Abstract
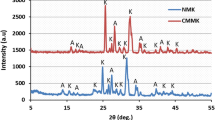
A binary mixture of humic acid and geothite was prepared and used to modify kaolinite to produce geothite–humic acid (GHA)-modified kaolinite adsorbent useful for the adsorption of Pb2+, Cd2+, Zn2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ from Single and Quinary (5) metal ion systems. The cation exchange capacity (CEC) and specific surface area of GHA-modified kaolinite clay adsorbent were found to be 40 meq/100 g and 13 m2/g, respectively, with the CEC being five times that of raw kaolinite clay (7.81 meq/100 g). The Langmuir–Freundlich equilibrium isotherm model gave better fit to experimental data as compared with other isotherm models. In Quinary metal ion system, the presence of Zn2+ and Cu2+ appears to have an antagonistic effect on the adsorption of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+, while the presence of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ shows a synergistic effect on the adsorption of Zn2+ and Cu2+. The GHA-modified kaolinite showed strong preference for the adsorption of Pb2+ in both metal ion systems. Brouers–Weron–Sotolongo (BWS) kinetic model gave better fit to kinetic data compared with other kinetic models used. Data from BWS kinetic model indicate that adsorption of metal ions onto GHA-modified adsorbent in both metal ion systems followed strictly, diffusion-controlled mechanism with adsorption reaction proceeding to 50 % equilibrium in <2 min in the Single metal ion system and <1 min in the Quinary metal ion system. Adsorption of metal ions onto GHA-modified kaolinite is fairly spontaneous and endothermic in nature in both metal ion systems although the rate of metal ion uptake and spontaneity of reaction are reduced in the Quinary metal ion system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale KO, Unuabonah EI, Olu-Owolabi BI (2005) Adsorption of some heavy metal ions on sulfate- and phosphate-modified Kaolin. Appl Clay Sci 29:145–148
Adebowale KO, Unuabonah EI, Olu-Owolabi BI (2006) The effect of some operating variables in the adsorption of lead and cadmium ions unto modified Kaolin clay. J Hazard Mater B134:130–139
Akpa OM, Unuabonah EI (2011) Small-sample corrected Akaike information criterion: an appropriate statistical tool for ranking of adsorption isotherm models. Desalination 272(1–3):20–26
Alekseeva TV, Zolotareva BN (2013) Fractionation of humic acids upon adsorption on Montmorillonite and Palygorskite. Eurasian Soil Sci 46:622–634
Aliyu AA, Aluko BA, Biliaminu KO (1996) Priority investment projects in the solid minerals sector. Raw materials Research and Development Council, Abuja, pp 12–14
Anderson O (1981) Chelation of cadmium. Environ Health Perspect 54:249–266
Apak R (2002) Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soil surfaces and similar substances. In Encyclopedia of surface & colloid science. Marcel Dekker, New York
Backes CA, McLaren RG, Rate AW (1995) Kinetics of cadmium and cobalt desorption from Iron and manganese oxides. J Hazard Mater B95:251–273
Bayat B (2002) Comparative study of adsorption properties of Turkish fly ashes I. The case of nickel(II), copper(II) and zinc(II). J Hazard Mater B10:285–300
Bhattacharyya KG, Gupta SS (2009) Calcined tetrabutylammonium kaolinite and montmorillonite and adsorption of Fe(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) from solution. Appl Clay Sci 46:216–221
Bhattacharyya KG, Gupta SS (2011) Removal of Cu(II) by natural and acid-activated clays: an insight of adsorption isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamics. Desalination 272:66–75
Buffle J (1985) Complexation reactions in aquatic systems: an analytical approach. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Chapman HD (1965) Cation exchange capacity. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis Part 2. Number 9 in the series Agronomy: American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, p 891–901
Choppin GR (1992) The role of natural organics in Radionuclide migration in natural aquifier systems. Radiochim Acta 113:58–59
Davies JA (1982) Adsorption of natural dissolved organic matter at the oxide/water interface. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:2381–2393
Echeverria J, Indurain J, Churio E, Garrido J (2003) Simultaneous effect of pH, temperature, ionic strength, and initial concentration on the retention of Ni on illite. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects 218:175–187
Gaspard S, Altenor S, Passe-Coutrin N, Ouensanga A, Brouers F (2006) Parameters from a new kinetic equation to evaluate activated carbons efficiency for water treatment. Water Res 40:3467–3477
Gimenez J, Martinez M, de Pablo J, Rovira M, Duro L (2007) Arsenic sorption onto natural hematite, magnetite and geothite. J Hazard Mater 141:575–580
Glover LJ II, Eick MJ, Brady PV (2002) Desorption kinetics of cadmium and lead from goethite: influence of time and organic acids. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:797–804
Grossi PR, Sparks DL (1994) Rapid kinetics of Cu(II) adsorption/desorption on goethite. Environ Sci Technol 28:1422–1429
Gupta SS, Bhattacharyya KG (2008) Immobilization of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) ions on Kaolinite and Montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium. J Environ Manag 87:46–58
Hiraide M (1992) Heavy metal complexed with humic substance in fresh water. Anal Sci 8:453–459
Ho Y-S (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater B136:681–689
Jalali M, Moradi F (2013) Competitive sorption of Cd, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn in polluted and unpolluted calcacerous soils. Environ Monit Assess 185:8831–8846
Jiang M, Wang Q, Jin X, Chen Z (2009) Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using modified and unmodified Kaolinite clay. J Hazard Mater 170:332–339
Journey JS, Anderson RM, Essington ME (2010) The adsorption of 2-Ketogluconate by geothite. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:1119–1128
Jung J, Cho Y-H, Hahn P (1998) Comparative study of Cu2+ adsorption on geothite, hematite and kaolinite: mechanistic approach. Bull Korean Chem Soc 19:324–327
Lackovic K, Angove MJ, Wells JD, Johnson BB (2003) Modelling the adsorption og Cd(II) onto Muloorina illite and related clay minerals. J Colloids Interface Sci 257:31–40
McBride MB (1994) Environmental soil chemistry. Oxford University Press, New York
McCarthy JF, Czerwinski KR, Sanford WE, Jardine PM, Marsh JD (1998) Mobilization of transuranic radionuclides from disposal trenches by natural organic matter. J Contam Hydrol 30:49–77
Myers RT (1981) Rules of coordination number of metal ions. J Chem Educ 58(9):681
Olu-Owolabi BI, Popoola DB, Unuabonah EI (2010) Removal of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution by Bentonite clay modified with binary mixture of goethite and humic acid. Water Air Soil Pollut 211:459–474
Plavsic M, Cosovic B, Miletic S (1991) Comparison of the behaviours of copper, cadmium and lead in the presence of humic acid in sodium chloride solutions. Anal Chim Acta 255:15–21
Qi BC, Aldrich C (2008) Adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions with tobacco dust. Bioresour Technol 99:5595–5601
Ricordel S, Taha S, Cisse I, Dorange G (2001) Heavy metals removal by adsorption onto peanut husks carbon: characterization, kinetic study and modeling. Sep Purif Technol 24:389–401
Saada A, Gaboriau H, Cornu S, Bardot F, Villieras F, Croue JP (2003) Adsorption of humic acid onto a kaolinite clay studied by high-resolution argon adsorption volumetry. Clay Miner 38:433–443
Saito T, Koopal LK, van Riemsdijk WH, Nagasaki S, Tanaka S (2004) Adsorption of humic acid on goethite: isotherms, charge adjustments, and potential profiles. Langmuir 20:689–700
Salman M, El-Eswed B, Khalili F (2007) Adsorption of humic acid on bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 38:51–56
Sears GW (1956) Determination of specific surface area of colloidal silica by titration with sodium hydroxide. J Anal Chem 28:1981–1983
Srivastava P, Singh B, Angove MJ (2005) Competitive adsorption behavior of heavy metals on kaolinite. J Colloids Interface Sci 290:28–38
Swift RS (1996) Organic matter characterization. In: Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA, Johnston CT, Summer ME (eds) Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods, vol 3. Soil Science Society of America (SSSA) book series 5, p 1011–1020
Takahashi Y, Minai Y, Ambe S, Makide Y, Ambe F (1999) Comparison of adsorption behavior of multiple inorganic ions on kaolinite and silica in the presence of humic acid using the multitracer technique. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:815–836
Taty-Costodes VC, Faudue H, Porte C, Delacroix A (2003) Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions, from aqueous solutions, by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. J Hazard Mater 105:121–142
Tipping E, Rey-Castro C, Bryan SE, Hamilton-Taylor J (2002) Al(III) and Fe(III) binding by humic substances in freshwaters, and implications for trace metal speciation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:3211–3224
Unuabonah EI, Adebowale KO, Olu-Owolabi BI (2007) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of lead(II) ions onto phosphate-modified kaolinite clay. J Hazard Mater 144:386–395
Unuabonah EI, Gunter C, Weber J, Lubahn S, Taubert A (2013) Hybrid clay: a new highly efficient Adsorbent for water treatment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1(8):966–973
Wang K, Xing B (2005) Structural and sorption characteristics of adsorbed humic acid on clay minerals. J Environ Qual 34:342–349
Wu J, West LJ, Stewart DI (2002) Effect of humic substances on Cu(II) solubility in kaolin-sand soil. J Hazard Mater B94:223–238
Yavuz O, Altunkaynak Y, Guzel F (2003) Removal of copper, cobalt and manganese from aqueous solution by kaolinite. Water Res 37:948–952
Zhao X-Q, Dong L-J, Cao Y, Mo S-J, Yi J-J, Xu Q-H (2013) Exfoliated LDHs modified with organic silicon reagent and their adsorption to metal ions from water. Chin J Inorg Chem 29(4):817–825
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate with thanks the Department of Chemistry, University of Ibadan and the Department of Chemical Sciences, Redeemer’s University for provision of Laboratory space and scientific equipment for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unuabonah, E.I., Olu-Owolabi, B.I. & Adebowale, K.O. Competitive adsorption of metal ions onto goethite–humic acid-modified kaolinite clay. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 1043–1054 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-0938-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-0938-y