Abstract
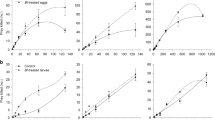
Bioinsecticides are being increasingly used to protect vegetable crops against herbivores, but data on the side effects of such strategy on the third trophic level are still required. We investigated the influence of the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD-1 strain and of the commercial bioinsecticide Agree® on the biological aspects of the predator Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) when feeding on Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae)-infected larvae. On average, infected larvae were consumed more often than the non-infected larvae throughout the predator nymphal development, and no effect on nymph survival was observed. Population growth parameters (R 0, r m, and λ) resulting from the fertility life tables did not differ among treatments. The results led to the conclusion that P. nigrispinus can be used in combination with the product Agree® or the strain HD-1 for the control of P. xylostella. The combined use of these control agents helps to maintain the balance of the ecosystem and contributes for the production of food for healthy human consumption.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves SB, Moraes SB (1998) Quantificação de inóculo de patógenos de insetos. In: Alves SB (ed) Controle microbiano de insetos. FEALQ, Piracicaba, pp 765–778
Brar SK, Verma M, Tyagi RD, Valéro JR (2006) Recent advances in downstream processing and formulations of Bacillus thuringiensis based pesticides. Process Biochem 41:323–342
Bravo A, Likitvivatanavong S, Gill SS, Soberón M (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: a story of a successful bioinsecticide. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:423–431
Carvalho VFP, Vacari AM, Pomari AF, De Bortoli CP, Ramalho DG, De Bortoli SA (2012) Interaction between the predator Podisus nigrispinus (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) and the entomopathogenic bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis. Environ Entomol 41:1454–1461
Castelo Branco M, França FH, Pontes LA, Amaral PST (2003) Avaliação da suscetibilidade a inseticidas em populações da traça-das-crucíferas de algumas áreas do Brasil. Hortic Bras 21:49–52
Corrêa-Ferreira BS, Moscardi F (1995) Seasonal occurrence and host spectrum of egg parasitoids associated with soybean stink bugs. Biol Control 5:196–202
De Bortoli SA, Otuka AK, Vacari AM, Martins MIEG, Volpe HXL (2011) Comparative biology and production costs of Podisus nigrispinus (Hempitera: Pentatomidae) when fed different types of prey. Biol Control 58:127–132
De Bortoli SA, Polanczyk RA, Vacari AM, De Bortoli CP, Duarte RT (2013) Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus, 1758): tactics for integrated pest management in Brassicaceae. In: Soloneski S, Larramendy M (eds) Weed and pest control conventional and new challenges. Intech, New York, pp 31–52
Evangelista Júnior WS, Manoel GC, Gondim Júnior MGC, Torres JB, Marques EJ (2004) Fitofagia de Podisus nigrispinus em algodoeiro e plantas daninhas. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 39:413–420
Ferré JM, van Rie J (2002) Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 47:501–533
Furlong BE, Wright DJ (1994) Examination of stability of resistance and cross resistance patterns to acylurea insect regulatorsin field populations of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella, from Malaysia. Pest Manag Sci 42:315–326
Glare TR, O’Callaghan M (2000) Bacillus thuringiensis: Biology, ecology and safety. Wiley, New York, p 350
González-Zamora JE, Camúñez S, Avilla C (2007) Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxins on developmental and reproductive characteristics of the predator Orius albidipennis (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) under laboratory conditions. Environ Entomol 36:1246–1253
Gravena S, Lara FM (1982) Controle integrado de pragas e receituário agronômico. In: Graziano Neto F (ed) Receituário agronômico. Agroedições, São Paulo, pp 123–161
Haverty MI (1982) Sensitivity of selected non target insects to the carrier of Dipel 4L in the laboratory. Environ Entomol 11:337–338
Hernandez-Martinez P, Navarro-Cerrillo G, Caccia S, De Maagd AR, Moar WJ, Ferré J, Escriche B, Herrero S (2010) Constitutive activation of the midgut response to Bacillus thuringiensis in Bt-resistant Spodoptera exigua. PloS ONE 5(9), e12795. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012795
Krebs CJ (1994) Ecology: the experimental analysis of distribution and abundance. Harper & Row, New York, p 801
Lin Q, Jin F, Hu Z, Chen H, Yin F, Li Z, Dong X, Zhang D, Ren S, Feng X (2013) Transcriptome analysis of chlorontraniliprole resistance development in the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella. PLoS ONE 8(8), e72314. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072314
Magalhães GO, Vacari AM, Laurentis VL, De Bortoli SA, Polanczyk RA (2015) Interactions of Bacillus thuringiensis and the predatory stink bug Podisus nigrispinus to control Plutella xylostella. J Appl Entomol 139:123–133
Maia AHN, Luiz AJB, Campanhola C (2000) Statistical inference on associated fertility life table parameters using Jackknife technique: computational aspects. J Econ Entomol 3:511–518
Medeiros RS, Ramalho FS, Lemos WP, Zanuncio JC (2000) Age-dependent fecundity and life-fertility tables for Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Het., Pentatomidae). J Appl Entomol 124:319–324
Mohaghegh J, De Clercq P, Tirry L (2000) Toxicity of selected insecticides to the spined soldier bug, Podisus maculiventris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Biocontrol Sci Techn 10:33–40
Nascimento ML, Capalbo DF, Moraes GJ, De Nardo EA, Maia AHN, Oliveira RCAL (1998) Effect of a formulation of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner var. kurstaki on Podisus nigrispinus Dallas (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae: Asopinae). J Invertebr Pathol 72:178–180
Perez CJ, Shelton AM (1997) Resistance of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) to Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner in Central America. J Econ Entomol 90:87–93
Peter G, Sengonca C (1992) Enhancement of the solitary parasitoid Apanteles rubecula March. (Hym. Braconidae) in cabbage fields cultivating different intercroppings. DGaaE 8:93–98
Romeis J, Meissle M, Bigler F (2006) Transgenic crops expressing Bacillus thuringiensis toxins and biological control. Nat Biotecnol 24:63–71
Saini ED (1985) Identification of the eggs of pentatomids (Heteroptera) found in soybean crops. Rev Appl Entomol 73:782–783
SAS Institute (2002) SAS/STAT: User’s Guide, version 9.0. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, p 5121
Silva-Torres CSA, Pontes IVAF, Torres JB, Barros R (2010) New records of natural enemies of Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) in Pernambuco, Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 39:835–838
Silva-Torres CSA, Torres JB, Barros R (2011) Can cruciferous agroecosystems grown under variable conditions influence biological control of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae)? Biocontol Sci Techn 21:625–641
Southwood TER (1978) Ecological methods. Chapman and Hall, London, p 524
Tabashnik BE (1994) Evolution of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 39:47–79
Tian JC, Wang XP, Long LP, Romeis J, Naranjo SE, Hellmich RL, Wang P, Earle ED, Shelton AM (2013) Bt crops producing Cry1Ac, Cry2Ab and Cry1F do not harm the green lacewing, Chrysoperla rufilabris. PloS ONE 8(3), e60125. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060125
Torres JB, Ruberson JR (2008) Interactions of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin in genetically engineered cotton with predatory heteropterans. Transgenic Res 17:345–354
Torres JB, Ruberson JR, Adang MJ (2006) Expression of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac protein in cotton plants, acquisition by pests and predators: a tritrophic analysis. Agric For Entomol 8:191–202
Vacari AM, Albergaria NMMS, Otuka AK, Dória HOS, Loureiro E, De Bortoli SA (2004) Seletividade de óleo de nim (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) sobre Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas, 1851) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Arq Inst Biol 71:190–194
Vacari AM, Otuka AK, De Bortoli SA (2007) Desenvolvimento de Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas, 1851) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) alimentado com lagartas de Diatraea saccharalis (Fabricius, 1794) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Arq Inst Biol 74:259–265
Vacari AM, De Bortoli SA, Goulart RM, Volpe HXL, Otuka AK, Veiga ACP (2013) Comparison of eggs, larvae, and pupae of Plutella xylostella as prey for Podisus nigrispinus. Ann Entomol Soc Am 106:235–242
Vivan LM, Torres JB, Veiga AFSL, Zanuncio JC (2002) Comportamento de predação e conversão alimentar de Podisus nigrispinus sobre a traça-do-tomateiro. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 37:581–587
Wright DJ, Iqbal M, Granero F, Ferré JA (1997) Change in a single midgut receptor in the diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella) is only part responsible for field resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. aizawai. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1814–1819
Xia Y, Lu Y, Shen J, Gao X, Qiu H, Li J (2014) Resistance monitoring for eight insecticides in Plutella xylostella in central China. Crop Protection 63:131–137
Zago HB, Siqueira HAA, Pereira EJG, Picanço MC, Barros R (2014) Resistance and behavioural response of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) populations to Bacillus thuringiensis formulations. Pest Manag Sci 70:488–495
Zalucki MP, Shabbir A, Silva R, Adamson D, Shu-Sheng L, Furlong MJ (2012) Estimating the economic cost of one of the world’s major insect pests, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae): just how long is a piece of string? J Econ Entomol 105:1115–1129
Zanuncio JC (2002) Uma década de estudos com percevejos predadores: Conquistas e desafios. In: Parra JRP, Botelho PSM, Corrêa-Ferreira BS, Bento JMS (eds) Controle Biológico no Brasil: Parasitoides e predadores. Manole, São Paulo, pp 495–528
Zanuncio TV, Zanuncio ZC, Batalha VC, Santos GP (1993) Efeito da alimentação com lagartas de Bombyx mori e larvas de Musca domestica no desenvolvimento de Podisus nigrolimbatus (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Rev Bras Entomol 37:273–277
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Ítalo Delalibera Jr – ESALQ/USP
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 394 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magalhães, G.O., Vacari, A.M., DE Bortoli, C.P. et al. Interactions Between Bt-Bioinsecticides and Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), a Predator of Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Neotrop Entomol 44, 521–527 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-015-0314-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-015-0314-5