Abstract
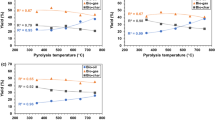
Cotton stalks and other agricultural crop residues are available in plenty and are very potential as an energy source in Saurashtra region. These residues are sometimes, burnt in the field itself which creates an adverse condition to soil health. The objective of this research study was to develop a pyrolyser, methodology, to identify the physical-chemical-thermal properties and elemental analysis of bio-char. A small capacity (5 kg/batch) biomass pyrolyser was designed and developed for making bio-char from the shredded cotton stalk as feed stalk. Pyrolysis at various experimental temperatures 200, 300, 400 and 500 °C and residence time 60, 120, 180 and 240 min carried out for optimal parameter estimation. The quality of bio-char obtained at 500 °C temperature and 240 min is best out of the all experimental parameters. The calorific value of bio-char measured 33.89 MJ/kg and contents of nitrogen 1.56%, carbon 79.30% with C/N ratio 50.83. Conversion of agricultural residues into bio-char, bio-oil and pyro-gas will be a good option to be used as fuel and a safe sustainable soil amendment of bio-char to improve fertility.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2015) World Energy Issues Monitor. Available at https://www.worldenergy.org/publications/2015/worldenergyissuesmonitor-2015. Accessed 12 June 2017
ASTM E870-82 (2013) Standard Test Methods for Analysis of Wood Fuels. In: ASTM International, West Conshohocken www.astm.org
Herbert L, Hosek I, Kripalani R (2012) The characterization and comparison of biochar produced from a decentralized reactor using forced air and natural draft pyrolysis. Dissertation, California polytechnic state university, San Luis Obispo materials engineering department, pp 0–36
Jahiru MI, Rasul MG, Chowdhury AA, Ashwath N (2012) Biofuels production through biomass pyrolysis. Energies 5(12):4952–5001
Kumar S, Masto RE, Ram LC, Sarkar P, George J, Selvi VA (2013) Biochar preparation from Parthenium hysterophorus and its potential use in soil application. Ecol Eng 55:67–72
Maiti S, Dey S, Purakayastha S, Ghosh B (2006) Physical and thermochemical characterization of rice husk char as a potential biomass energy source. Bioresour Technol 97(16):2065–2070
McHenry MP (2009) Agricultural Bio-char production, renewable energy generation and farm carbon sequestration in Western Australia: certainty, uncertainty and risk. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129:1–7
Meyer S, Glaser B, Quicker P (2011) Technical, economical, and climate-related aspects of bio-char production technologies: a literature review. Environ Sci Technol 45(22):9473–9483
Novak JM, Lima I, Xing B, Gaskin JW, Steiner C, Das KC, Schomberg H (2009) Characterization of designer bio-char produced at different temperatures and their effects on a loamy sand. Ann Environ Sci 3:195–206
Ryu C, Sharifi VN, Swithenbank J (2007) Waste pyrolysis and generation of storable char. Int J Energy Res 31:177–191
Sohi S, Krull E, Lopez Capel E, Bol R (2010) A review of bio-char and its use and function in soil. Adv Agron 105:47–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(10)05002-9
Venkatesh G, Srinivarao C, Venkateswarlu B, Gopinath KA, Prasad JNVS, Raddy Sanjeeva B, Sasikala C, Rao GR, Ramesh Babu PV (2013) Operational process for bio-char preparation from castor bean stalk and its characterization for soil application. Indian Journal of dryland Agricultural. Res Dev 28(2):21–26
Funding
This study is timely financially supported to develop and test pyrolyser by the authorities of Renewable Energy Engineering Department, CAET, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh (Gujarat), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6392 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makavana, J.M., Kalaiya, S.V., Dulawat, M.S. et al. Development and performance evaluation of batch type biomass pyrolyser for agricultural residue. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 12, 5067–5074 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01105-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01105-1