Abstract
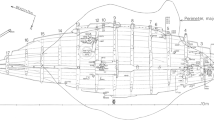
The Dor 2002/2 shipwreck provides evidence of a 15-m-long vessel built to a high standard, and adds essential information to our knowledge of the construction of small vessels that plied the Eastern Mediterranean during the late Ottoman period. During the underwater excavations of the shipwreck, two metal objects were retrieved: a wooden heart (rigging element) with an iron ring-bolt, and a broken iron chain link with a piece of metal cable. This study aims to understand the manufacturing processes of the objects, and to propose their possible dating. The artifacts were studied by archaeometallurgical testing methods, including, HH-XRF, metallographic stereo, light and SEM–EDS microscopy, and microhardness tests. The results revealed that the ring-bolt was made of ferrite phase with preferred oriented slag inclusions microstructure, as typical for indirect smelted wrought-iron. The chain link was made of gray cast-iron. The suggested date of the shipwreck was 1800; however, based on the archaeometallurgical test results, it is suggested that the two iron artifacts were manufactured between the years 1839 and 1856. This research demonstrates the important contribution of the study of metal finds to the dating of shipwrecks.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Kahanov, Ship reconstruction, documentation, and in situ recording, in The Oxford Handbook of Maritime Archaeology, ed. by A. Catambis, B. Ford, D.L. Hamilton (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2011), pp. 161–181
D. Cvikel, Y. Kahanov, H. Goren, E. Boaretto, K. Raveh, Napoleon Bonaparte’s adventure in Tantura Lagoon: historical and archaeological evidence. Israel Explor. J. 58(2), 199–219 (2008)
Fonds français 11275. Lettres et pièces diverses relatives à l’expédition d’Egypte. Lambert – fol. 200. Bibliothèque nationale de France, archives et manuscrits.
D. Cvikel, Y. Kahanov, The Dor 2002/2 shipwreck. Archaeol. Marit. Mediter. 3, 79–98 (2006)
D. Cvikel, Y. Kahanov, The Ottoman period shipwrecks of Dor (Tantura) lagoon, Israel. Archeol. Postmediev. 18, 177–188 (2014)
G. Biddlecombe, The Art of Rigging Containing an Explanation of Terms and Phrases, and the Progressive Method of Rigging Expressly Adapted for Sailing Ships (Charles Wilson, London, 1848)
P. Kemp (ed.), The Oxford Companion to Ships and the Sea (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1976)
D. Lever, The Young Sea Officer’s Sheet Anchor, or a Key to the Leading of Rigging, and to Practical Seamanship (John Richardson, London, 1819)
J. Lees, The Masting and Rigging of English Ships of War 1625–1860 (Naval Institute Press, Annapolis, 2007)
K.H. Marquardt, Eighteenth-Century Rig and Rigging (Conway, London, 2003)
D. Ashkenazi, E. Mentovich, Y. Kahanov, D. Cvikel, O. Barkai, A. Aronson, Archaeometallurgical investigation of iron artifacts from shipwrecks: a review, in Archaeology, New Approaches in Theory and Techniques, ed. by I. Ollich-Castanyer (InTech Publisher, Rijeka, 2012), pp. 169–186
Y. Kahanov, E. Stern, A. Stern, R. Ronen, D. Cvikel, D. Ashkenazi, What ship? Who fired the cannonballs at the wall in Akko? An archaeometallurgical and historical study. Hist. Metall. 46(2), 98–110 (2012)
E.D. Mentovich, D.S. Schreiber, Y. Goren, Y. Kahanov, H. Goren, D. Cvikel, D. Ashkenazi, New insights regarding the Akko 1 shipwreck: a metallurgic and petrographic investigation of the cannonballs. J. Archaeol. Sci. 37(10), 2520–2528 (2010)
M.L. Wayman, Archaeometallurgical contributions to a better understanding of the past. Mater. Charact. 45(4), 259–267 (2000)
V.F. Buchwald, H. Wivel, Slag analysis as a method for the characterization and provenancing of ancient iron objects. Mater. Charact. 40, 73–96 (1998)
M. Cavallini, Thermodynamics applied to iron smelting techniques. Appl. Phys. A 113(4), 1049–1053 (2013)
J.L. Coze, Purification of iron and steels a continuous effort from 2000 BC to AD 2000. Mater. Trans. 41(1), 219–232 (2000)
J. Bénard, A. Michel, J. Philibert, J. Talbot, Métallurgie Générale (Masson, Paris, 1984)
R.F. Tylecote, A History of Metallurgy (The Metals Society, London, 1992)
R.F. Tylecote, J.W.B. Black, The effect of hydrogen reduction on the properties of ferrous materials. Stud. Conserv. 25, 87–96 (1980)
N. North, M. Owens, C. Pearson, Thermal stability of cast and wrought marine iron. Stud. Conserv. 21(4), 192–197 (1976)
W.K.V. Gale, The Bessemer steelmaking process. Trans. Newcom. Soc. 46(1), 17–26 (1973)
J.C. Martin, Strands that stands: using wire rope to date and identify archaeological sites. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 43(1), 151–161 (2014)
D.A. Scott, Metallography and Microstructure of Ancient and Historic Metals (Getty Conservation Institute, Santa Monica, 1991)
S. Barella, C. Mapelli, W. Nicodemi, A leap into the beginning of the metal age: recrystallization and carburizing. La Metall. Ital. 4, 9–16 (2008)
C. Mapelli, W. Nicodemi, R.F. Riva, Microstructural investigation of a medieval sword produced in 12th Century AD. ISIJ Int. 47(7), 1050–1057 (2007)
J. Perttula, Wootz Damascus steel of ancient orient. Scand. J. Metall. 33, 92–97 (2004)
J.V.G. Adelantado, M.A.F. Eres, F.M.V. Algarra, J.P. Vicente, F.B. Reig, Analytical study by SEM/EDX and metallographic techniques of materials used in the iron production process during the Iberian period. Talanta 60, 895–910 (2003)
M. Goodway, History of casting, in ASM Metals Handbook, Vol. 15: Casting, ed. by H.J. Frissell (ASM International, OH, 1996), pp. 12–54
J.S. Park, M.E. Hall, The use of white cast iron in ancient Korea. Inst. Archaeo-Metall. Stud. 25, 9–13 (2005)
W. Xu, M. Ferry, Y. Wang, Influence of alloying elements on as-cast microstructure and strength of gray iron. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 390, 326–333 (2005)
T.S. Wiltzen, M.L. Wayman, Steel files as chronological markers in North American fur trade sites. Archaeometry 41, 117–135 (1999)
A.N. Shugar, Portable X-ray fluorescence and archaeology: limitations of the instrument and suggested methods to achieve desired results, in Archaeological Chemistry VIII, ed. by R.A. Armitage, J.H. Burton (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 2013), pp. 173–193
S. Balos, A. Benscoter, A. Pense, Roman mystery iron blades from Serbia. Mater. Charact. 60, 271–276 (2009)
D. Cvikel, D. Ashkenazi, A. Stern, Y. Kahanov, Archaeometallurgical analysis of a 12-pdr wrought-iron cannonball from the Akko 1 shipwreck, Israel. Mater. Charact. 83, 198–211 (2013)
J.F. Lancaster, The physics of fusion welding. Part 1: The electric arc in welding. Electric power applications. IEE Proc. B 134(5), 233–254 (1987)
R.F. Stanescu, A single pass butt-welded pipe finite element method computer simulation, Unpublished PhD Dissertation, Carleton University, 2005
M.E. Rogers, Domestic Life in Palestine (Pob and Hitchcock, Cincinnati, 1865)
G. Robinson, Travels in Palestine and Syria Volume I: Palestine (Henry Colrurn, London, 1837)
Acknowledgments
The underwater excavation and research of Dor 2002/2 was partially supported by Lord Jacobs from London, the Israel Science Foundation, the Sir Maurice Hatter Fellowship for Maritime Studies, the Fraenkel Fellowship Committee, the Hecht Trust, and anonymous donors, to whom the authors are grateful. The authors are grateful to Dr. Z. Barkay, the Wolfson Applied Materials Research Centre, Tel Aviv University, and R. Malmazada, Microtech Ltd (Israel), for their valuable assistance. Thanks are due to the licensee for allowing the publication of this work; B. Doron for the English editing; and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cvikel, D., Ashkenazi, D. The Dor 2002/2 Shipwreck, Israel: Characterization of Surviving Ironwork. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 5, 16–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-015-0249-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-015-0249-6