Abstract
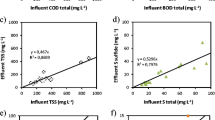
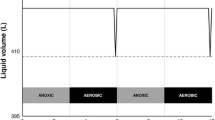
Effluent from full-scale and bench-scale upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactors (UASBRs) was aerated by surface aerator. The monitoring parameters used for process were oxidation reduction potential (ORP), dissolved oxygen (DO), chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Experiments were conducted on effluents of bench-scale 56-L UASB reactor as well as on the effluents from four UASB-based sewage treatment plants (STPs) of capacities ranging from 34 to 70 ML/d (million liters per day). The linear relationship between DO and ORP indicates the sensitivity of ORP. The rate of DO transfer depends on ORP, DO deficit, nature and concentration of BOD or COD. The ORP values increased with aeration time indicating improvement in redox status. The oxygen demand of anaerobically treated effluent proceeds in three-stage initial S-BOD exertion followed by CBOD exertion and subsequently NBOD exertion. The optimum condition for BOD, COD and sulfide removal was 120–140 min characterized by DO content of 4–5 mg/L. Sulfides removal rate of 80% and BOD of 30 mg/L desired discharge standards were obtained.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Bastos RKX, Calijuri ML, Bevilacqua PD, Rios EN, Dias EHO (2010) Post-treatment of UASB reactor effluent in waste stabilization ponds and in horizontal flow constructed wetlands: a comparative study in pilot scale in Southeast Brazil. Water Sci Technol 61(4):995–1002
Bastos RKX, Rios EN, Bevilacqua PD, Andrade RC (2011) UASB-polishing ponds design parameters: contributions from a pilot scale study in southeast Brazil. Water Sci Technol 63(6):1276–1281
Bressani-Ribeiro T, Almeida PGS, Volcke EIP, Chernicharo CAL (2018) Trickling filters following anaerobic sewage treatment: state of the art and perspectives. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 4:1721–1738
Degremont (1979) Water treatment handbook, 5th edn. Wiley, New York
Draaijer H, Maas JAW, Schaapman JE, Khan A (1992) Performance of the 5 MLD UASB reactor for sewage treatment at Kanpur, India. Water Sci Technol 25(7):123–133
Heduit A, Thevenot DR (1989) Relation between redox potential and oxygen levels in activated—sludge reactors. Water Sci Technol 21:947–956
Khan AA, Gaur Rubia Z, Mehrotra I, Diamantis V, Lew B, Kazmi AA (2014) Performance assessment of different STPs based on UASB followed by aerobic post treatment systems. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:43
Lie E, Welander T (1994) Influence of dissolved oxygen and oxidation–reduction potential on the denitrification rate of activated sludge. Water Sci Technol 30(6):91–100
Machdar I, Matsuura N, Kodera H, Ohashi A (2014) Prospective combined system of UASB and DHS reactor for the treatment of domestic wastewater in Jakarta. J Water Environ Technol 12(6):459–468
Maharjan N, Nomoto N, Tagawa T, Okubo T, Uemura S, Khalil N, Hatamoto M, Yamaguchi T, Harada H (2018) Assessment of UASB–DHS technology for sewage treatment: a comparative study from a sustainability perspective. Environ Technol 6:1–8
Mason IG, Mclachlan RI, Gerard DT (2006) A double exponential model for biochemical oxygen demand. Bioresour Technol 97(2):273–282
Mohapatra DP, Ghangrekar MM, Mitra A, Brar SK (2012) Sewage treatment in integrated system of UASB reactor and duckweed pond and reuse for aquaculture. Environ Technol 33(10–12):1445–1453
Ramalho RS (1983) Introduction to wastewater treatment processes, 2nd edn. Academic press, New York
Sato N, Okubo T, Onodera T, Ohashi A, Harada H (2006) Prospects for a self-sustainable sewage treatment system: a case study on full-scale UASB system in India’s Yamuna River Basin. J Environ Manag 80(3):198–207
Sawyer CN, Mccarty PL, Parkin GF (2000) Chemistry for environmental engineering, 4th edn. Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, Delhi
Singh KS, Harada H, Viraraghavan T (1996) Low-Strength wastewater treatment by a UASB reactor. Bioresour Technol 55:187–194
Tawfik A, Klapwijk B, El- Gohary F, Lettinga G (2005) Potentials of using a rotating biological contactor (RBC) for post-treatment of anaerobically pre-treated domestic wastewater. Biochem Eng J 25:89–98
Torres P, Foresti E (2001) Domestic sewage treatment in pilot system composed of UASB and SBR reactors. Water Sci Technol 44(4):247–253
Van Haandel AC, Lettinga G (1994) Anaerobic sewage treatment—a practical guide for regions with a hot climate. Wiley, Chichester
Von Sperling M, Freire VH, de Lemos Chernicharo CA (2001) Performance evaluation of a UASB-activated sludge system treating municipal wastewater. Water Sci Technol 43(11):323–328
Walia R, Mehrotra I, Kumar P (2011) Evaluation of polishing of the effluent from UASB reactor by diffusers. Int J Environ Waste Manag 9(1–2):154–168
Acknowledgements
The first author received scholarship from MHRD, New Delhi, for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walia, R., Kumar, P. & Mehrotra, I. Post-treatment of effluent from UASB reactor by surface aerator. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 983–992 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02351-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02351-1