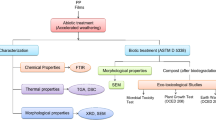
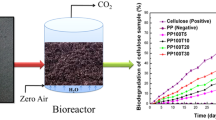
Abstract
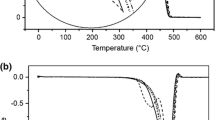
The present work studies the effects of abiotic pretreatment on the properties and biodegradability of the modified cobalt stearate pro-degradant filled polypropylene films, and on the eco-toxicity of their biodegraded products. Before abiotic pretreatment, their processability was confirmed by rheological studies. After abiotic pretreatment, FTIR revealed their carbonyl index increased on increasing the pro-degradant loading. Their GPC results showed significant decrease in molecular weight, thus indicating chain scission and intermediate formation. Their thermal stability also reduced as demonstrated by TGA. Their DSC and XRD analyses showed decreased crystallinity thereby indicating increased biodegradability. Their biodegradation was measured following ASTM D 5338, which showed a significant increase with abiotic pretreatment and the same was substantiated by GPC. The biodegradation kinetics followed Komilis model which showed that the degradation rate reached a maximum of 0.407–0.730% per day at 15–25th day. Readily hydrolysable carbon and its hydrolysis rate constant substantially enhanced with modified pro-degradant content. High readily hydrolyzable carbon rate constant caused the occurrence of a prominent growth phase. SEM also confirmed that the surface morphology of each film became increasingly rougher subsequent to both abiotic and biotic treatments, and with increasing pro-degradant loading. The eco-toxicity tests confirmed the nontoxicity of biodegraded products. The work thus illustrated that the films can have useful packaging applications.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASTM:
-
American Society for Testing and Materials
- CaSt:
-
Calcium stearate
- CEL:
-
Microcrystalline cellulose
- CFU:
-
Colony forming units
- CoSt:
-
Cobalt stearate
- CuSt:
-
Copper stearate
- DDR:
-
Draw-down ratio
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- DTA:
-
Differential thermal analysis
- DTG:
-
Differential themogravimetry
- FeSt:
-
Iron stearate
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- HDPE:
-
High-density polyethylene
- HT-GPC:
-
High-temperature gel permeation chromatography
- ISO:
-
International Organization for Standardization
- LDPE:
-
Low-density polyethylene
- LLDPE:
-
Linear low-density polyethylene
- MFI:
-
Melt flow index
- MgSt:
-
Magnesium stearate
- MnSt:
-
Manganese stearate
- OECD:
-
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
- PDI:
-
Polydispersity index
- PE:
-
Polyethylene
- PDI:
-
Polydispersity index
- PHA:
-
Poly(hydroxyalkanoates)
- PHB:
-
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)
- phr:
-
Parts per hundred of resin
- PLA:
-
Polylactic acid/polylactide
- PP:
-
Polypropylene
- RID:
-
Refractive index detector
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TG:
-
Thermogravimetry
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetric analysis
- TOC:
-
Total organic carbon
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- ZnSt:
-
Zinc stearate
- C :
-
Duration of lag phase during the initial phase of biodegradation before the onset of CO2 production
- C aq0 :
-
Initial mineralizable intermediate carbon (%)
- C m0 :
-
Initial moderately hydrolysable solid carbon (%)
- CO 2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- CO 2 (Th) :
-
Theoretical carbon dioxide
- C r0 :
-
Initial readily hydrolysable solid carbon (%)
- C s0 :
-
Initial slowly hydrolysable solid carbon (%)
- Da :
-
Dalton
- G' :
-
Storage modulus
- G" :
-
Loss modulus
- \(\Delta H_{c}\) :
-
Enthalpy of crystallization
- \(\Delta H_{f}\) :
-
Enthalpy of fusion
- k aq :
-
Rate constant for mineralizable water-soluble C-CO2
- k m :
-
Moderately first-order hydrolysis rate constant
- k r :
-
Readily first-order hydrolysis rate constant
- k s :
-
Slowly first-order hydrolysis rate constant
- \(\overline{{M_{n} }}\) :
-
Number average molecular weight
- \(\overline{{M_{w} }}\) :
-
Weighted average molecular weight
- MPa :
-
Mega Pascal
- T :
-
Absolute temperature (K)
- T c :
-
Crystallization temperature
- T g :
-
Glass transition temperature
- T i :
-
Initial degradation temperature
- T m :
-
Melting temperature
- \(T_{\max }\) :
-
Maximum degradation temperature
- T f :
-
Final degradation temperature
- X c :
-
Degree of crystallinity
References
Hejna A, Barczewski M, Kosmela P, Mysiukiewicz O, Aniśko J, Sulima P, Przyborowski JA, Saeb MR (2022) The impact of thermomechanical and chemical treatment of waste Brewers’ spent grain and soil biodegradation of sustainable mater-Bi-based biocomposites. Waste Manag 154:260–271
Song YK, Hong SH, Eo S, Shim WJ (2023) Fragmentation of nano-and microplastics from virgin-and additive-containing polypropylene by accelerated photooxidation. Environ Pollut 327:121590
Darwish MSA, Mostafa MH, Hussein LI, Abdaleem AH, Elsawy MA (2021) Preparation, characterization, mechanical and biodegradation behavior of polypropylene-chitosan/ZnO nanocomposite. Polym-Plast Technol Mater 60:1630–1640
Subramaniam M, Sharma S, Gupta A, Abdullah N (2018) Enhanced degradation properties of polypropylene integrated with iron and cobalt stearates and its synthetic application. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46028
Antelava A, Constantinou A, Bumajdad A, Manos G, Dewil R, Al-Salem SM (2020) Identification of commercial oxo-biodegradable plastics: study of UV induced degradation in an effort to combat plastic waste accumulation. J Polym Environ 28:2364–2376
Gioia C, Giacobazzi G, Vannini M, Totaro G, Sisti L, Colonna M, Marchese P, Celli A (2021) End of life of biodegradable plastics: composting versus Re/upcycling. Chemsuschem 14:4167–4175
Jain K, Bhunia H, Sudhakara Reddy M (2018) Degradation of polypropylene–poly-L-lactide blend by bacteria isolated from compost. Bioremed J 22:73–90
Xian Z-N, Yin C-F, Zheng L, Zhou N-Y, Xu Y (2023) Biodegradation of additive-free polypropylene by bacterial consortia enriched from the ocean and from the gut of Tenebrio molitor larvae. Sci Total Environ 892:164721
Wu Z, Shi W, Valencak TG, Zhang Y, Liu G, Ren D (2023) Biodegradation of conventional plastics: candidate organisms and potential mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 885:163908
Sable S, Ahuja S, Bhunia H (2020) Biodegradation kinetic modeling of acrylic acid-grafted polypropylene during thermophilic phase of composting. Iran Polym J 29:735–747
Rana AK, Thakur MK, Saini AK, Mokhta SK, Moradi O, Rydzkowski T, Alsanie WF, Wang Q, Grammatikos S, Thakur VK (2022) Recent developments in microbial degradation of polypropylene: integrated approaches towards a sustainable environment. Sci Total Environ 826:154056
Khosravi A, Fereidoon A, Khorasani MM, Naderi G, Ganjali MR, Zarrintaj P, Saeb MR, Gutiérrez TJ (2020) Soft and hard sections from cellulose-reinforced poly(lactic acid)-based food packaging films: a critical review. Food Packag Shelf Life 23:100429
Mandal DK, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK, Kumar A, Madhu G, Nando GB (2018) Biodegradation of pro-oxidant filled polypropylene films and evaluation of the ecotoxicological impact. J Polym Environ 26:1061–1071
Hayoune F, Chelouche S, Trache D, Zitouni S, Grohens Y (2020) Thermal decomposition kinetics and lifetime prediction of a PP/PLA blend supplemented with iron stearate during artificial aging. Thermochim Acta 690:178700
Ammala A, Bateman S, Dean K, Petinakis E, Sangwan P, Wong S, Yuan Q, Yu L, Patrick C, Leong KH (2011) An overview of degradable and biodegradable polyolefins. Progress Polym Sci 36:1015–1049
Fontanella S, Bonhomme S, Brusson J-M, Pitteri S, Samuel G, Pichon G, Lacoste J, Fromageot D, Lemaire J, Delort A-M (2013) Comparison of biodegradability of various polypropylene films containing pro-oxidant additives based on Mn, Mn/Fe or Co. Polym Degrad Stabil 98:875–884
Nguyen DM, Do TVV, Grillet A-C, Thuc HH, Thuc CNH (2016) Biodegradability of polymer film based on low density polyethylene and cassava starch. Inter Biodeter Biodegrad 115:257–265
Contat-Rodrigo L (2013) Thermal characterization of the oxo-degradation of polypropylene containing a pro-oxidant/pro-degradant additive. Polym Degrad Stabil 98:2117–2124
Al-Salem SM, Sultan HH, Karam HJ, Al-Dhafeeri AT (2019) Determination of biodegradation rate of commercial oxo-biodegradable polyethylene film products using ASTM D 5988. J Polym Res 26:157
Kalita NK, Bhasney SM, Mudenur C, Kalamdhad A, Katiyar V (2020) End-of-life evaluation and biodegradation of poly(lactic acid)(PLA)/polycaprolactone(PCL)/microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) polyblends under composting conditions. Chemosphere 247:125875
Arutchelvi J, Sudhakar M, Arkatkar A, Doble M, Bhaduri S, Uppara PV (2008) Biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene. Indian J Biotechnol 7:9–22
Mandal DK, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK, Chaudhari CV, Dubey KA, Varshney L (2018) Morphology, rheology and biodegradation of oxo-degradable polypropylene/polylactide blends. J Polym Eng 38:239–249
Sable S, Mandal DK, Ahuja S, Bhunia H (2019) Biodegradation kinetic modeling of oxo-biodegradable polypropylene/polylactide/nanoclay blends and composites under controlled composting conditions. J Environ Manag 249:109186
Sable S, Ahuja S, Bhunia H (2021) Preparation and characterization of oxo-degradable polypropylene composites containing a modified pro-oxidant. J Polym Environ 29:721–733
Fechine GJM, Rosa DS, Rezende ME, Demarquette NR (2009) Effect of UV radiation and pro-oxidant on PP biodegradability. Polym Eng Sci 49:123–128
Bensaad F, Belhaneche-Bensemra N (2018) Effects of calcium stearate as pro-oxidant agent on the natural aging of polypropylene. J Polym Eng 38:715–721
Sable S, Ahuja S, Bhunia H (2020) Studies on biodegradability of cobalt stearate filled polypropylene after abiotic treatment. J Polym Environ 28:2236–2252
Islam NM, Othman N, Ahmad Z, Ismail H (2010) Effect of pro-degradant additives concentration on aging properties of polypropylene films. Polym Plast Technol Eng 49:272–278
Montagna LS, Catto AL, de Camargo Forte MM, Chiellini E, Corti A, Morelli A, Campomanes Santana RM (2015) Comparative assessment of degradation in aqueous medium of polypropylene films doped with transition metal free (experimental) and transition metal containing (commercial) pro-oxidant/pro-degradant additives after exposure to controlled UV radiation. Polym Degrad Stabil 120:186–192
Moo-Tun NM, Valadez-González A, Uribe-Calderon JA (2018) Thermo-oxidative aging of low density polyethylene blown films in presence of cellulose nanocrystals and a pro-oxidant additive. Polym Bull 75:3149–3169
Madhu G, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK, Nando GB (2016) Physico-mechanical properties and biodegradation of oxo-degradable HDPE/PLA blends. Polym Sci Ser A 58:57–75
Komilis DP (2006) A kinetic analysis of solid waste composting at optimal conditions. Waste Manag 26:82–91
Leejarkpai T, Suwanmanee U, Rudeekit Y, Mungcharoen T (2011) Biodegradable kinetics of plastics under controlled composting conditions. Waste Manag 31:1153–1161
Al-Salem SM, Al-Hazza’a A, Karam HJ, Al-Wadi MH, Al-Dhafeeri A, Al-Rowaih AA (2019) Insights into the evaluation of the abiotic and biotic degradation rate of commercial pro-oxidant filled polyethylene (PE) thin films. J Environ Manag 250:109475
Ahuja S, Arya RK (2018) Laplace Transform treatment for chemical engineering systems: whether to use 0− or 0+? Chem Eng Technol 41:875–882
Ahuja S (2015) Discontinuity analysis for the treatment of nonlinear lumped-parameter systems for singular inputs. Theor Found Chem Eng 49:612–621
Ahuja S, Arya RK (2017) Comparison of the performances of different reduced forms of a condenser model. Chem EngTechnoL 40:1630–1637
Sable S, Ahuja S, Bhunia H (2021) Biodegradation kinetic modeling of pro-oxidant filled polypropylene composites under thermophilic composting conditions after abiotic treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:21231–21244
Mandal DK, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK, Chaudhari CV, Dubey KA, Varshney L, Kumar A (2021) Preparation and characterization of polypropylene/polylactide blends and nanocomposites and their biodegradation study. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 34:725–744
OECD test No. 208 (2006) Terrestial plant growth test: guideline for testing chemicals. Plant growth test, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264070066-en
OECD test No. 207 (1984) Guideline for testing chemicals. Earthworm, acute toxicity tests. Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264070042-en
Liu W, Liu B, Wang X (2013) Morphology, rheological properties, and crystallization behavior of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. Inter J Polym Mater 62:164–171
Arkatkar A, Arutchelvi J, Bhaduri S, Uppara PV, Doble M (2009) Degradation of unpretreated and thermally pretreated polypropylene by soil consortia. Inter Biodeter Biodegrad 63:106–111
Sudhakar M, Trishul A, Doble M, Kumar KS, Jahan SS, Inbakandan D, Viduthalai RR, Umadevi VR, Murthy PS, Venkatesan R (2007) Biofouling and biodegradation of polyolefins in ocean waters. Polym Degrad Stabil 92:1743–1752
Islam NZM, Othman N, Ahmad Z, Ismail H (2011) Effect of pro-degradant additive on photo-oxidative aging of polypropylene film. Sains Malaysiana 40:803–808
Santhoskumar AU, Palanivelu K (2012) A new additive formulation to enhance photo and biodegradation characteristics of polypropylene. Inter J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 61:793–808
Das MP, Kumar S (2013) Comparative study of germination rate and plant growth by secondary metabolites and in vitro LDPE biodegraded fragments by microbes. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 21:134–136
Montagna LS, da Camargo Forte MM, Santana RMC (2013) Induced degradation of polypropylene with an organic pro-degradant additive. J Mater Sci Eng A 3:123–131
Rosa DS, Grillo D, Bardi MAG, Calil MR, Guedes CGF, Ramires EC, Frollini E (2009) Mechanical, thermal and morphological characterization of polypropylene/biodegradable polyester blends with additives. Polym Test 28:836–842
Pablos JL, Abrusci C, Marín I, López-Marín J, Catalina F, Espí E, Corrales T (2010) Photodegradation of polyethylenes: comparative effect of Fe and Ca-stearates as pro-oxidant additives. Polym Degrad Stabil 95:2057–2064
Jain K, Madhu G, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK, Nando GB, Reddy MS (2015) Physico-mechanical characterization and biodegradability behavior of polypropylene/poly(L-lactide) polymer blends. J Polym Eng 35:407–415
Sugumaran V, Bhunia H, Narula AK (2018) Evaluation of Biodegradability of Potato Peel Powder Based Polyolefin Biocomposites. J Polym Environ 26:2049–2060
Kalita NK, Bhasney SM, Kalamdhad A, Katiyar V (2020) Biodegradable kinetics and behavior of bio-based polyblends under simulated aerobic composting conditions. J Environ Manag 261:110211
Muthukumar T, Aravinthan A, Mukesh D (2010) Effect of environment on the degradation of starch and pro-oxidant blended polyolefins. Polym Degrad Stabil 95:1988–1993
El-Arnaouty M, Abdel Ghaffar A, El Shafey HM (2008) Radiation-induced graft copolymerization of acrylic acid/acrylonitrile onto LDPE and PET films and its biodegradability. J Appl Polym Sci 107:744–754
Arráez FJ, Arnal ML, Müller AJ (2018) Thermal and UV degradation of polypropylene with pro-oxidant. Abiotic characterization. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46088
Stloukal P, Pekařová S, Kalendova A, Mattausch H, Laske S, Holzer C, Chitu L, Bodner S, Maier G, Slouf M, Koutny M (2015) Kinetics and mechanism of the biodegradation of PLA/clay nanocomposites during thermophilic phase of composting process. Waste Manag 42:31–40
Stloukal P, Jandikova G, Koutny M, Sedlařík V (2016) Carbodiimide additive to control hydrolytic stability and biodegradability of PLA. Polym Test 54:19–28
Stloukal P, Kucharczyk P (2017) Acceleration of polylactide degradation under biotic and abiotic conditions through utilization of a new, experimental, highly compatible additive. Polym Degrad Stabil 142:217–225
Commereuc S, Vaillant D, Philippart JL, Lacoste J, Lemaire J, Carlsson DJ (1997) Photo and thermal decomposition of iPP hydroperoxides. Polym Degrad Stabil 57:175–182
Kalita NK, Nagar MK, Mudenur C, Kalamdhad A, Katiyar V (2019) Biodegradation of modified poly(lactic acid) based biocomposite films under thermophilic composting conditions. Polym Test 76:522–536
Benítez A, Sánchez JJ, Arnal ML, Müller AJ, Rodríguez O, Morales G (2013) Abiotic degradation of LDPE and LLDPE formulated with a pro-oxidant additive. Polym Degrad Stabil 98:490–501
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, UK
Acknowledgements
The project file number for this research work is 22(00745)/17/EMR-II, and all of the authors are grateful to CSIR (GoI) for financial support. For his invaluable advice, we especially thank Dr. P. K. Bajpai, retired professor at TIET in Patiala, Punjab. For the compounding facilities used in this work, we would want to thank Dr. V. Goel of IOCL Faridabad, India.
Funding
All the data obtained and generated during this study are provided in the paper and supplementary material. Any clarification will be provided on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sable, S., Ahuja, S. Properties and biodegradation modeling of abiotically treated modified-cobalt stearate filled polypropylene films. Iran Polym J 32, 1607–1626 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-023-01228-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-023-01228-y