Abstract
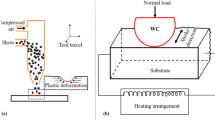
Few works are devoted to study the microstructure effect on tribological behaviors of contacting materials. The most of them are only focused on wear and without fixing the hardness and/or the chemical composition. A contribution is proposed by investigating the combined effects of microstructure and abrasive particle size. Friction tests are performed for steel pins characterized by various microstructures with similar hardness level (around 410 \( {H_{\text{V}}} \)) and chemical composition. The microstructures are composed of a quenched martensitic microstructure, a tempered martensitic microstructure, and ferrite–martensite dual-phase microstructures with various martensite colony morphologies. These pins slide against abrasive papers with various particle sizes, from 15 to 200 μm, under different normal loads from 50 to 110 N. Dual-phase microstructures enhance friction and wear behaviors. Among these microstructures, compared to fine and fibrous martensite colony morphologies, coarse and equiaxed martensite colonies minimize friction coefficient and wear rate. It is worth noting that for a given load, a transition in friction behavior is observed for a critical particle size (CPS) which depends on microstructure and normal load. This study also showed that whatever the microstructure and the abrasive particle sizes, friction coefficients decrease with increasing normal load. However, for wear rate, a reverse trend is observed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Holmberg, A. Erdemir, Global impact of friction on energy consumption, economy and environment. FME Trans. 43(3), 181–185 (2001)
C. Trevisiol, A. Jourani, S. Bouvier, Effect of martensite volume fraction and abrasive particles size on friction and wear behaviour of a low alloy steel. Tribol. Int. 113, 411–425 (2017)
N.B. Dube, I.M. Hutchings, Influence of particle fracture in the high-stress and low-stress abrasive wear of steel. Wear 233–235, 246–256 (1999)
A. Jourani, B. Hagège, B. Bouvier, M. Bigerelle, H. Zahouani, Influence of abrasive grain geometry on friction coefficient and wear rate in belt finishing. Tribol. Int. 59, 30–37 (2013)
A. Jourani, S. Bouvier, Friction and wear mechanisms of 316L stainless steel in dry sliding contact: effect of abrasive particle size. Tribol. Trans. 58(1), 131–139 (2015)
M. Singh, D.P. Mondal, A.K. Jha, A.H. Yegneswarn, High stress abrasive wear behavior of sillimanite-reinforced Al-alloy matrix composite: a factorial design approach. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 12(3), 331–338 (2003)
A.K. Jha, A. Gachake, B.K. Prasad, R. Dasgupta, M. Singh, A.H. Yegneswaran, High stress abrasive wear behavior of some hardfaced surfaces produced by thermal spraying. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 11(1), 37–45 (2002)
A. Jourani, M. Dursapt, H. Hamdi, J. Rech, H. Zahouani, Effect of the belt grinding on the surface texture: modelling of the contact and abrasive wear. Wear 259(7–12), 1137–1143 (2005)
S. Harsha, D.K. Dwivedi, A. Agarwal, Performance of flame sprayed Ni-WC coating under abrasive wear conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 17(1), 104–110 (2008)
R.M. Muñoz Riofano, L.C. Casteletti, P.A.P. Nascente, Effect of ion nitriding on the abrasive wear resistance of ultrahigh-strength steels with different silicon contents. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 14(1), 75–84 (2005)
A. Misra, I. Finnie, On the size effect in abrasive and erosive wear. Wear 65, 359–373 (1981)
M.M. Khruschov, Principles of abrasive wear. Wear 28, 69–88 (1974)
R. Gåhlin, S. Jacobson, The particle size effect in abrasion studied by controlled abrasive surfaces. Wear 224, 18–125 (1999)
E. Rabinowicz, A. Mutis, Effect of abrasive particle size on wear. Wear 8, 381–390 (1965)
C. Trevisiol, A. Jourani, S. Bouvier, Effect of hardness, microstructure, normal load and abrasive size on friction and on wear behaviour of 35NCD16 steel. Wear 388–389, 101–111 (2017)
J. Wahlström, L. Olander, U. Olofsson, A pin-on-disc study focusing on how different load levels affect the concentration and size distribution of airborne wear particles from the disc brake materials. Tribol. Lett. 46, 195–204 (2012)
K. Hokkirigawa, K. Kato, Z.Z. Li, The effect of hardness on the transition of the abrasive wear mechanism of steels. Wear 123, 241–251 (1988)
J. Goddard, H. Wilman, A theory of friction and wear during the abrasion of metals. Wear 5, 114–135 (1962)
H. Somekawa, S. Maeda, T. Hirayama, T. Matsuoka, T. Inoue, T. Mukai, Microstructural evolution during dry wear test in magnesium and Mg-Y alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 561, 371–377 (2013)
P. Xu, B. Bai, F. Yin, H. Fang, K. Nagai, Microstructure control and wear resistance of grain boundary allotriomorphic ferrite/granular bainite duplex steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 385, 65–73 (2004)
O.P. Modi, P. Pandit, D.P. Mondal, B.K. Prasad, A.H. Yegneswaran, A. Chrysanthou, High-stress abrasive wear response of 0.2% carbon dual phase steel: effects of microstructural features and experimental conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 458, 303–311 (2007)
X. Xu, W. Xu, F.H. Ederveen, S. van der Zwaag, Design of low hardness abrasion resistant steels. Wear 301, 89–93 (2013)
X. Xu, S. Van der Zwaag, W. Xu, The effect of ferrite-martensite morphology on the scratch and abrasive wear behaviour of a dual phase construction steel. Wear 348–349, 148–157 (2016)
D.A. Rigney, The roles of hardness in the sliding behavior of materials. Wear 175, 63–69 (1994)
K.-H. ZumGahr, Microstructure and Wear of Material, Tribology Series, vol. 10 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1987)
H. Saghafian, S. Kheirandish, Correlating microstructural features with wear resistance of dual phase steel. Mater. Lett. 61, 3059–3063 (2007)
V. Abouei, H. Saghafian, S. Kheirandish, Dry sliding oxidative wear in plain carbon dual phase steel. J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 14(4), 43–48 (2001)
J.J. Coronado, S.A. Rodríguez, A. Sinatora, Effect of particle hardness on mild–severe wear transition of hard second phase materials. Wear 301(1–2), 82–88 (2013)
H. Ghassemi-Armaki, R. Maaß, S.P. Bhat, S. Sriram, J.R. Greer, K.S. Kumar, Deformation response of ferrite and martensite in a dual-phase steel. Acta Mater. 62, 197–211 (2014)
G.R. Speich, W.C. Leslie, Tempering of steel. Metall. Trans. 3(5), 1043–1054 (1972)
C. Zhang, Q. Wang, J. Ren, R. Li, M. Wang, F. Zhang, K. Sun, Effect of martensitic morphology on mechanical properties of an as-quenched and tempered 25CrMo48V steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 534, 339–346 (2012)
R. Tyagi, S.K. Nath, S. Ray, Effect of martensite content on friction and oxidative wear behavior of 0.42 Pct carbon dual-phase steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33, 3479–3488 (2002)
P. Movahed, S. Kolahgar, S.P.H. Marashi, M. Pouranvari, N. Parvin, The effect of intercritical heat treatment temperature on the tensile properties and work hardening behavior of ferrite-martensite dual phase steel sheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 518, 1–6 (2009)
M. Calcagnotto, Y. Adachi, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, Deformation and fracture mechanisms in fine- and ultrafine-grained ferrite/martensite dual-phase steels and the effect of aging. Acta Mater. 59, 658–670 (2011)
N.J. Kim, G. Thomas, Effects of morphology on the mechanical behavior of a dual phase Fe/2Si/0.1 C steel. Metall. Trans. A 12, 483–489 (1981)
M. Jafari, S. Ziaei-Rad, N. Saeidi, M. Jamshidian, Micromechanical analysis of martensite distribution on strain localization in dual phase steels by scanning electron microscopy and crystal plasticity simulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 670, 57–67 (2016)
N. Saeidi, F. Ashrafizadeh, B. Niroumand, Development of a new ultrafine grained dual phase steel and examination of the effect of grain size on tensile deformation behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 599, 145–149 (2014)
A. Karmakar, M. Ghosh, D. Chakrabarti, Cold-rolling and inter-critical annealing of low-carbon steel: effect of initial microstructure and heating-rate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 564, 389–399 (2013)
M. Calcagnotto, Y. Adachi, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, Deformation and fracture mechanisms in fine- and ultrafine-grained ferrite/martensite dual-phase steels and the effect of aging. Acta Mater. 59, 658–670 (2011)
J. Zhang, H. Di, Y. Deng, R.D.K. Misra, Effect of martensite morphology and volume fraction on strain hardening and fracture behavior of martensite–ferrite dual phase steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 627, 230–240 (2015)
F.P. Bowden, D. Tabor, The Friction and Lubrication of Solids (Clarendon, Oxford, 1954)
A. Jourani, Effect of roughness geometries in contact mechanics. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 51(2), 127–138 (2015)
A.P. Mercer, I.M. Hutchings, The deterioration of bonded abrasive papers during the wear of metals. Wear 132, 77–97 (1989)
A. Jourani, A new 3D numerical model of rough contact: influence of mode of surface deformation on real area of contact and pressure distribution. ASME J Tribol. 137(1), Art No. 011401 (2014)
A. Jourani, M. Bigerelle, L. Petit, H. Zahouani, Local coefficient of friction, subsurface stresses and temperature distribution during sliding contact. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 38(1), 44–56 (2010)
S. Bhowmick, B.K. Show, Effect of prior heat treatment on wear behaviour of 0·23% carbon dual phase steel. Can. Metall. Q. 53(1), 93–99 (2014)
J.J. Coronado, A. Sinatora, Effect of abrasive size on wear of metallic materials and its relationship with microchips morphology and wear micromechanisms: part 1. Wear 271, 1794–1803 (2011)
D.V. De Pellegrin, A.A. Torrance, E. Haran, Wear mechanisms and scale effects in two-body abrasion. Wear 266, 13–20 (2009)
A. Jourani, A. Dellaleau, M. Dursapt, F. Sidoroff, H. Zahouani, Effect of local slopes of roughness during contact between solids. Rev. Eur. Elem. 14(2–3), 271–286 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trevisiol, C., Jourani, A. & Bouvier, S. Effect of Martensite Morphology on Tribological Behaviour of a Low-Alloy Steel. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 8, 123–134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-018-0503-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-018-0503-9