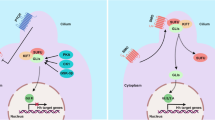
Abstract
Purpose
Previous studies have indicated that Hedgehog signaling is essential for gastric cancer development, but its precise role is still unclear. The aim of this study was to clarify the role of Hedgehog signaling in gastric cancer development.
Methods
The expression of key Hedgehog signaling components in clinical samples of sequential gastric cancer stages was assessed by immunohistochemistry. The roles and regulatory mechanisms of Hedgehog signaling in human gastric cancer cells and normal gastric epithelial cells were investigated using multiple cell biological approaches and cDNA microarray analyses.
Results
Hedgehog signaling was found to be abnormally activated in a ligand-independent manner during gastric cancer development. Gli1 over-expression and reduced SuFu expression were found to be typical events in gastric cancer tissues. Gli1 over-expression was found to correlate with a poorly differentiated histology, advanced clinical stage, membrane serosa infiltration and lymph node metastasis in patients with gastric cancer. Data obtained from multiple cell biological assays showed that human gastric cancer cells require active Hedgehog signaling for survival, proliferation, migration and colony formation. N-Shh treatment significantly enhanced the migration, invasion and colony formation of gastric cancer cells. Moreover, the results of cDNA microarray analyses indicated that after treatment with cyclopamine or GANT61 (inhibitors of Hedgehog signaling), differentially expressed genes in gastric cancer cells were enriched in the apoptosis and MAPK pathways. Inhibitors of the Hedgehog pathway were found to suppress gastric cancer cell growth via apoptosis induction.
Conclusions
Our findings indicate a vital role of the activated Hedgehog signaling pathway in promoting gastric initiation and progression. The Hedgehog signaling pathway may serve as a target for gastric cancer therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.J. Scales, F.J. de Sauvage, Mechanisms of Hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 30, 303–312 (2009)
L.G. Harris, R.S. Samant, L.A. Shevde, Hedgehog signaling: networking to nurture a promalignant tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer Res. 9, 1165–1174 (2011)
K.E. Ryan, C. Chiang, Hedgehog secretion and signal transduction in vertebrates. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 17905–17913 (2012)
J. Jiang, C.C. Hui, Hedgehog signaling in development and cancer. Dev. Cell 15, 801–812 (2008)
J.L. Merchant, Hedgehog signalling in gut development, physiology and cancer. J. Physiol. 590, 421–432 (2012)
A.M. Kenney, D.H. Rowitch, Sonic hedgehog promotes G(1) cyclin expression and sustained cell cycle progression in mammalian neuronal precursors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 9055–9067 (2000)
X. Chen, A. Horiuchi, N. Kikuchi, R. Osada, J. Yoshida, T. Shiozawa, I. Konishi, Hedgehog signal pathway is activated in ovarian carcinomas, correlating with cell proliferation: it’s inhibition leads to growth suppression and apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 98, 68–76 (2007)
A.E. Oro, K.M. Higgins, Z. Hu, J.M. Bonifas, E.H. Epstein Jr., M.P. Scott, Basal cell carcinomas in mice overexpressing sonic hedgehog. Science 276, 817–821 (1997)
E. Nieuwenhuis, C.C. Hui, Hedgehog signaling and congenital malformations. Clin. Genet. 67, 193–208 (2005)
S.S. Karhadkar, G.S. Bova, N. Abdallah, S. Dhara, D. Gardner, A. Maitra, J.T. Isaacs, D.M. Berman, P.A. Beachy, Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and metastasis. Nature 431, 707–712 (2004)
X. Liao, M.K. Siu, C.W. Au, E.S. Wong, H.Y. Chan, P.P. Ip, H.Y. Ngan, A.N. Cheung, Aberrant activation of hedgehog signaling pathway in ovarian cancers: effect on prognosis, cell invasion and differentiation. Carcinogenesis 30, 131–140 (2009)
F.G. Xu, Q.Y. Ma, Z. Wang, Blockade of hedgehog signaling pathway as a therapeutic strategy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 283, 119–124 (2009)
M. Fukaya, N. Isohata, H. Ohta, K. Aoyagi, T. Ochiya, N. Saeki, K. Yanagihara, Y. Nakanishi, H. Taniguchi, H. Sakamoto, T. Shimoda, Y. Nimura, T. Yoshida, H. Sasaki, Hedgehog signal activation in gastric pit cell and in diffuse-type gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 131, 14–29 (2006)
C. Xiao, S.A. Ogle, M.A. Schumacher, M.A. Orr-Asman, M.L. Miller, N. Lertkowit, A. Varro, F. Hollande, Y. Zavros, Loss of parietal cell expression of Sonic hedgehog induces hypergastrinemia and hyperproliferation of surface mucous cells. Gastroenterology 138(550–561), e551–e558 (2010)
Y.A. Yoo, M.H. Kang, H.J. Lee, B.H. Kim, J.K. Park, H.K. Kim, J.S. Kim, S.C. Oh, Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71, 7061–7070 (2011)
M. Waghray, Y. Zavros, M. Saqui-Salces, M. El-Zaatari, C.B. Alamelumangapuram, A. Todisco, K.A. Eaton, J.L. Merchant, Interleukin-1beta promotes gastric atrophy through suppression of Sonic Hedgehog. Gastroenterology 138(562–572), e561–e562 (2010)
A. Shiotani, H. Iishi, N. Uedo, S. Ishiguro, M. Tatsuta, Y. Nakae, M. Kumamoto, J.L. Merchant, Evidence that loss of sonic hedgehog is an indicator of Helicobater pylori-induced atrophic gastritis progressing to gastric cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 100, 581–587 (2005)
T.M. Hall, J.A. Porter, P.A. Beachy, D.J. Leahy, A potential catalytic site revealed by the 1.7-A crystal structure of the amino-terminal signalling domain of Sonic hedgehog. Nature 378, 212–216 (1995)
R.G. Chubet, B.L. Brizzard, Vectors for expression and secretion of FLAG epitope-tagged proteins in mammalian cells. Biotechniques 20, 136–141 (1996)
R. Yan, Y. Yang, Y. Zeng, G. Zou, Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of Lindera strychnifolia essential oils and extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 121, 451–455 (2009)
C.C. Liang, A.Y. Park, J.L. Guan, In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2, 329–333 (2007)
J.B. Wang, W.J. Wu, R.A. Cerione, Cdc42 and Ras cooperate to mediate cellular transformation by intersectin-L. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 22883–22891 (2005)
H. Elmasri, E. Ghelfi, C.W. Yu, S. Traphagen, M. Cernadas, H. Cao, G.P. Shi, J. Plutzky, M. Sahin, G. Hotamisligil, S. Cataltepe, Endothelial cell-fatty acid binding protein 4 promotes angiogenesis: role of stem cell factor/c-kit pathway. Angiogenesis 15, 457–468 (2012)
D.N. Dhanasekaran, E.P. Reddy, JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 27, 6245–6251 (2008)
M. Gupta, S.K. Gupta, B. Hoffman, D.A. Liebermann, Gadd45a and Gadd45b protect hematopoietic cells from UV-induced apoptosis via distinct signaling pathways, including p38 activation and JNK inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 17552–17558 (2006)
R.J. Dickinson, S.M. Keyse, Diverse physiological functions for dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases. J. Cell Sci. 119, 4607–4615 (2006)
T. Tanos, M.J. Marinissen, F.C. Leskow, D. Hochbaum, H. Martinetto, J.S. Gutkind, O.A. Coso, Phosphorylation of c-Fos by members of the p38 MAPK family. Role in the AP-1 response to UV light. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 18842–18852 (2005)
P. Correa, Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process–First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Res. 52, 6735–6740 (1992)
L.H. Wang, Y.L. Choi, X.Y. Hua, Y.K. Shin, Y.J. Song, S.J. Youn, H.Y. Yun, S.M. Park, W.J. Kim, H.J. Kim, J.S. Choi, S.H. Kim, Increased expression of sonic hedgehog and altered methylation of its promoter region in gastric cancer and its related lesions. Mod. Pathol. 19, 675–683 (2006)
G.I. Evan, K.H. Vousden, Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature 411, 342–348 (2001)
M.C. Hollander, Q. Zhan, I. Bae, A.J. Fornace Jr., Mammalian GADD34, an apoptosis- and DNA damage-inducible gene. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 13731–13737 (1997)
B. Yi, M. Zhang, R. Schwartz-Albiez, Y. Cao, Mechanisms of the apoptosis induced by CD176 antibody in human leukemic cells. Int. J. Oncol. 38, 1565–1573 (2011)
H.J. Cho, S.M. Park, E.M. Hwang, K.E. Baek, I.K. Kim, I.K. Nam, M.J. Im, S.H. Park, S. Bae, J.Y. Park, J. Yoo, Gadd45b mediates Fas-induced apoptosis by enhancing the interaction between p38 and retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 25500–25505 (2010)
J. Seoane, H.V. Le, J. Massague, Myc suppression of the p21(Cip1) Cdk inhibitor influences the outcome of the p53 response to DNA damage. Nature 419, 729–734 (2002)
Z. Klase, R. Winograd, J. Davis, L. Carpio, R. Hildreth, M. Heydarian, S. Fu, T. McCaffrey, E. Meiri, M. Ayash-Rashkovsky, S. Gilad, Z. Bentwich, F. Kashanchi, HIV-1 TAR miRNA protects against apoptosis by altering cellular gene expression. Retrovirology 6, 18 (2009)
O. Nesic, G.Y. Xu, D. McAdoo, K.W. High, C. Hulsebosch, R. Perez-Pol, IL-1 receptor antagonist prevents apoptosis and caspase-3 activation after spinal cord injury. J. Neurotrauma 18, 947–956 (2001)
D. Sarkar, Z.Z. Su, I.V. Lebedeva, M. Sauane, R.V. Gopalkrishnan, K. Valerie, P. Dent, P.B. Fisher, mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 10054–10059 (2002)
J.M. Fear, P.J. Hansen, Developmental changes in expression of genes involved in regulation of apoptosis in the bovine preimplantation embryo. Biol. Reprod. 84, 43–51 (2011)
A.S. Dhillon, S. Hagan, O. Rath, W. Kolch, MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 26, 3279–3290 (2007)
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Libin Deng and Miss Yujia Zhou for analysis of cDNA microarray data. Further, we greatly acknowledge Drs. Yong Li and Xuan Huang for the technical assistance. This work was supported in part by grants from the China National Basic Research Program (2010CB535001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31260278, 81060095 and 31171359), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (2009GZY0209, 20114BAB205035, 20114BAB215029) and the National Science and Technology Major Projects program for “Major New Drugs Innovation and Development” of China (2011ZX09302-007-03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, R., Peng, X., Yuan, X. et al. Suppression of growth and migration by blocking the hedgehog signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 36, 421–435 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-013-0149-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-013-0149-1