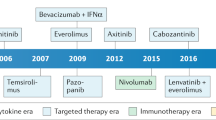
Abstract
Background
In recent years, there have been great improvements in the therapy of renal cell carcinoma. Nevertheless, the therapeutic effect varies significantly from person to person. To discern the effective treatment for different populations, predictive molecular biomarkers in response to target, immunological, and combined therapies are widely studied.
Conclusion
This review summarized those studies from three perspectives (SNPs, mutation, and expression level) and listed the relationship between biomarkers and therapeutic effect, highlighting the great potential of predictive molecular biomarkers in metastatic RCC therapy. However, due to a series of reasons, most of these findings require further validation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68(1), 7–30 (2018)
T.K. Choueiri, R.J. Motzer, Systemic Therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 376(4), 354–366 (2017)
T. Klatte et al., Understanding the natural biology of kidney cancer: implications for targeted cancer therapy. Rev. Urol. 9(2), 47–56 (2007)
B.I. Rini, S.C. Campbell, B. Escudier, Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 373(9669), 1119–1132 (2009)
K. Yamazaki et al., Overexpression of KIT in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 22(6), 847–852 (2003)
E. Jonasch, J. Gao, W.K. Rathmell, Renal cell carcinoma. BMJ 349, g4797 (2014)
H. Moch et al., The 2022 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur. Urol. 82(5), 458–468 (2022)
C.A. Grandinetti, B.R. Goldspiel, Sorafenib and sunitinib: novel targeted therapies for renal cell cancer. Pharmacotherapy 27(8), 1125–1144 (2007)
Y. Adachi et al., Inhibition of FGFR reactivates IFNgamma signaling in tumor cells to enhance the combined antitumor activity of lenvatinib with anti-PD-1 antibodies. Cancer Res 82(2), 292–306 (2022)
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature. 499(7456), 43–49 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12222
G. Hudes et al., Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 356(22), 2271–2281 (2007)
X. Sheng et al., Efficacy and safety of vorolanib plus everolimus in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a three-arm, randomised, double-blind, multicentre phase III study (CONCEPT). Eur. J. Cancer 178, 205–215 (2023)
J.A. Garcia, B.I. Rini, Recent progress in the management of advanced renal cell carcinoma. CA Cancer J. Clin. 57(2), 112–125 (2007)
G. Fyfe et al., Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 13(3), 688–696 (1995)
J.C. Yang et al., Randomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 21(16), 3127–3132 (2003)
D.F. McDermott et al., Randomized phase III trial of high-dose interleukin-2 versus subcutaneous interleukin-2 and interferon in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 23(1), 133–141 (2005)
S. Pyrhonen et al., Prospective randomized trial of interferon alfa-2a plus vinblastine versus vinblastine alone in patients with advanced renal cell cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 17(9), 2859–2867 (1999)
Interferon-alpha and survival in metastatic renal carcinoma: early results of a randomised controlled trial. Medical Research Council Renal Cancer Collaborators. Lancet 353(9146), 14–7 (1999)
J. Folkman, Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin. Oncol. 29(6 Suppl 16), 15–18 (2002)
E.D. Deeks, G.M. Keating, Sunitinib. Drugs 66(17), 2255–66 (2006). (discussion 2267-8)
G.S. Papaetis, K.N. Syrigos, Sunitinib: a multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the era of molecular cancer therapies. BioDrugs 23(6), 377–389 (2009)
D. Romero, Belzutifan has potential in RCC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 18(6), 322 (2021)
L.R. Medina et al., Update on the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. World J. Clin. Oncol. 13(1), 1–8 (2022)
N. Gavrielatou et al., Biomarkers for immunotherapy response in head and neck cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 84, 101977 (2020)
D.M. Pardoll, The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12(4), 252–264 (2012)
A.E. Kam, A. Masood, R.T. Shroff, Current and emerging therapies for advanced biliary tract cancers. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6(11), 956–969 (2021)
What are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)? (2022–3–22)[2022–12–21] (2022)
A.E. Koch et al., Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science 258(5089), 1798–1801 (1992)
D. Huang et al., Interleukin-8 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic agent sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70(3), 1063–1071 (2010)
D. Hacking et al., Increased in vivo transcription of an IL-8 haplotype associated with respiratory syncytial virus disease-susceptibility. Genes Immun. 5(4), 274–282 (2004)
A. Yuan et al., The role of interleukin-8 in cancer cells and microenvironment interaction. Front. Biosci. 10, 853–865 (2005)
B.I. Rini et al., Identification of prognostic genomic markers in patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 28(15_suppl), 4501–4501 (2010)
C.F. Xu et al., IL8 polymorphisms and overall survival in pazopanib- or sunitinib-treated patients with renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 112(7), 1190–1198 (2015)
P.C. Brooks, R.A. Clark, D.A. Cheresh, Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264(5158), 569–571 (1994)
J.S. Desgrosellier, D.A. Cheresh, Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10(1), 9–22 (2010)
D.J. Crona et al., Genetic variants of VEGFA and FLT4 are determinants of survival in renal cell carcinoma patients treated with sorafenib. Cancer Res. 79(1), 231–241 (2019)
M.S. Del, Z. Salah, R.I. Aqeilan, WWOX: its genomics, partners, and functions. J. Cell. Biochem. 108(4), 737–745 (2009)
A. Kaipainen et al., Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 gene becomes restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92(8), 3566–3570 (1995)
N.R. Smith et al., Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 are localized primarily to the vasculature in human primary solid cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 16(14), 3548–3561 (2010)
N. Ferrara, VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2(10), 795–803 (2002)
H. Gerhardt et al., VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J. Cell Biol. 161(6), 1163–1177 (2003)
T. Veikkola et al., Regulation of angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer Res. 60(2), 203–212 (2000)
T. Tammela et al., Blocking VEGFR-3 suppresses angiogenic sprouting and vascular network formation. Nature 454(7204), 656–660 (2008)
A. Grothey, L.M. Ellis, Targeting angiogenesis driven by vascular endothelial growth factors using antibody-based therapies. Cancer J. 14(3), 170–177 (2008)
N.L. Ainsworth, J.S. Lee, T. Eisen, Impact of anti-angiogenic treatments on metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 9(12), 1793–1805 (2009)
J. Garcia-Donas et al., Single nucleotide polymorphism associations with response and toxic effects in patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma treated with first-line sunitinib: a multicentre, observational, prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 12(12), 1143–1150 (2011)
J. Garcia-Donas et al., Prospective study assessing hypoxia-related proteins as markers for the outcome of treatment with sunitinib in advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 24(9), 2409–2414 (2013)
V.M. Leppanen et al., Structural and mechanistic insights into VEGF receptor 3 ligand binding and activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(32), 12960–12965 (2013)
D.J. George et al., Phase III trial of adjuvant sunitinib in patients with high-risk renal cell carcinoma: exploratory pharmacogenomic analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 25(4), 1165–1173 (2019)
J. Dornbusch et al., Evaluation of polymorphisms in angiogenesis-related genes as predictive and prognostic markers for sunitinib-treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 142(6), 1171–1182 (2016)
B.I. Rini, Vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 115(10 Suppl), 2306–2312 (2009)
C.G. Dietrich, A. Geier, E.R. Oude, ABC of oral bioavailability: transporters as gatekeepers in the gut. Gut 52(12), 1788–1795 (2003)
A.A. van der Veldt et al., Genetic polymorphisms associated with a prolonged progression-free survival in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with sunitinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 17(3), 620–629 (2011)
M.H. Diekstra et al., Association analysis of genetic polymorphisms in genes related to sunitinib pharmacokinetics, specifically clearance of sunitinib and SU12662. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 96(1), 81–89 (2014)
M.H. Diekstra et al., CYP3A5 and ABCB1 polymorphisms as predictors for sunitinib outcome in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 68(4), 621–629 (2015)
N.P. van Erp, H. Gelderblom, H.J. Guchelaar, Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 35(8), 692–706 (2009)
R.G. Tirona, W. Lee, B.F. Leake, L.B. Lan, C.B. Cline, V. Lamba, F. Parviz, S.A. Duncan, Y. Inoue, F.J. Gonzalez, E.G. Schuetz, R.B. Kim, The orphan nuclear receptor HNF4alpha determines PXR- and CAR-mediated xenobiotic induction of CYP3A4. Nat. Med. 9(2) 220–4 (2003)
MUTATION. (2022)
C.L. Cowey, W.K. Rathmell, VHL gene mutations in renal cell carcinoma: role as a biomarker of disease outcome and drug efficacy. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 11(2), 94–101 (2009)
A. Arreola, L.B. Payne, M.H. Julian, A.A. de Cubas, A.B. Daniels, S. Taylor, H. Zhao, J. Darden, V.L. Bautch, W.K. Rathmell, J.C. Chappell, Von Hippel-Lindau mutations disrupt vascular patterning and maturation via Notch. JCI Insight. 3(4), e92193 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.92193
W.J. Kaelin, The von hippel-lindau tumor suppressor protein: an update. Methods Enzymol. 435, 371–383 (2007)
R.J. Motzer et al., Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 356(2), 115–124 (2007)
B. Escudier et al., Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 356(2), 125–134 (2007)
B.I. Rini et al., Clinical response to therapy targeted at vascular endothelial growth factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: impact of patient characteristics and Von Hippel-Lindau gene status. BJU Int. 98(4), 756–762 (2006)
J. Zhou et al., VHL and DNA damage repair pathway alterations as potential clinical biomarkers for first-line TKIs in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Cell. Oncol. 45(4), 677–687 (2022)
Y. Sato et al., Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 45(8), 860–867 (2013)
S. Pena-Llopis et al., BAP1 loss defines a new class of renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 44(7), 751–759 (2012)
I. Varela et al., Exome sequencing identifies frequent mutation of the SWI/SNF complex gene PBRM1 in renal carcinoma. Nature 469(7331), 539–542 (2011)
A.P. Fay et al., Whole-exome sequencing in two extreme phenotypes of response to VEGF-targeted therapies in patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 14(7), 820–824 (2016)
M.H. Voss et al., Genomically annotated risk model for advanced renal-cell carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 19(12), 1688–1698 (2018)
J.J. Hsieh et al., Genomic biomarkers of a randomized trial comparing first-line everolimus and sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 71(3), 405–414 (2017)
M.I. Carlo et al., Genomic alterations and outcomes with VEGF-targeted therapy in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Kidney Cancer 1(1), 49–56 (2017)
B. Jee, E. Seo, K. Park, Y.R. Kim, S.J. Byeon, S.M. Lee, J.H. Chung, W. Song, H.H. Sung, H.G. Jeon, B.C. Jeong, S.I. Seo, S.S. Jeon, H.M. Lee, S.H. Park, W.Y. Park, M. Kang, Molecular subtypes based on genomic and transcriptomic features correlate with the responsiveness to immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 14(10), 2354 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14102354
R.J. Motzer et al., Molecular subsets in renal cancer determine outcome to checkpoint and angiogenesis blockade. Cancer Cell 38(6), 803-817.e4 (2020)
S. Chang, S. Yim, H. Park, The cancer driver genes IDH1/2, JARID1C/ KDM5C, and UTX/ KDM6A: crosstalk between histone demethylation and hypoxic reprogramming in cancer metabolism. Exp Mol Med 51(6), 1–17 (2019)
M. Dratwa et al., TERT-regulation and roles in cancer formation. Front. Immunol. 11, 589929 (2020)
F. Rodier et al., Persistent DNA damage signalling triggers senescence-associated inflammatory cytokine secretion. Nat. Cell Biol. 11(8), 973–979 (2009)
J.P. Coppe et al., Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol. 6(12), 2853–2868 (2008)
J.P. Coppe et al., Secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor by primary human fibroblasts at senescence. J. Biol. Chem. 281(40), 29568–29574 (2006)
K. Ohuchida et al., Radiation to stromal fibroblasts increases invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells through tumor-stromal interactions. Cancer Res. 64(9), 3215–3222 (2004)
A. Tripathi, E. Lin, N. Agarwal, Biomarkers in metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Transl. Med. 7(S6), S203–S203 (2019)
T. Rampias, et al., The lysine-specific methyltransferase KMT2C/MLL3 regulates DNA repair components in cancer. EMBO Rep. 20(3) (2019)
J. Shen, Z. Ju, W. Zhao, L. Wang, Y. Peng, Z. Ge, Z.D. Nagel, J. Zou, C. Wang, P. Kapoor, X. Ma, D. Ma, J. Liang, S. Song, J. Liu, L.D. Samson, J.A. Ajani, G.M. Li, H. Liang, et al., ARID1A deficiency promotes mutability and potentiates therapeutic antitumor immunity unleashed by immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Med. 24(5), 556–562 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0012-z
J.S. Brown et al., Targeting DNA repair in cancer: beyond PARP inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 7(1), 20–37 (2017)
Y.E.A. Ged, Alterations in DNA damage repair (DDR) genes and outcomes to systemic therapy in 225 immune-oncology (IO) versus tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treated metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mccRCC) patients (pts). J. Clin. Oncol. (2019)
A. Raj, A. van Oudenaarden, Nature, nurture, or chance: stochastic gene expression and its consequences. Cell. 135(2), 216–226 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.050
C. Sun, R. Mezzadra, T.N. Schumacher, Regulation and function of the PD-L1 checkpoint. Immunity 48(3), 434–452 (2018)
Y. Ishida et al., Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 11(11), 3887–3895 (1992)
J.H. Yearley et al., PD-L2 expression in human tumors: relevance to anti-PD-1 therapy in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 23(12), 3158–3167 (2017)
L.K. Gauen et al., Interactions of p59fyn and ZAP-70 with T-cell receptor activation motifs: defining the nature of a signalling motif. Mol. Cell Biol. 14(6), 3729–3741 (1994)
D.B. Straus, A. Weiss, Genetic evidence for the involvement of the lck tyrosine kinase in signal transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell 70(4), 585–593 (1992)
K.M. Zak et al., Structure of the complex of human programmed death 1, PD-1, and its ligand PD-L1. Structure 23(12), 2341–2348 (2015)
M.J. Butte et al., Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically with the B7–1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses. Immunity 27(1), 111–122 (2007)
T.T. Chang et al., Studies in B7-deficient mice reveal a critical role for B7 costimulation in both induction and effector phases of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 190(5), 733–740 (1999)
T.J. Curiel et al., Blockade of B7–H1 improves myeloid dendritic cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Nat. Med. 9(5), 562–567 (2003)
H. Dong et al., B7–H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat. Med. 5(12), 1365–1369 (1999)
G.J. Freeman et al., Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 192(7), 1027–1034 (2000)
M.E. Keir et al., Tissue expression of PD-L1 mediates peripheral T cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 203(4), 883–895 (2006)
Y.E. Latchman et al., PD-L1-deficient mice show that PD-L1 on T cells, antigen-presenting cells, and host tissues negatively regulates T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101(29), 10691–10696 (2004)
E.J. Wherry, M. Kurachi, Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 15(8), 486–499 (2015)
F. Hirano et al., Blockade of B7–H1 and PD-1 by monoclonal antibodies potentiates cancer therapeutic immunity. Cancer Res. 65(3), 1089–1096 (2005)
D.L. Barber et al., Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439(7077), 682–687 (2006)
T. Azuma et al., B7–H1 is a ubiquitous antiapoptotic receptor on cancer cells. Blood 111(7), 3635–3643 (2008)
M. Gato-Canas et al., PDL1 signals through conserved sequence motifs to overcome interferon-mediated cytotoxicity. Cell Rep. 20(8), 1818–1829 (2017)
K.K. Frese, K.L. Simpson, C. Dive, Small cell lung cancer enters the era of precision medicine. Cancer Cell 39(3), 297–299 (2021)
A. Carretero-Gonzalez, et al., The value of PD-L1 expression as predictive biomarker in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Cancers (Basel) 12(7) (2020)
R.J. Motzer, N.M. Tannir, D.F. McDermott, O. Arén Frontera, B. Melichar, T.K. Choueiri, E.R. Plimack, P. Barthélémy, C. Porta, S. George, T. Powles, F. Donskov, V. Neiman, C.K. Kollmannsberger, P. Salman, H. Gurney, R. Hawkins, A. Ravaud, M.O. Grimm, et al., Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 378(14), 1277–1290 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1712126
R.J. Motzer et al., Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 380(12), 1103–1115 (2019)
A. Guida et al., Finding predictive factors for immunotherapy in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: What are we looking for? Cancer Treat Rev 94, 102157 (2021)
R. Sharma et al., Determinants of resistance to VEGF-TKI and immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40(1), 186 (2021)
Z. Song et al., RCAN1.4 acts as a suppressor of cancer progression and sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 372(2), 118–128 (2018)
R. Adelaiye-Ogala et al., EZH2 modifies sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma by kinome reprogramming. Cancer Res. 77(23), 6651–6666 (2017)
J. Zhao, J.L. Guan, Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28(1–2), 35–49 (2009)
D. You et al., FAK mediates a compensatory survival signal parallel to PI3K-AKT in PTEN-null T-ALL cells. Cell Rep. 10(12), 2055–2068 (2015)
K. Kataoka, M. Kurokawa, Ecotropic viral integration site 1, stem cell self-renewal and leukemogenesis. Cancer Sci. 103(8), 1371–1377 (2012)
A. Yoshimi et al., Evi1 represses PTEN expression and activates PI3K/AKT/mTOR via interactions with polycomb proteins. Blood 117(13), 3617–3628 (2011)
S. Lugthart et al., Aberrant DNA hypermethylation signature in acute myeloid leukemia directed by EVI1. Blood 117(1), 234–241 (2011)
L. Palomero et al., EVI1 as a prognostic and predictive biomarker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancers 12(2), 300 (2020)
C. Li, Automating dChip: toward reproducible sharing of microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 231 (2008)
M.L. Ascierto et al., The intratumoral balance between metabolic and immunologic gene expression is associated with anti-PD-1 response in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 4(9), 726–733 (2016)
W. Li et al., M2-polarization -relatedCNTNAP1 gene might be a novel immunotherapeutic target and biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. IUBMB Life 74(5), 391–407 (2022)
D. Bosse, M. Ong, Evolution in upfront treatment strategies for metastatic RCC. Nat. Rev. Urol. 17(2), 73–74 (2020)
D.M. Miller et al., c-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin. Cancer Res. 18(20), 5546–5553 (2012)
P. Maroto, E.F.N. Esteban, C-myc as a new predictive biomarker for sunitinib in metastatic renal clear cell carcinoma (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2012)
Y. Bao, A. Jiang, K. Dong, X. Gan, W. Gong, Z. Wu, B. Liu, Y. Bao, J. Wang, L. Wang, DDX39 as a predictor of clinical prognosis and immune checkpoint therapy efficacy in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17(12), 3158–3172 (2021). https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.62553
C.F. Xu et al., Pazopanib efficacy in renal cell carcinoma: evidence for predictive genetic markers in angiogenesis-related and exposure-related genes. J. Clin. Oncol. 29(18), 2557–2564 (2011)
Y. Qu et al., PAK1 expression determines poor prognosis and immune evasion in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Urol. Oncol. 38(4), 293–304 (2020)
J. Merhautova et al., miR-155 and miR-484 are associated with time to progression in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 1–5 (2015)
X. Tian et al., Identification of prognostic biomarkers in papillary renal cell carcinoma and PTTG1 may serve as a biomarker for predicting immunotherapy response. Ann. Med. 54(1), 211–226 (2022)
M. Bouattour et al., Recent developments of c-Met as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67(3), 1132–1149 (2018)
S. Halabi et al., Tissue based biomarkers in non-clear cell RCC: correlative analysis from the ASPEN clinical trial. Kidney Cancer J. 19(3), 64–72 (2021)
S. Storkel et al., Classification of renal cell carcinoma: Workgroup No. 1. Union Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC) and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC). Cancer 80(5), 987–9 (1997)
M.B. Amin et al., Prognostic impact of histologic subtyping of adult renal epithelial neoplasms: an experience of 405 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 26(3), 281–291 (2002)
C.G. Przybycin, A.M. Cronin, F. Darvishian, A. Gopalan, H.A. Al-Ahmadie, S.W. Fine, Y.B. Chen, M. Bernstein, P. Russo, V.E. Reuter, S.K. Tickoo, Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of 203 tumors in 200 patients with primary resection at a single institution. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 35(7), 962–970 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e31821a455d
J. Lennartsson, L. Ronnstrand, Stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit: from basic science to clinical implications. Physiol. Rev. 92(4), 1619–1649 (2012)
A. Marchetti, M. Rosellini, V. Mollica, A. Rizzo, E. Tassinari, G. Nuvola, A. Cimadamore, M. Santoni, M. Fiorentino, R. Montironi, F. Massari, The molecular characteristics of non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: what’s the story morning glory? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(12), 6237 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126237
G. Gezgin et al., Genetic evolution of uveal melanoma guides the development of an inflammatory microenvironment. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 66(7), 903–912 (2017)
A. Boilève, et al., Immune checkpoint inhibitors in MITF family translocation renal cell carcinomas and genetic correlates of exceptional responders. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 6(1) (2018)
J. Walton et al., PBRM1, SETD2 and BAP1 - the trinity of 3p in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 20(2), 96–115 (2023)
C. Xu, H. Ball, N. Bing, Association of genetic markers in angiogenesis- or exposure-related genes with overall survival in pazopanib treated patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. (2011)
A. Taguchi, N. Ohmiya, K. Shirai, N. Mabuchi, A. Itoh, Y. Hirooka, Y. Niwa, H. Goto, Interleukin-8 promoter polymorphism increases the risk of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer in Japan. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 14(11 Pt 1), 2487–2493 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0326
S.C. Tang et al., Brain accumulation of sunitinib is restricted by P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) and can be enhanced by oral elacridar and sunitinib coadministration. Int. J. Cancer 130(1), 223–233 (2012)
Y. Chu et al., Association of ABCB1 and FLT3 polymorphisms with toxicities and survival in asian patients receiving sunitinib for renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 10(8), e0134102 (2015)
E. Shiuan et al., Clinical features and multiplatform molecular analysis assist in understanding patient response to Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancers 13(6), 1475 (2021)
J.M. Taube et al., Association of PD-1, PD-1 ligands, and other features of the tumor immune microenvironment with response to anti–PD-1 therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 20(19), 5064–5074 (2014)
T.K. Choueiri, L. Albiges, J.B.A.G. Haanen, Biomarker analyses from JAVELIN Renal 101: Avelumab + axitinib (A+ Ax) versus sunitinib (S) in advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. (2019)
J.E. Darnell Jr., STATs and gene regulation. Science. 277(5332), 1630–1635 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5332.1630
J.F. Bromberg, M.H. Wrzeszczynska, G. Devgan, Y. Zhao, R.G. Pestell, C. Albanese, J.E. Darnell Jr., Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell. 98(3), 295–303 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81959-5
M.K. Wendt, N. Balanis, C.R. Carlin, W.P. Schiemann, STAT3 and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in carcinomas. JAKSTAT. 3(1), e28975 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4161/jkst.28975
H. Yu, R. Jove, The STATs of cancer--new molecular targets come of age. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4(2), 97–105 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1275
K. Yamamoto, T. Hara, T. Nakagawa, M. Hirai, H. Miyake, M. Fujisawa, I. Yano, Association of expression levels or activation status of STAT3 with treatment outcomes of sunitinib in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Target. Oncol. 13(3), 371–378 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-018-0563-4
R. Hoefflin et al., HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha differently regulate tumour development and inflammation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in mice. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 4111 (2020)
J. Eswaran et al., Molecular pathways: targeting p21-activated kinase 1 signaling in cancer–opportunities, challenges, and limitations. Clin. Cancer Res. 18(14), 3743–3749 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weijie Yan wrote the main part of the article. Naiqiao Hou, Wei Zhai & Junhua Zheng guided writing, offering suggestions to revise, reviewed and agreed upon the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics declarations
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, W., Hou, N., Zheng, J. et al. Predictive genomic biomarkers of therapeutic effects in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Oncol. 46, 1559–1575 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00827-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-023-00827-4