmigid HM, Morsi MM, Hussien NA, Alyamani AA, Alhuthal NA, Albukhaty S (2022) Green synthesis of phosphorous-containing hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (nHAP) as a novel nano-fertilizer: preliminary assessment on pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Nanomaterials 12(9):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091527
Abdollahdokht D, Gao Y, Faramarz S, Poustforoosh A, Abbasi M, Asadikaram G, Nematollahi MH (2022) Conventional agrochemicals towards nano-biopesticides: an overview on recent advances. Chem Biol Technol Agric 9(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-021-00281-0
Adisa IO, Pullagurala VLR, Peralta-Videa JR, Dimkpa CO, Elmer WH, Gardea-Torresdey JL, White JC (2019) Recent advances in nano-enabled fertilizers and pesticides: a critical review of mechanisms of action. Environ Sci Nano 6(7):2002–2030. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EN00265K
Ahmed K, Mikhail WZ, Sobhy HM, Radwan EMM, El Din TS, Youssef A (2019) Effect of lambda-cyahalothrin as nanopesticide on cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Egypt J Chem 62(7):1263–1275. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2019.6871.1581
Ahmed T, Ren H, Noman M, Shahid M, Liu M, Ali MA, Zhang J, Tian Y, Qi X, Li B (2021) Green synthesis and characterization of zirconium oxide nanoparticles by using a native Enterobacter sp. and its antifungal activity against bayberry twig blight disease pathogen Pestalotiopsis versicolor. Nonimpact 21:100281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2020.100281
Aksakal FI, Arslan H (2020) Detoxification and reproductive system-related gene expression following exposure to Cu (OH)2 nanopesticide in water flea (Daphnia magna Straus 1820). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(6):6103–6111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07414-x
Aksakal FI, Sisman T (2020) Developmental toxicity induced by Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide in zebrafish embryos. Environ Toxicol 35(12):1289–1298. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22993
Ali F, Tariq M, Shaheen FA, Zainab T, Gulzar A (2019) Toxicity of different plant extracts and green silver nanoparticles against Plutella xylostella (lepidoptera: plutellida). Plant Protect 3(3):151–159. https://doi.org/10.33804/pp.003.03.3112
Assalin MR, dos Santos LDL, de Souza DRC, Rosa MA, Duarte RRM, Castanha RF, Donaire PPR, Durán N (2019) Nanoformulation as a tool for improvement of thiamethoxam encapsulation and evaluation of ecotoxicological impacts. Energy Ecol Environ 4(6):310–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-019-00138-1
Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG, Benelli G, Losic D, Rani PU, Desneux N (2018) Nanoparticles for pest control: current status and future perspectives. J Pest Sci 91(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0898-0
Awad M, Ibrahim EDS, Osman EI, Elmenofy WH, Mahmoud AWM, Atia MA, Moustafa MA (2022) Nano-insecticides against the black cutworm Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): toxicity, development, enzyme activity, and DNA mutagenicity. PLoS ONE 17(2):0254285. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0254285
Bahrulolum H, Nooraei S, Javanshir N, Tarrahimofrad H, Mirbagheri VS, Easton AJ, Ahmadian G (2021) Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using microorganisms and their application in the agrifood sector. J Nanobiotechnol 19(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00834-3
Bai C, Tang M (2020) Toxicological study of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in zebrafish. J Appl Toxicol 40(1):37–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3910
Barrera-Méndez F, Miranda-Sánchez D, Sánchez-Rangel D, Bonilla-Landa I, Rodríguez-Haas B, Monribot-Villanueva JL, Olivares-Romero JL (2019) Propiconazole nanoencapsulation in biodegradable polymers to obtain pesticide-controlled delivery systems. J Mex Chem Soc 63(1):50–60. https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v63i1.564
Barrios AC, Rico CM, Trujillo-Reyes J, Medina-Velo IA, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2016) Effects of uncoated and citric acid coated cerium oxide nanoparticles, bulk cerium oxide, cerium acetate, and citric acid on tomato plants. Sci Total Environ 563:956–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.143
Basit F, Asghar S, Ahmed T, Ijaz U, Noman M, Hu J, Liang X, Guan Y (2022) Facile synthesis of nanomaterials as nanofertilizers: a novel way for sustainable crop production. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20950-3
Besha AT, Liu Y, Fang C, Bekele DN, Naidu R (2020) Assessing the interactions between micropollutants and nanoparticles in engineered and natural aquatic environments. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 50(2):135–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1629799
Bharani RA, Namasivayam SKR (2017) Biogenic silver nanoparticles mediated stress on developmental period and gut physiology of major lepidopteran pest Spodoptera litura (Fab.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)—an eco-friendly approach of insect pest control. J Environ Chem Eng 5(1):453–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.023
Bhattacharyya A, Bhaumik A, Rani PU, Mandal S, Epidi TT (2010) Nano-particles—a recent approach to insect pest control. Afr J Biotechnol 9(24):3489–3493
Bhattacharyya A, Prasad R, Buhroo AA, Duraisamy P, Yousuf I, Umadevi M, Bindhu MR, Govindarajan M, Khanday AL (2016) One-pot fabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Solanum lycopersicum: an eco-friendly and potent control tool against rose aphid Macrosiphum rosae. J Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4679410
Bizymis AP, Tzia C (2021) Edible films and coatings: properties for the selection of the components, evolution through composites and nanomaterials, and safety issues. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1934652
Blahova J, Cocilovo C, Plhalova L, Svobodova Z, Faggio C (2020) Embryotoxicity of atrazine and its degradation products to early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 77:103370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103370
Buteler M, Sofie SW, Weaver DK, Driscoll D, Muretta J, Stadler T (2015) Development of nanoalumina dust as insecticide against Sitophilus oryzae and Rhyzopertha dominica. Int J Pest Manag 61(1):80–89. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670874.2014.1001008
Camara MC, Campos EVR, Monteiro RA, Santo Pereira ADE, de Freitas Proença PL, Fraceto LF (2019) Development of stimuli-responsive nano-based pesticides: emerging opportunities for agriculture. J Nanobiotechnol 17(1):100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-019-0533-8
Campos EV, Proença PL, Oliveira JL, Pereira AE, de Morais Ribeiro LN, Fernandes FO, Gonçalves KC, Polanczyk RA, Pasquoto-Stigliani T, Lima R, Melville CC (2018) Carvacrol and linalool co-loaded in β-cyclodextrin-grafted chitosan nanoparticles as sustainable biopesticide aiming pest control. Sci Rep 8(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26043-x
Carley LN, Panchagavi R, Song X, Davenport S, Bergemann CM, McCumber AW, Gunsch CK, Simonin M (2020) Long-term effects of copper nanopesticides on soil and sediment community diversity in two outdoor mesocosm experiments. Environ Sci Technol 54(14):8878–8889. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00510
Chaud M, Souto EB, Zielinska A, Severino P, Batain F, Oliveira-Junior J, Alves T (2021) Nanopesticides in agriculture: benefits and challenge in agricultural productivity, toxicological risks to human health and environment. Toxics 9(6):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9060131
Chhipa H (2017) Nanofertilizers and nanopesticides for agriculture. Environ Chem Lett 15(1):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-016-0600-4
Chhipa H (2019) Applications of nanotechnology in agriculture. In: Gurtler V, Ball AS, Soni S (eds) Methods in microbiology. Academic Press, Cambridge, vol 46, pp 115–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mim.2019.01.002
Christofoli M, Costa ECC, Bicalho KU, de Cássia DV, Peixoto MF, Alves CCF, Araújo WL, de Melo CC (2015) Insecticidal effect of nanoencapsulated essential oils from Zanthoxylum rhoifolium (Rutaceae) in Bemisia tabaci populations. Ind Crops Prod 70:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.03.025
Clemente Z, Grillo R, Jonsson M, Santos NZP, Feitosa LO, Lima R, Fraceto LF (2014) Ecotoxicological evaluation of poly (ε-caprolactone) nanocapsules containing triazine herbicides. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(7):4911–4917. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2014.8681
Conway JR, Beaulieu AL, Beaulieu NL, Mazer SJ, Keller AA (2015) Environmental stresses increase photosynthetic disruption by metal oxide nanomaterials in a soil-grown plant. ACS Nano 9(12):11737–11749. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b03091
Cota-Arriola O, Onofre Cortez-Rocha M, Burgos-Hernández A, Marina Ezquerra-Brauer J, Plascencia-Jatomea M (2013) Controlled release matrices and micro/nanoparticles of chitosan with antimicrobial potential: development of new strategies for microbial control in agriculture. J Sci Food Agric 93(7):1525–1536. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6060
Cota-Ruiz K, Ye Y, Valdes C, Deng C, Wang Y, Hernández-Viezcas JA, Duarte-Gardea M, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2020) Copper nanowires as nanofertilizers for alfalfa plants: understanding nano-bio systems interactions from microbial genomics, plant molecular responses and spectroscopic studies. Sci Total Environ 742:140572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140572
Cui JG, Mo DM, Jiang Y, Gan CF, Li WG, Wu A, Li XY, Xiao JA, Hu Q, Yuan HY, Huang YM (2019) Fabrication, characterization, and insecticidal activity evaluation of emamectin benzoate–sodium lignosulfonate nanoformulation with pH-responsivity. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(43):19741–19751. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6060
DBT (2020) Department of Biotechnology. Guidelines for evaluation of nano-based agri-input and food products in India. https://dbtindia.gov.in/sites/default/files/Guidlines%20Document_0.pdf Accessed 16 Oct. 2022)
de Albuquerque FP, de Oliveira JL, dos Santos ML, Richardi VS, da Silva MAN, Pompêo MLM, Fraceto LF, Carlos VM (2021) Use of nontarget organism Chironomus sancticaroli to study the toxic effects of nanoatrazine. Ecotoxicology 30(4):733–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02400-x
de Andrade LL, Santo Pereira ADE, Fraceto LF, dos Reis Martinez CB (2019) Can atrazine loaded nanocapsules reduce the toxic effects of this herbicide on the fish Prochilodus lineatus? A multibiomarker approach. Sci Total Environ 663:548–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.380
Deka B, Babu A, Baruah C, Barthakur M (2021) Nanopesticides: a systematic review of their prospects with special reference to tea pest management. Front Nutr 8:686131. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.686131
Deng R, Lin D, Zhu L, Majumdar S, White JC, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Xing B (2017) Nanoparticle interactions with co-existing contaminants: joint toxicity, bioaccumulation and risk. Nanotoxicology 11(5):591–612. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2017.1343404
Dev A, Srivastava AK, Karmakar S (2018) Nanomaterial toxicity for plants. Environ Chem Lett 16(1):85–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0667-6
Dhananjayan V, Jayakumar S, Ravichandran B (2020) Conventional methods of pesticide application in agricultural field and fate of the pesticides in the environment and human health. In: Controlled release of pesticides for sustainable agriculture. pp 1–39 Springer: Cham https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23396-9_1
Dima C, Assadpour E, Dima S, Jafari SM (2020) Bioactive-loaded nanocarriers for functional foods: from designing to bioavailability. Curr Opin Food Sci 332:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2019.11.006
Dong J, Chen W, Qin D, Chen Y, Li J, Wang C, Yu Y, Feng J, Du X (2021) Cyclodextrin polymer-valved MoS2-embedded mesoporous silica nanopesticides toward hierarchical targets via multidimensional stimuli of biological and natural environments. J Hazard Mater 419:126404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126404
Duhan JS, Kumar R, Kumar N, Kaur P, Nehra K, Duhan S (2017) Nanotechnology: the new perspective in precision agriculture. Biotechnol Rep 15:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.03.002
EFSA Scientific Committee More S, Bampidis V, Benford D, Bragard C, Halldorsson T, Hernández-Jerez A, Hougaard Bennekou S, Koutsoumanis K, Lambré C, Schoonjans R (2021) Guidance on risk assessment of nanomaterials to be applied in the food and feed chain: human and animal health. EFSA J 19(8):06768. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6768
Elango G, Roopan SM, Dhamodaran KI, Elumalai K, Al-Dhabi NA, Arasu MV (2016) Spectroscopic investigation of biosynthesized nickel nanoparticles and its larvicidal, pesticidal activities. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 162:162–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.06.045
Elek N, Hoffman R, Raviv U, Resh R, Ishaaya I, Magdassi S (2010) Novaluron nanoparticles: formation and potential use in controlling agricultural insect pests. Colloids Surf a: Physicochem Eng Asp 372(1–3):66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.09.034
EPA (2021) United States Environmental Protection Agency. what are biopesticides? (Updated on July 15, 2021) https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/what-are-biopesticides. Accessed 10 Jan 2022
Fabiyi OA, Olatunji GA, Saadu AO (2018) Suppression of Heterodera Sacchari in rice with agricultural waste-silver nano particles. J Solid Waste Technol Manag 44(2):87–91. https://doi.org/10.5276/JSWTM.2018.87
Faria M, Prats E, Ramírez JRR, Bellot M, Bedrossiantz J, Pagano M, Valls A, Gomez-Canela C, Porta JM, Mestres J, Garcia-Reyero N, Faggio C, Oliván LMG, Raldua D (2021) Androgenic activation, impairment of the monoaminergic system and altered behavior in zebrafish larvae exposed to environmental concentrations of fenitrothion. Sci Total Environ 775:145671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145671
Fojtová D, Vašíčková J, Grillo R, Bílková Z, Šimek Z, Neuwirthová N, Kah M, Hofman J (2019) Nanoformulations can significantly affect pesticide degradation and uptake by earthworms and plants. Environ Chem 16(6):470–481. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN19057
Forim MR, Costa ES, Da Silva MFDGF, Fernandes JB, Mondego JM, Boiça Junior AL (2013) Development of a new method to prepare nano-/microparticles loaded with extracts of Azadirachta indica, their characterization and use in controlling Plutella xylostella. J Agric Food Chem 61(38):9131–9139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf403187y
Forouhar Vajargah M, Mohamadi Yalsuyi A, Hedayati A, Faggio C (2018) Histopathological lesions and toxicity in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L 1758) induced by copper nanoparticles. Microsc Res Tech 81(7):724–729. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23028
Forouhar Vajargah M, Imanpoor MR, Shabani A, Hedayati A, Faggio C (2019) Effect of long-term exposure of silver nanoparticles on growth indices, hematological and biochemical parameters and gonad histology of male goldfish (Carassius auratus gibelio). Microsc Res Tech 82(7):1224–1230. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23271
Forouhar Vajargah M, Yalsuyi AM, Sattari M, Prokić MD, Faggio C (2020) Effects of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) on parturition time, survival rate and reproductive success of guppy fish. Poecilia Reticulata J Clust Sci 31(2):499–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01664-y
Forouhar Vajargah M, Namin JI, Mohsenpour R, Yalsuyi AM, Prokić MD, Faggio C (2021) Histological effects of sublethal concentrations of insecticide Lindane on intestinal tissue of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Vet Res Commun 45(4):373–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-021-09818-y
Gahukar RT, Das RK (2020) Plant-derived nanopesticides for agricultural pest control: challenges and prospects. Nanotechnol Environ Eng 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-020-0066-2
Gharaei A, Karimi M, Mirdar J, Miri M, Faggio C (2020) Population growth of Brachionus calyciflorus affected by deltamethrin and imidacloprid insecticides. Iran J Fish Sci 19(2):588–601
Gilbertson LM, Pourzahedi L, Laughton S, Gao X, Zimmerman JB, Theis TL, Westerhoff P, Lowry GV (2020) Guiding the design space for nanotechnology to advance sustainable crop production. Nat Nanotechnol 15(9):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0706-5
Giongo AMM, Vendramim JD, Forim MR (2016) Evaluation of neem-based nanoformulations as alternative to control fall armyworm. Ciênc Agrotec 40(1):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542016000100002
Gogos A, Knauer K, Bucheli TD (2012) Nanomaterials in plant protection and fertilization: current state, foreseen applications, and research priorities. J Agric Food Chem 60(39):9781–9792. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf302154y
Gottardo S, Mech A, Drbohlavová J, Małyska A, Bøwadt S, Sintes JR, Rauscher H (2021) Towards safe and sustainable innovation in nanotechnology: state-of-play for smart nanomaterials. NanoImpact 21:100297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2021.100297
Grillo R, Fraceto LF, Amorim MJ, Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Schoonjans R, Chaudhry Q (2021) Ecotoxicological and regulatory aspects of environmental sustainability of nanopesticides. J Hazard Mater 404:124148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124148
Guo H, White JC, Wang Z, Xing B (2018) Nano-enabled fertilizers to control the release and use efficiency of nutrients. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 6:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2018.07.009
Hofmann T, Lowry GV, Ghoshal S, Tufenkji N, Brambilla D, Dutcher JR, Gilbertson LM, Giraldo JP, Kinsella JM, Landry MP, Wilkinson KJ (2020) Technology readiness and overcoming barriers to sustainably implement nanotechnology-enabled plant agriculture. Nat Food 1(7):416–425. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-020-0110-1
Hua KH, Wang HC, Chung RS, Hsu JC (2015) Calcium carbonate nanoparticles can enhance plant nutrition and insect pest tolerance. J Pestic Sci 40(4):208–213. https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.D15-025
Huang B, Chen F, Shen Y, Qian K, Wang Y, Sun C, Zhao X, Cui B, Gao F, Zeng Z, Cui H (2018) Advances in targeted pesticides with environmentally responsive controlled release by nanotechnology. Nanomaterials 8(2):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020102
Jacques MT, Oliveira JL, Campos EV, Fraceto LF, Ávila DS (2017) Safety assessment of nanopesticides using the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.045
Jafer FS, Annon MR (2018) Larvicidal effect of pure and green-synthesized silver nanoparticles against Tribolium castaneum (herb.) and Callosobruchus maculatus (fab.). J Glob Pharma Technol 10(3):448–454
Kah M (2015) Nanopesticides and nanofertilizers: emerging contaminants or opportunities for risk mitigation? Front Chem 3:64. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2015.00064
Kah M, Weniger AK, Hofmann T (2016) Impacts of (nano) formulations on the fate of an insecticide in soil and consequences for environmental exposure assessment. Environ Sci Technol 50(20):10960–10967. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02477
Kah M, Kookana RS, Gogos A, Bucheli TD (2018) A critical evaluation of nanopesticides and nanofertilizers against their conventional analogues. Nat Nanotechnol 13(8):677–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0131-1
Kah M, Johnston LJ, Kookana RS, Bruce W, Haase A, Ritz V, Dinglasan J, Doak S, Garelick H, Gubala V (2021) Comprehensive framework for human health risk assessment of nanopesticides. Nat Nanotechnol 16(9):955–964. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00964-7
Kamaraj C, Gandhi PR, Elango G, Karthi S, Chung IM, Rajakumar G (2018) Novel and environmental friendly approach; Impact of Neem (Azadirachta indica) gum nano formulation (NGNF) on Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) and Spodoptera litura (Fab.). Int J Biol Macromol 107:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.145
Kantrao S, Ravindra MA, Akbar SMD, Jayanthi PK, Venkataraman A (2017) Effect of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on growth and development of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): interaction with midgut protease. J Asia Pac Entomol 20(2):583–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2017.03.018
Khodakovskaya M, Dervishi E, Mahmood M, Xu Y, Li Z, Watanabe F, Biris AS (2009) Carbon nanotubes are able to penetrate plant seed coat and dramatically affect seed germination and plant growth. ACS Nano 3(10):3221–3227. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900887m
Khoshraftar Z, Safekordi AA, Shamel A, Zaefizadeh M (2020a) Evaluation of insecticidal activity of nanoformulation of Melia azedarach (leaf) extract as a safe environmental insecticide. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17(2):1159–1170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02448-7
Khoshraftar Z, Safekordi AA, Shamel A, Zaefizadeh M (2020b) Synthesis of natural nanopesticides with the origin of Eucalyptus globulus extract for pest control. Green Chem Lett Rev 12(3):286–298. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2019.1643930
Khoshraftar Z, Shamel A, Safekordi AA, Ardjmand M, Zaefizadeh M (2020c) Natural nanopesticides with origin of Plantago major seeds extract for Tribolium castaneum control. J Nanostruct Chem 10(3):255–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-020-00346-w
Khot LR, Sankaran S, Maja JM, Ehsani R, Schuster EW (2012) Applications of nanomaterials in agricultural production and crop protection: a review. Crop Prot 35:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2012.01.007
Knaak N, Fiuza LM (2010) Potential of essential plant oils to control insects and microorganisms. Neotrop Biol Conserv 5(2):120–132. https://doi.org/10.4013/4757
Kobetičová K, Černý R (2017) Ecotoxicology of building materials: a critical review of recent studies J Clean. Prod 165:500–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.161
Kookana RS, Boxall AB, Reeves PT, Ashauer R, Beulke S, Chaudhry Q, Cornelis G, Fernandes TF, Gan J, Kah M, Van den Brink PJ (2014) Nanopesticides: guiding principles for regulatory evaluation of environmental risks. J Agric Food Chem 62(19):4227–4240. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf500232f
Kumar S, Bhanjana G, Sharma A, Sidhu MC, Dilbaghi N (2014) Synthesis, characterization and on field evaluation of pesticide loaded sodium alginate nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 101:1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.025
Kumar S, Chauhan N, Gopal M, Kumar R, Dilbaghi N (2015) Development and evaluation of alginate–chitosan nanocapsules for controlled release of acetamiprid. Int J Biol Macromol 81:631–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.062
Kumar S, Nehra M, Dilbaghi N, Marrazza G, Hassan AA, Kim KH (2019) Nano-based smart pesticide formulations: emerging opportunities for agriculture. J Control Release 294:131–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.12.012
Lai RW, Yeung KW, Yung M, Djurišić AB, Giesy JP, Leung KM (2018) Regulation of engineered nanomaterials: current challenges, insights and future directions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(4):3060–3077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9489-0
León-Silva S, Fernández-Luqueño F, López-Valdez F (2016) Silver nanoparticles (AgNP) in the environment: a review of potential risks on human and environmental health. Water Air Soil Pollut 227(9):306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3022-9
Li L, Xu Z, Kah M, Lin D, Filser J (2019) Nanopesticides: a comprehensive assessment of environmental risk is needed before widespread agricultural application. Environ Sci Technol 53(14):7923–7924. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03146
Li P, Huang Y, Fu C, Jiang SX, Peng W, Jia Y, Peng H, Zhang P, Manzie N, Mitter N, Xu ZP (2021) Eco-friendly biomolecule-nanomaterial hybrids as next-generation agrochemicals for topical delivery. Eco Mater 3(5):12132. https://doi.org/10.1002/eom2.12132
Loha KM, Shakil NA, Kumar J, Singh MK, Srivastava C (2012) Bio-efficacy evaluation of nanoformulations of β-cyfluthrin against Callosobruchus maculatus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J Environ Sci Health B 47(7):687–691. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.669254
Lowry GV, Avellan A, Gilbertson LM (2019) Opportunities and challenges for nanotechnology in the agri-tech revolution. Nat Nanotechnol 14(6):517–522. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0461-7
Mittal D, Kaur G, Singh P, Yadav K, Ali SA (2020) Nanoparticle-based sustainable agriculture and food science: recent advances and future outlook. Front Nanotechnol 2:10
Mohd Firdaus MA, Agatz A, Hodson ME, Al-Khazrajy OS, Boxall AB (2018) Fate, uptake, and distribution of nanoencapsulated pesticides in soil–earthworm systems and implications for environmental risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 37(5):1420–1429. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4094
Mohsenpour R, Mousavi-Sabet H, Hedayati A, Rezaei A, Yalsuyi AM, Faggio C (2020) In vitro effects of silver nanoparticles on gills morphology of female Guppy (Poecilia reticulate) after a short-term exposure. Microsc Res Tech 83(12):1552–1557. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23549
Mustapha T, Misni N, Ithnin NR, Daskum AM, Unyah NZ (2022) A review on plants and microorganisms mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles, role of plants metabolites and applications. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(2):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020674
Nayak AK (2010) Hydroxyapatite synthesis methodologies: an overview. Int J Chem Tech Res 2(2):903–907
Ndukwu MC, Ikechukwu-Edeh CE, Nwakuba NR, Okosa I, Horsefall IT, Orji FN (2020) Nanomaterials application in greenhouse structures, crop processing machinery, packaging materials and agro-biomass conversion. Mater Sci for Energy Technol 3:690–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2020.07.006
Nuruzzaman MD, Rahman MM, Liu Y, Naidu R (2016) Nanoencapsulation, nano-guard for pesticides: a new window for safe application. J Agric Food Chem 64(7):1447–1483. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05214
OECD (2022) Organisation for economic co-operation and development. Important issues on risk assessment of manufactured nanomaterials. Series on the Safety of Manufactured Nanomaterials No 103:1–90
Oliveira HC, Stolf-Moreira R, Martinez CB, Sousa GF, Grillo R, de Jesus MB, Fraceto LF (2015) Evaluation of the side effects of poly (epsilon-caprolactone) nanocapsules containing atrazine toward maize plants. Front Chem 3:61. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2015.00061
Oliveira CR, Domingues CE, de Melo NF, Roat TC, Malaspina O, Jones-Costa M, Silva-Zacarin EC, Fraceto LF (2019a) Nanopesticide based on botanical insecticide pyrethrum and its potential effects on honeybees. Chemosphere 236:124282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019a.07.013
Oliveira CR, Garcia TD, Franco-Belussi L, Salla RF, Souza BFS, de Melo NFS, Irazusta SP, Jones-Costa M, Silva-Zacarin ECM, Fraceto LF (2019b) Pyrethrum extract encapsulated in nanoparticles: Toxicity studies based on genotoxic and hematological effects in bullfrog tadpoles. Environ Pollut 253:1009–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.037
Pandey G (2018) Challenges and future prospects of agri-nanotechnology for sustainable agriculture in India. Environ Technol Innov 11:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.06.012
Pandey A, Srivastava S, Aggarwal N, Srivastava C, Adholeya A, Kochar M (2020) Assessment of the pesticidal behaviour of diacyl hydrazine-based ready-to-use nanoformulations. Chem Biol Technol Agric 7(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-020-0177-9
Papanikolaou NE, Kalaitzaki A, Karamaouna F, Michaelakis A, Papadimitriou V, Dourtoglou V, Papachristos DP (2018) Nano-formulation enhances insecticidal activity of natural pyrethrins against Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and retains their harmless effect to non-target predators. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(11):10243–10249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8596-2
Pascoli M, Jacques MT, Agarrayua DA, Avila DS, Lima R, Fraceto LF (2019) Neem oil based nanopesticide as an environmentally-friendly formulation for applications in sustainable agriculture: an ecotoxicological perspective. Sci Total Environ 677:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.345
Peng F, Wang X, Zhang W, Shi X, Cheng C, Hou W, Lin X, Xiao X, Li J (2022) Nanopesticide formulation from pyraclostrobin and graphene oxide as a nanocarrier and application in controlling plant fungal pathogens. Nanomaterials 12(7):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071112
Petrovici A, Strungaru SA, Nicoara M, Robea MA, Solcan C, Faggio C (2020) Toxicity of deltamethrin to zebrafish gonads revealed by cellular biomarkers. J Mar Sci Eng 8(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020073
Pho QH, Losic D, Ostrikov K, Tran NN, Hessel V (2020) Perspectives on plasma-assisted synthesis of N-doped nanoparticles as nanopesticides for pest control in crops. React Chem Eng 5:1374–1396. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RE00069H
Plhalova L, Blahova J, Divisova L, Enevova V, Casuscelli di Tocco F, Faggio C, Tichy F, Vecerek V, Svobodova Z (2018) The effects of subchronic exposure to NeemAzal T/S on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chem Ecol 34(3):199–210. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2017.1420176
Pradhan S, Roy I, Lodh G, Patra P, Choudhury SR, Samanta A, Goswami A (2013) Entomotoxicity and biosafety assessment of PEGylated acephate nanoparticles: a biologically safe alternative to neurotoxic pesticides. J Environ Sci Health B 48(7):559–569. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2013.774891
Prado-Audelo D, Luisa M, Bernal-Chávez SA, Gutiérrez-Ruíz SC, Hernández-Parra H, Kerdan IG, Reyna-González JM, Sharifi-Rad J, Leyva-Gómez G (2022) Stability phenomena associated with the development of polymer-based nanopesticides. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5766199
Preisler AC, Pereira AE, Campos EV, Dalazen G, Fraceto LF, Oliveira HC (2020) Atrazine nanoencapsulation improves pre-emergence herbicidal activity against Bidens pilosa without enhancing long-term residual effect on Glycine max. Pest Manag Sci 76(1):141–149. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5482
Qi SY, Xu XL, Ma WZ, Deng SL, Lian ZX, Yu K (2022) Effects of organochlorine pesticide residues in maternal body on infants. Front Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.890307
Rabea EI, Badawy ME, Rogge TM, Stevens CV, Höfte M, Steurbaut W, Smagghe G (2005) Insecticidal and fungicidal activity of new synthesized chitosan derivatives. Pest Manag Sci 61(10):951–960. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1085
Radovanović TB, Gavrilović BR, Petrović TG, Despotović SG, Gavrić JP, Kijanović A, Mirč M, Kolarov NT, Faggio C, Prokić MD (2021) Impact of desiccation pre-exposure on deltamethrin-induced oxidative stress in Bombina variegata juveniles. Comp Biochem Physiol Part c: Toxicol Pharmacol 250:109191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109191
Rai M, Ingle A (2012) Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(2):287–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3969-4
Rajput V, Minkina T, Mazarji M, Shende S, Sushkova S, Mandzhieva S, Burachevskaya M, Chaplygin V, Singh A, Jatav H (2020) Accumulation of nanoparticles in the soil-plant systems and their effects on human health. Ann Agric Sci 65(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2020.08.001
Rashidian G, Lazado CC, Mahboub HH, Mohammadi-Aloucheh R, Prokić MD, Nada HS, Faggio C (2021) Chemically and green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles alter key immunological molecules in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) skin mucus. Int J Mol Sci 22(6):3270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063270
Raza A, Razzaq A, Mehmood SS, Zou X, Zhang X, Lv Y, Xu J (2019) Impact of climate change on crops adaptation and strategies to tackle its outcome: a review. Plants 8(2):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8020034
Reig CS, Lopez AD, Ramos MH, Ballester VAC (2014) Nanomaterials: a map for their selection in food packaging applications. Packag Technol Sci 27(11):839–866. https://doi.org/10.1002/pts.2076
Rocha AG, Oliveira BMS, Melo CR, Sampaio TS, Blank AF, Lima AD, Nunes RS, Araújo APA, Cristaldo PF, Bacci L (2018) Lethal effect and behavioral responses of leaf-cutting ants to essential oil of Pogostemon cablin (Lamiaceae) and its nanoformulation. Neotrop Entomol 47(6):769–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-018-0615-6
Roy A, Sharma A, Yadav S, Jule LT, Krishnaraj R (2021) Nanomaterials for remediation of environmental pollutants. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1764647
Saha S, Chukwuka AV, Mukherjee D, Patnaik L, Nayak S, Dhara K, Saha NC, Faggio C (2021) Chronic effects of diazinon® exposures using integrated biomarker responses in freshwater walking catfish Clarias batrachus. Appl Sci 11(22):10902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210902
Sahayaraj K (2014) Novel biosilver nanoparticles and their biological utility: an overview. Int J Pharm 4(1):26–39
Sahayaraj K, Rajesh S (2011) Bionanoparticles: synthesis and antimicrobial applications. Sci against Microbial Pathogens: Commun Curr Res Technol Adv 23:228–244
Saini P, Gopal M, Kumar R, Gogoi R (2015) Residue, dissipation, and safety evaluation of pyridalyl nanoformulation in Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus [L.] Moench). Environ Monit Assess 187(3):123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4361-5
Sankar MV, Abideen S (2015) Pesticidal effect of green synthesized silver and lead nanoparticles using Avicennia marina against grain storage pest Sitophilus oryzae. Int J Nanomater Biostruct 5(3):32–39
Saratale RG, Karuppusamy I, Saratale GD, Pugazhendhi A, Kumar G, Park Y, Ghodake GS, Bharagava RN, Banu JR, Shin HS (2018) A comprehensive review on green nanomaterials using biological systems: recent perception and their future applications. Colloids Surf B 170:20–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.045
Sarkar MR, Rashid MHO, Rahman A, Kafi MA, Hosen MI, Rahman MS, Khan MN (2022) Recent advances in nanomaterials based sustainable agriculture: An overview. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 18:100687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100687
Shakil NA, Singh MK, Pandey A, Kumar J, Pankaj Parmar VS, Singh MK, Pandey RP, Watterson AC (2010) Development of poly (ethylene glycol) based amphiphilic copolymers for controlled release delivery of carbofuran. J Macromol Sci Pure Appl Chem 47(3):241–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601320903527038
Sharma S, Dar OI, Singh K, Kaur A, Faggio C (2021a) Triclosan elicited biochemical and transcriptomic alterations in Labeo rohita larvae. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 88:103748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2021a.103748
Sharma S, Iqbal Dar O, Andotra M, Sharma S, Kaur A, Faggio C (2021b) Environmentally relevant concentrations of Triclosan induce cyto-genotoxicity and biochemical alterations in the hatchlings of Labeo rohita. Appl Sci 11(21):10478. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110478
Shekhar S, Sharma S, Kumar A, Taneja A, Sharma B (2021) The framework of nanopesticides: a paradigm in biodiversity. Adv Mater 2(20):6569–6588. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00329A
Shoaib A, Waqas M, Elabasy A, Cheng X, Zhang Q, Shi Z (2018) Preparation and characterization of emamectin benzoate nanoformulations based on colloidal delivery systems and use in controlling Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). RSC Adv 8(28):15687–15697. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01913D
Simonin M, Colman BP, Tang W, Judy JD, Anderson SM, Bergemann CM, Rocca JD, Unrine JM, Cassar N, Bernhardt ES (2018) Plant and microbial responses to repeated Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide exposures under different fertilization levels in an agro-ecosystem. Front Microbiol 9:1769. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01769
Song S, Wang Y, Xie J, Sun B, Zhou N, Shen H, Shen J (2019) Carboxymethyl chitosan modified carbon nanoparticle for controlled emamectin benzoate delivery: improved solubility, pH-responsive release, and sustainable pest control. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(37):34258–34267. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b12564
Stadler T, Lopez Garcia GP, Gitto JG, Buteler M (2017) Nanostructured alumina: biocidal properties and mechanism of action of a novel insecticide powder. Bull Insectol 70(1):17–25
Stara A, Bellinvia R, Velisek J, Strouhova A, Kouba A, Faggio C (2019a) Acute exposure of common yabby (Cherax destructor) to the neonicotinoid pesticide. Sci Total Environ 665:718–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.202
Stara A, Kubec J, Zuskova E, Buric M, Faggio C, Kouba A, Velisek J (2019b) Effects of S-metolachlor and its degradation product metolachlor OA on marbled crayfish (Procambarus virginalis). Chemosphere 224:616–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.187
Stara A, Pagano M, Capillo G, Fabrello J, Sandova M, Albano M, Zuskova E, Velisek J, Matozzo V, Faggio C (2020) Acute effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on Mytilus galloprovincialis: a case study with the active compound thiacloprid and the commercial formulation calypso 480 SC. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 203:110980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110980
Stara A, Pagano M, Albano M, Savoca S, Di Bella G, Albergamo A, Koutkova Z, Sandova M, Velisek J, Fabrello J, Matozzo V, Faggio C (2021) Effects of long-term exposure of Mytilus galloprovincialis to thiacloprid: a multibiomarker approach. Environ Pollut 289:117892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117892
Sundström JF, Albihn A, Boqvist S, Ljungvall K, Marstorp H, Martiin C, Nyberg K, Vågsholm I, Yuen J, Magnusson U (2014) Future threats to agricultural food production posed by environmental degradation, climate change, and animal and plant diseases—a risk analysis in three economic and climate settings. Food Secur 6(2):201–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-014-0331-y
Tan W, Gao Q, Deng C, Wang Y, Lee WY, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2018) Foliar exposure of Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide to basil (Ocimum basilicum): variety-dependent copper translocation and biochemical responses. J Agric Food Chem 66(13):3358–3366. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00339
Tang C, Li Y, Pun J, Osman ASM, Tam KC (2019) Polydopamine microcapsules from cellulose nanocrystal stabilized Pickering emulsions for essential oil and pesticide encapsulation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 570:403–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.03.049
Vali S, Majidiyan N, Yalsuyi AM, Vajargah MF, Prokić MD, Faggio C (2022) Ecotoxicological effects of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) on parturition time, survival rate, reproductive success and blood parameters of adult common molly (Poecilia sphenops) and their larvae. Water 14(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020144
Vasseghian Y, Arunkumar P, Joo SW, Gnanasekaran L, Kamyab H, Rajendran S, Balakrishnan D, Chelliapan S, Klemeš JJ (2022) Metal-organic framework-enabled pesticides are an emerging tool for sustainable cleaner production and environmental hazard reduction. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133966
Vignardi CP, Muller EB, Tran K, Couture J, Means JC, Murray J, Ortiz C, Keller AA, Sanchez NS, Lenihan HS (2020) Conventional and nano-copper pesticide are equally toxic to the estuarine amphipod Leptocheirus plumulosus. Aquat Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105481
Vryzas Z (2018) Pesticide fate in soil-sediment-water environment in relation to contamination preventing actions. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 4:5–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2018.03.001
Walker GW, Kookana RS, Smith NE, Kah M, Doolette CL, Reeves PT, Navarro DA (2017) Ecological risk assessment of nano-enabled pesticides: a perspective on problem formulation. J Agric Food Chem 66(26):6480–6486. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02373
Walker GW, Kookana RS, Smith NE, Kah M, Doolette CL, Reeves PT, Lovell W, Anderson DJ, Turney TW, Navarro DA (2018) Ecological risk assessment of nano-enabled pesticides: a perspective on problem formulation. J Agric Food Chem 66(26):6480–6486. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02373
Wang Z, Yue L, Dhankher OP, Xing B (2020) Nano-enabled improvements of growth and nutritional quality in food plants driven by rhizosphere processes. Environ Int 142:105831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105831
Wang D, Saleh NB, Byro A, Zepp R, Sahle-Demessie E, Luxton TP, Ho KT, Burgess RM, Flury M, White JC, Su C (2022) Nano-enabled pesticides for sustainable agriculture and global food security. Nat Nanotechnol 17(4):347–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01082-8
Wu H, Li Z (2022) Recent advances in nano-enabled agriculture for improving plant performance. Crop J 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.06.002
Xiang Y, Zhang G, Chi Y, Cai D, Wu Z (2017) Fabrication of a controllable nanopesticide system with magnetic collectability. Chem Eng J 328:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.046
Yalsuyi AM, Vajargah MF, Hajimoradloo A, Galangash MM, Prokić MD, Faggio C (2021) Evaluation of behavioral changes and tissue damages in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) after exposure to the herbicide glyphosate. Vet Sci 8(10):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100218
Yang FL, Li XG, Zhu F, Lei CL (2009) Structural characterization of nanoparticles loaded with garlic essential oil and their insecticidal activity against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst,) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J Agric Food Chem 57(21):10156–10162. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9023118
Ye X, Liu M, Zhao N, Xiao C, Xu H, Jia J (2022) Targeted delivery of emamectin benzoate by functionalized polysuccinimide nanoparticles for the flowering cabbage and controlling Plutella xylostella. Pest Manag Sci 78(2):758–769. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6689
Yearla SR, Padmasree K (2016) Exploitation of subabul stem lignin as a matrix in controlled release agrochemical nanoformulations: a case study with herbicide diuron. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(18):18085–18098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6983-8
Yu M, Sun C, Xue Y, Liu C, Qiu D, Cui B, Zhang Y, Cui H, Zeng Z (2019) Tannic acid-based nanopesticides coating with highly improved foliage adhesion to enhance foliar retention. RSC Adv 9(46):27096–27104. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA05843E
Yusefi-Tanha E, Fallah S, Rostamnejadi A, Pokhrel LR (2020) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) as a novel nanofertilizer: Influence on seed yield and antioxidant defense system in soil grown soybean (Glycine max cv. Kowsar). Sci Total Environ 738:140240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140240
Zahir AA, Bagavan A, Kamaraj C, Elango G, Rahuman AA (2012) Efficacy of plant-mediated synthesized silver nanoparticles against Sitophilus oryzae. J Biopestic 5:95–102
Zhao L, Huang Y, Hannah-Bick C, Fulton AN, Keller AA (2016) Application of metabolomics to assess the impact of Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide on the nutritional value of lettuce (Lactuca sativa): enhanced Cu intake and reduced antioxidants. NanoImpact 3:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2016.08.005
Zhao L, Hu Q, Huang Y, Fulton AN, Hannah-Bick C, Adeleye AS, Keller AA (2017a) Activation of antioxidant and detoxification gene expression in cucumber plant s exposed to a Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide. Environ Sci Nano 4(8):1750–1760. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EN00358G
Zhao L, Hu Q, Huang Y, Keller AA (2017b) Response at genetic, metabolic, and physiological levels of maize (Zea mays) exposed to a Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(9):8294–8301. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01968
Zhao L, Huang Y, Adeleye AS, Keller AA (2017c) Metabolomics reveals Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide-activated anti-oxidative pathways and decreased beneficial antioxidants in spinach leaves. Environ Sci Technol 51(17):10184–10194. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02163
Zhao X, Cui H, Wang Y, Sun C, Cui B, Zeng Z (2017d) Development strategies and prospects of nano-based smart pesticide formulation. J Agric Food Chem 66(26):6504–6512. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02004
Zheng L, Hong F, Lu S, Liu C (2005) Effect of nano-TiO2 on strength of naturally aged seeds and growth of spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 104(1):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1385/bter:104:1:083
Zulfiqar F, Navarro M, Ashraf M, Akram NA, Munné-Bosch S (2019) Nanofertilizer use for sustainable agriculture: advantages and limitations. Plant Sci 289:110270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110270
Funding
This study was supported by Postdoctoral fellowship for Maharajan Kannan and the author thank Biology Institute, Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, China, for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KM contributed to conceptualization, methodology, literature survey, writing—original draft, and supervision; BN contributed to literature survey and writing—original draft; JS contributed to methodology, literature survey, and writing—original draft; GZ contributed to literature survey and writing—review and editing; DH was involved in literature survey and writing—original draft; YZ performed writing—review and editing, and supervision; MR performed writing—review and editing; CF performed writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Xu Han.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kannan, M., Bojan, N., Swaminathan, J. et al. Nanopesticides in agricultural pest management and their environmental risks: a review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 10507–10532 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04795-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04795-y