Abstract
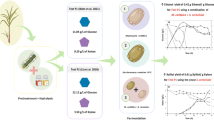
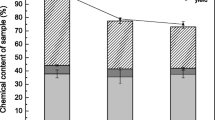
Researches on second-generation ethanol, produced from agroindustrial wastes, have demanded special attention as a possible solution to energy sustainability. Such production is based on lignocellulosic fiber conversion, which generates fermentable sugars that are biotransformed into ethanol. This work aimed at evaluating ethanol production by the yeast Pichia stipitis ATCC 58376 in the hemicellulosic hydrolysate of sunflower meal biomass, a subproduct generated by sunflower oil manufactures. Sunflower meal was submitted to dilute acid hydrolysis with 6 % (w/v) H2SO4 in autoclave, at 121 °C, for 20 min and resulted in a hemicellulosic hydrolysate with high concentration of sugars (24.98 g/L xylose, 26.55 g/L glucose, and 6.51 g/L arabinose) and low amounts of toxic compounds (3.04 g/L total phenols, 0.58 g/L acetic acid, 0.40 g/L furfural, and 0.09 g/L hydroxymethylfurfural). The fermentations of the detoxified hydrolysate were conducted in Erlenmeyer flasks at 30 °C, initial pH 5.5, under different agitation speeds (100, 150, and 200 rpm). The best ethanol production (8.8 g/L ethanol, yield of 0.23 g/g, and productivity of 0.12 g/L h) was attained at 200 rpm. The results demonstrate that sunflower meal is a promising biomass for ethanol production from its hemicellulosic fraction. In addition, the hemicellulosic hydrolysate has the advantage of not requiring a sugar concentration step, which contributes to the economic viability of the process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joshi B, Bhatt MR, Sharma D, Joshi J, Malla R, Sreerama L (2011) Lignocellulosic ethanol production: current practices and recent developments. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 6(8):172–182
Zhang W, Geng A (2012) Improved ethanol production by a xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strain constructed through a modified genome shuffling method. Biotechnol Fuel 5:1–11
Canilha L, Chandel AK, Milessi TSS, Antunes FAF, Freitas WLC, Felipe MGA, Silva SS (2012) Bioconversion of sugarcane biomass into ethanol: an overview about composition, pretreatment methods, detoxification of hydrolysates, enzymatic saccharification, and ethanol fermentation. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2012/989572
Lee SH, Kodaki T, Park YC, Seo JH (2012) Effects of NADH-preferring xylose reductase expression on ethanol production from xylose in xylose-metabolizing recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol 158(4):184–91
Agbogbo FK, Coward-Kelly G (2008) Cellulosic ethanol production using the naturally occurring xylose-fermenting yeast, Pichia stipitis. Biotechnol Lett 30(9):1515–1524
Bettiga M, Bengtsson O, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2009) Arabinose and xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing a fungal pentose utilization pathway. Microb Cell Fact 8:40
Nigam JN (2001) Development of xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis for ethanol production through adaptation on hardwood hemicellulosic acid prehydrolysate. J Appl Microbiol 90:208–215
Nigam JN (2001) Ethanol production from wheat straw hemicellulose hydrolysate by Pichia stipitis. J Biotechnol 87(1):17–27
Agbogbo FK, Wenger KS (2007) Production of ethanol from corn stover hemicellulose hydrolyzate using Pichia stipitis. J Ind Microbiol Biot 34:723–727
Kurian JK, Minu AK, Aditi B, Kishore VVN (2010) Bioconversion of hemicellulose hydrolysate of sweet sorghum bagasse to ethanol by using Pichia stipitis NCIM 3947 and Debaryomyces hansenii sp. Bioresource 5(4):2404–1416
Lin TH, Huang CF, Guo GL, Hwang WS, Huang SL (2012) Pilot-scale ethanol production from rice straw hydrolysates using xylose-fermenting Pichia stipitis. Bioresour Technol 116:314–319
Evon P, Vandenbossche V, Ponta-Lier PY, Rigal L (2009) Aqueous extraction of residual oil from sunflower press cake using a twin-screw extruder: feasibility study. Ind Crop Prod 29(2–3):455–465
Sakthiselvan P, Naveena B, Partha N (2012) Effect of medium composition and ultrasonication on xylanase production by Trichoderma harzianum MTCC 4358 on novel substrate. Afr J Biotechnol 11(57):12067–12077
Ramachandran S, Singh SK, Larroche C, Soccol CR, Pandey A (2007) Oil cakes and their biotechnological applications—a review. Bioresour Technol 98(10):2000–2009
Mushtaq T, Sarwar M, Ahmad G, Mirza MA, Ahmad T, Noreen U, Mushtaq MMH, Kamran Z (2009) Influence of sunflower meal based diets supplemented with exogenous enzyme and digestible lysine on performance, digestibility and carcass response of broiler chickens. Anim Feed Sci Tech 149(3–4):275–286
Lozano NBS, Vidal AT, Martínez-Liorens S, Mérida SN, Blanco JE, López AM, Torres MP, Cerdá MJ (2007) Growth and economic profit of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) fed sunflower meal. Aquaculture 272(1–4):528–534
Musharaf (1991) Effect of graded levels of sunflower seed meal in broiler diets. Anim Feed Sci Tech 33(1–2):129–137
Telli-Okur M, Eken-Saraçoğlu N (2006) Ethanol production from sunflower seed hull hydrolysate by Pichia stipitis under uncontrolled pH conditions in a bioreactor. Turkish J Eng Environ Sci 30:317–322
Telli-Okur M, Eken-Saraçoğlu N (2008) Fermentation of sunflower seed hull hydrolysate to ethanol by Pichia stipitis. Bioresour Technol 99(7):2162–2169
Jargalsaikhan O, Saraçoglu N (2009) Application of experimental design method for ethanol production by fermentation of sunflower seed hull hydrolysate using Pichia stipitis NRRL-124. Chem Eng Commun 196:93–103
Sharma SK, Kaira KL, Kocher GS (2004) Fermentation of enzymatic hydrolysate of sunflower hulls for ethanol production and its scale-up. Biomass Bioenergy 27:399–402
Kamireddy SR, Schaefer C, Defrese M, Degenstein J, Ji Y (2012) Pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of sunflower hulls for fermentable sugar production. Int J Agric Biol Eng 5(1):62–70
Gouveia ER, Nascimento RT, Souto-Maior AM (2009) Validação de metodologia para a caracterização química de bagaço de cana-de-açúcar. Quím Nova 32:1500–1503
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol 299:152–178
Demirbas A (2006) Effect of temperature on pyrolysis products from four nut shells. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 76:285–289
Ruiz E, Romero I, Moya M, Cara C, Vidal JD, Castro E (2013) Dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of sunflower stalks for sugar production. Bioresour Technol 140:292–298
Martin C, Alriksson B, Sjode A, Nilvebrant NO, Jonsson LJ (2007) Dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of agricultural and agro-industrial residues for ethanol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 137:339–352
Bellido C, Bolado S, Coca M, Lucas S, González-Benito G, García-Cubero MT (2011) Effect of inhibitors formed during wheat straw pretreatment on ethanol fermentation by Pichia stipitis. Bioresour Technol 102:10868–10874
Silva JPA, Mussatto SI, Roberto IC, Teixeira JA (2011) Ethanol production from xylose by Pichia stipitis NRRL Y-7124 in a stirred tank bioreactor. Braz J Chem Eng 28(1):151–156
Sánchez S, Bravo V, Castro E, Moya AJ, Camacho F (2002) The fermentation of mixtures of D-glucose and D-xylose by Candida shehatae, Pichia stipitis or Pachysolen tannophilus to produce ethanol. J Chem Technol Biot 77(6):641–648
Agbogbo FK, Coward-Kelly G, Torry-Smith M, Wenger KS (2006) Fermentation of glucose/xylose mixtures using Pichia stipitis. Process Biochem 41(11):2333–2336
Skoog K, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1990) Effect of oxygenation on xylose fermentation by Pichia stipitis. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(11):3389–3394
Stoutenburg RM, Perrotta JA, Amidon TE, Nakas JP (2008) Ethanol production from a membrane purified hemicellulosic hydrolysate derived from sugar maple by Pichia stipitis NRRL Y-7124. Bioresource 3(4):1349–1358
Silva JP, Mussatto SI, Roberto IC (2010) The influence of initial xylose concentration, agitation, and aeration on ethanol production by Pichia stipitis from rice straw hemicellulosic hydrolysate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162(5):1306–1315
Shupe AM, Liu S (2012) Effect of agitation rate on ethanol production from sugar maple hemicellulosic hydrolysate by Pichia stipitis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168(1):29–36
Van Zyl C, Prior BA, du Preez JC (1991) Acetic acid inhibition of D-xylose fermentation by Pichia stipitis. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:82–86
Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1991) Xylose metabolism by Pichia stipitis: the effect of ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:656–661
Sene L, Arruda PV, Oliveira SMM, Felipe MGA (2011) Evaluation of sorghum straw hemicellulosic hydrolysate for biotechnological production of xylitol by Candida guilliermondii. Braz J Microbiol 42(3):1141–1146
Scordia D, Consentino SL, Lee JW, Jeffries TW (2012) Bioconversion of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) hemicellulose hydrolysate to ethanol by Scheffersomyces stipitis CBS6054. Biomass Bioenerg 39:296–305
Arruda PV, Felipe MG (2009) Role of glycerol addition on xylose-to-xylitol bioconversion by Candida guilliermondii. Curr Microbiol 58(3):274–278
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the company Caramuru SA for providing the sunflower meal and the Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq) and Itaipu Technological Park (PTI) for master’s degree scholarship to Danielle Camargo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camargo, D., Sene, L. Production of ethanol from the hemicellulosic fraction of sunflower meal biomass. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 4, 87–93 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-013-0096-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-013-0096-0