Abstract
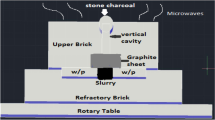
This paper presents an experimental study on the tensile strength of 1018 mild steel plates joined by microwave welding. Three different microwave ovens with rated power of 800, 850, and 900 W and fixed frequency of 2.45 GHz were used in the present investigation. A nickel (Ni)-based metallic powder (50 μm) was used as an interfacing material between the bulk pieces. Charcoal was used as a susceptor material to facilitate microwave hybrid heating. The rated power of the microwave oven and the welding time and temperature were the principal variables that were controlled to provide the necessary combination of heat to form the weld. The response surface methodology (Box–Behnken method) was chosen to design the experiments. The results show that, with increasing rated power of the microwave oven, the tensile strength decreases, while the tensile strength increases with increasing welding time and temperature. From analysis of variance it is concluded that the welding temperature contributes most, followed by the rated power and welding time. The optimum values of rated power and welding time and temperature were found to be 800 W, 1,000 s, and 800 °C to obtain the maximum tensile strength (predicted 245.2 MPa). There was approximately 4.06 % error between the experimental and modeled results for tensile strength.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 February 2019
The Editor has retracted this article (1) because concerns have been raised regarding some of the figures. Figure 3 part B appears to be a copy of Figure 3 part A, with some alterations.
21 February 2019
The Editor has retracted this article (1) because concerns have been raised regarding some of the figures. Figure��3 part B appears to be a copy of Figure��3 part A, with some alterations.
References
P.K.D.V. Yarlagadda, T.S. Chong, Characterisation of materials behaviour in microwave joining of ceramics. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 84(1–3), 162–174 (1998)
J.M. Hill, T.R. Marchant, Modeling microwave heating. Appl. Math. Model. 20(1), 3–15 (1996)
H.S. Ku, F. Siu, E. Siores, J.A.R. Ball, A.S. Blicblau, Application of fixed and variable frequency microwave (VFM) facilities in polymeric materials processing and joining. J. Mater. Process. 113, 184–188 (2001)
H.S. Ku, F. Siu, E. Siores, J.A.R. Ball, Variable frequency microwave (VFM) processing facilities and application in processing thermoplastic matrix composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 139, 291–295 (2003)
P.K.D.V. Yarlagadda, S.-H. Hsu, Experimental studies on comparison of microwave curing and thermal curing of epoxy resins used for alternative mould materials. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 155–156, 1532–1538 (2004)
A. Ahmed, E. Siores, Microwave joining of 48% alumina–32% zirconia–20% silica ceramics. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 118(1–3), 88–94 (2001)
R. Benıtez, A. Fuentes, K. Lozano, Effects of microwave assisted heating of carbon nanofiber reinforced high density polyethylene. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 190, 324–331 (2007)
C. Leonelli, P. Veronesi, L. Denti, A. Gatto, L. Iuliano, Microwave assisted sintering of green metal parts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 205(1–3), 489–496 (2008)
H.S. Ku, T. Yusaf, Processing of composites using variable and fixed frequency microwave facilities. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 5, 185–205 (2008)
D. Gupta, P.M. Bhovi, A.K. Sharma, S. Dutta, Development and characterization of microwave composite cladding. J. Manuf. Process. 14, 243–249 (2012)
P.K. Bajpai, I. Singh, J. Madaan, Joining of natural fiber reinforced composites using microwave energy: experimental and finite element study. Mater. Des. 35, 596–602 (2012)
A. Olofinjana, P.K.D.V. Yarlagadda, A. Oloyede, Microwave processing of adhesive joints using a temperature controlled feedback system. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 41(2), 209–225 (2001)
B.B. Balzer, J. McNabb, Significant effect of microwave curing on tensile strength of carbon fiber composites. J. Ind. Technol. 24(3), 1–9 (2008)
M.S. Srinath, A.K. Sharma, P. Kumar, Investigation on microstructural and mechanical properties of microwave processed dissimilar joints. J. Manuf. Process. 13(2), 141–146 (2011)
M.S. Srinath, A.K. Sharma, P. Kumar, A new approach to joining of bulk copper using microwave energy. Mater. Des. 32(5), 2685–2694 (2011)
E. Colombini, R. Rosa, P. Veronesi, M. Cavallini, G. Poli, C. Leonelli, Microwave ignited combustion synthesis as a joining technique for dissimilar materials: modeling and experimental results. Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth. 21(1), 25–31 (2012)
P. Gupta, S. Kumar, A. Kumar, Study of joint formed by tungsten carbide bearing alloy through microwave welding. Mater. Manuf. Process. 28(5), 601–604 (2013)
D.C. Montgomery, Design and Analysis of Experiments, 5th edn. (Wiley-India, New Delhi, 2007), p. 427
S.P. Dwivedi, S. Kumar, A. Kumar, Effect of turning parameters on surface roughness of A356/5% SiC composite produced by electromagnetic stir casting. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26(12), 3973–3979 (2012)
Ch.R. Buffler, Microwave Cooking and Processing (Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Editor has retracted this article because concerns have been raised regarding some of the figures. Figure 3 part B appears to be a copy of Figure 3 part A, with some alterations. The images in Figure 5 parts A, B, C, and D appear to be the same image, with minor alterations to obscure similarities. In Figure 6B, there is an apparent symmetry between the top half and bottom half of the figure (along a horizontal line through the center of the image), which indicates this image may have been created by copying the bottom portion onto the top with a rotation. Therefore the conclusions of this article are unreliable.
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, S.P., Sharma, S. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Effect of Process Parameters on Tensile Strength of 1018 Mild Steel Joints Fabricated by Microwave Welding. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 3, 58–69 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-013-0109-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-013-0109-1