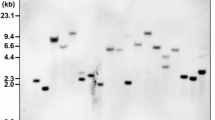
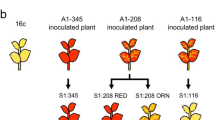
Abstract
Homology-dependent gene silencing (HDGS) is a resistance mechanism against homologous transgene introduction or virus infection in various organisms. In plants in particular, HDGS phenomena in homologous DNA or RNA sequences can cause gene silencing. In this study, GUS-silenced transgenic lines were developed by agroinfiltration with the i35S binary vector for inducing targeted de novo CaMV 35S promoter methylation. Agroinfiltration with i35S triggered inheritable de novo methylation of the CaMV 35S promoter and CAAT box region by HDGS. Moreover, targeted de novo CaMV 35S promoter methylation appeared to be controlled by the expression of SUVH9, which is involved in endogenous DNA methylation and hyper-methylation of the introduced promoter. In summary, this study demonstrated that targeted de novo CaMV 35S promoter methylation may be subjected to an HDGS mechanism that can downregulate gene expression and maintain the heritable stability of the methylated promoter.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Andrieu A, Breitler JC, Siré C, Meynard D, Gantet P, Guiderdoni E (2012) An in planta, Agrobacterium-mediated transient gene expression method for inducing gene silencing in rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves. Rice (N Y) 5:23
Aufsatz W, Mette MF, van der Winden J, Matzke AJ, Matzke M (2002) RNA-directed DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16499–16506
Battraw MJ, Hall TC (1990) Histochemical analysis of CaMV 35S promoter-β-glucuronidase gene expression in transgenic rice plants. Plant Mol Biol 15:527–538
Bhaskar PB, Venkateshwaran M, Wu L, Ané JM, Jiang J (2009) Agrobacterium-mediated transient gene expression and silencing: a rapid tool for functional gene assay in potato. PLoS ONE 4:e5812
Brunaud V, Balzergue S, Dubreucq B, Aubourg S, Samson F, Chauvin S, Bechtold N, Cruaud C, DeRose R, Pelletier G, Lepiniec L, Caboche M, Lecharny A (2002) T-DNA integration into the Arabidopsis genome depends on sequences of pre-insertion sites. EMBO Rep 3:1152–1157
Cogoni C, Macino G (1999) Homology-dependent gene silencing in plants and fungi: a number of variations on the same theme. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:657–662
Dietz-Pfeilstetter A (2010) Stability of transgene expression as a challenge for genetic engineering. Plant Sci 179:164–167
Eamens A, Wang MB, Smith NA, Waterhouse PM (2008) RNA silencing in plants: yesterday, today, and tomorrow. Plant Physiol 147:456–468
Fauser F, Schiml S, Puchta H (2014) Both CRISPR/Cas-based nucleases and nickases can be used efficiently for genome engineering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 79:348–359
Hetzl J, Foerster AM, Raidl G, Mittelsten Scheid O (2007) CyMATE: a new tool for methylation analysis of plant genomic DNA after bisulphite sequencing. Plant J 51:526–536
Holzberg S, Brosio P, Gross C, Pogue GP (2002) Barley stripe mosaic virus-induced gene silencing in a monocot plant. Plant J 30:315–327
Hristova E, Fal K, Klemme L, Windels D, Bucher E (2015) HISTONE DEACETYLASE6 controls gene expression patterning and DNA methylation-independent euchromatic silencing. Plant Physiol 168:1298–1308
Jefferson RA (1988) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Johnson LM, Law JA, Khattar A, Henderson IR, Jacobsen SE (2008) SRA-domain proteins required for DRM2-mediated de novo DNA methylation. PLoS Genet 4:e1000280
Jyotishwaran G, Kotresha D, Selvaraj T, Srideshikan SM, Rajvanshi PK, Jayabaskaran C (2007) A modified freeze-thaw method for efficient transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Curr Sci 93:770–772
Kanazawa A, O’Dell M, Hellens RP (2007) The binding of nuclear factors to the as-1 element in the CaMV 35S promoter is affected by cytosine methylation in vitro. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 9:435–441
Kosugi S, Ohashi Y, Nakajima K, Arai Y (1990) An improved assay for beta-glucuronidase in transformed-cells—methanol almost completely suppresses a putative endogenous beta-glucuronidase activity. Plant Sci 70:133–140
Kwak MS, Oh MJ, Lee SW, Shin JS, Paek KH, Bae JM (2007) A strong constitutive gene expression system derived from ibAGP1 promoter and its transit peptide. Plant Cell Rep 26:1253–1262
Lam E, Benfey PN, Gilmartin PM, Fang RX, Chua NH (1989) Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7890–7894
Lee GH, Sohn SH, Park EY, Park YD (2012) Aberrant promoter methylation occurred from multicopy transgene and SU(VAR)3–9 homolog 9 (SUVH9) gene in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. Funct Plant Biol 39:764–773. https://doi.org/10.1071/fp12051
Lee GH, Park EY, Park YD (2014) Transgene instability due to promoter hypermethylation and deletion in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 55:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-014-0103-9
Lee GH, Yu JG, Park YD (2015) Development of an effective PCR technique for analyzing T-DNA integration sites in Brassica species and its application. Hortic Sci Technol 33:242–250
Lee GH, Lee GS, Park YD (2018) New hairpin RNAi vector with Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis intron for gene silencing in plants. Hortic Sci Technol 36:266–279. https://doi.org/10.12972/kjhst.20170035
Liu C, Lu F, Cui X, Cao X (2010) Histone methylation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:395–420
Liu X, Yu CW, Duan J, Luo M, Wang K, Tian G, Cui Y, Wu K (2012) HDA6 directly interacts with DNA methyltransferase MET1 and maintains transposable element silencing in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 158:119–129
Liu ZW, Shao CR, Zhang CJ, Zhou JX, Zhang SW, Li L, Chen S, Huang HW, Cai T, He XJ (2014) The SET domain proteins SUVH2 and SUVH9 are required for Pol V occupancy at RNA-directed DNA methylation loci. PLoS Genet 10:e1003948
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and 2−[− ΔΔC(T)]method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Matsumoto S, Ito Y, Hosoi T, Takahashi Y, Machida Y (1990) Integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA into a tobacco chromosome: possible involvement of DNA homology between T-DNA and plant DNA. Mol Gen Genet 224:309–316
Matzke AJ, Matzke MA (1998) Position effects and epigenetic silencing of plant transgenes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:142–148
Matzke MA, Mosher RA (2014) RNA-directed DNA methylation: an epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity. Nat Rev Genet 15:394–408
Matzke MA, Primig M, Trnovsky J, Matzke AJM (1989) Reversible methylation and inactivation of marker genes in sequentially transformed tobacco plants. EMBO J 8:643–649
Matzke MA, Mette MF, Aufsatz W, Jakowitsch J, Matzke AJ (1999) Host defenses to parasitic sequences and the evolution of epigenetic control mechanisms. Genetica 107:271–287
Mayerhofer R, Koncz-Kalman Z, Nawrath C, Bakkeren G, Crameri A, Angelis K, Redei GP, Schell J, Hohn B, Koncz C (1991) T-DNA integration: a mode of illegitimate recombination in plants. EMBO J 10:697–704
McDonald JF, Matzke MA, Matzke AJ (2005) Host defenses to transposable elements and the evolution of genomic imprinting. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:242–249
Mette MF, Aufsatz W, van der Winden J, Matzke MA, Matzke AJ (2000) Transcriptional silencing and promoter methylation triggered by double-stranded RNA. EMBO J 19:5194–5201
Mishiba K, Nishihara M, Nakatsuka T, Abe Y, Hirano H, Yokoi T, Kikuchi A, Yamamura S (2005) Consistent transcriptional silencing of 35S-driven transgenes in gentian. Plant J 44:541–556
Mueller E, Gilbert J, Davenport G, Brigneti G, Baulcombe DC (1995) Homology-dependent resistance: transgenic virus resistance in plants related to homology-dependent gene silencing. Plant J 7:1001–1013
Myronovskyi M, Welle E, Fedorenko V, Luzhetskyy A (2011) Beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile reporter in actinomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5370–5383
Nardi CF, Villarreal NM, Dotto MC, Ariza MT, Vallarino JG, Martínez GA, Valpuesta V, Civello PM (2016) Influence of plant growth regulators on Expansin2 expression in strawberry fruit. Cloning and functional analysis of FaEXP2 promoter region. Postharvest Biol Technol 114:17–28
Naumann U, Daxinger L, Kanno T, Eun C, Long Q, Lorkovic ZJ, Matzke M, Matzke AJ (2011) Genetic evidence that DNA methyltransferase DRM2 has a direct catalytic role in RNA-directed DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 187:977–979
Odell JT, Nagy F, Chua NH (1985) Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Nature 313:810–812
Park YD, Kim HS (2000) Expression and inheritance patterns of GUS gene driven by an endosperm-specific promoter in transgenic Tobacco. Hortic Sci Technol 18:594–598
Park YD, Papp I, Moscone EA, Iglesias VA, Vaucheret H, Matzke AJ, Matzke MA (1996) Gene silencing mediated by promoter homology occurs at the level of transcription and results in meiotically heritable alterations in methylation and gene activity. Plant J 9:183–194
Passricha N, Saifi S, Khatodia S, Tuteja N (2016) Assessing zygosity in progeny of transgenic plants: current methods and perspectives. J Biol Methods 3:e46
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual: cold spring. Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Stephan D, Slabber C, George G, Ninov V, Francis KP, Burger JT (2011) Visualization of plant viral suppressor silencing activity in intact leaf lamina by quantitative fluorescent imaging. Plant Methods 7:25
Stroud H, Greenberg MV, Feng S, Bernatavichute YV, Jacobsen SE (2013) Comprehensive analysis of silencing mutants reveals complex regulation of the Arabidopsis methylome. Cell 152:352–364
Tanabe N, Tamoi M, Shigeoka S (2015) The sweet potato RbcS gene (IbRbcS1) promoter confers high-level and green tissue-specific expression of the GUS reporter gene in transgenic Arabidopsis. Gene 567:244–250
Tang W, Luo XY, Sanmuels V (2001) Gene silencing: double-stranded RNA mediated mRNA degradation and gene inactivation. Cell Res 11:181–186
Tang W, Newton RJ, Weidner DA (2007) Genetic transformation and gene silencing mediated by multiple copies of a transgene in eastern white pine. J Exp Bot 58:545–554
Till S, Ladurner AG (2007) RNA Pol IV plays catch with Argonaute 4. Cell 131:643–645
Ülker B, Allen GC, Thompson WF, Spiker S, Weissinger AK (1999) A tobacco MAR increases transgene expression and protects against gene silencing in the progeny of transgenic tobacco plants. Plant J 18:253–263
Vaucheret H, Fagard M (2001) Transcriptional gene silencing in plants: targets, inducers and regulators. Trends Genet 17:29–35
Wassenegger M (2000) RNA-directed DNA methylation. Plant Mol Biol 43:203–220
Wielopolska A, Townley H, Moore I, Waterhouse P, Helliwell C (2005) A high-throughput inducible RNAi vector for plants. Plant Biotechnol J 3:583–590
Zemach A, Kim MY, Hsieh PH, Coleman-Derr D, Eshed-Williams L, Thao K, Harmer SL, Zilberman D (2013) The Arabidopsis nucleosome remodeler DDM1 allows DNA methyltransferases to access H1-containing heterochromatin. Cell 153:193–205
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out with the support of the “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ01365201)”, Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G-HL performed the majority of the experiments and data analysis. Y-DP designed the experiments and analyzed data. G-HL and Y-DP wrote manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sung-Chur Sim.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, GH., Park, YD. Targeted de novo promoter methylation for gene silencing is maintained in the next generation of a transgenic tobacco plant. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 61, 291–303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00205-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00205-w