Abstract
Announced as one of the top 10 research breakthroughs in 2016, perovskite solar cells (PSC) have advanced rapidly as an established photovoltaic technology. The power conversion efficiency (PCE) of PSCs has increased quickly from 3.8% to 23.7% within a period of just 7 years. This very high PCE has been achieved by using perovskite compounds with lead (Pb) as the divalent metal ion. However, for further scale-up and commercialization, the toxicity of Pb has been identified as one of the key drawbacks for this technology. Numerous avenues for development of lead-free low-toxicity perovskite absorbers have been pursued. The unclear effect of using low-toxicity materials on optimal performance with suitable characteristics has motivated the writing of this review. Results from low-toxicity perovskite solar cells utilizing partial or complete substitution of the Pb2+ cation as the absorber layer are discussed in detail. Moreover, we discuss the limitations of low-toxicity absorber materials. This review summarizes the key points of film quality control, degradation effect, Pb replacement suitability, and photovoltaic performance of reported low toxicity alternate perovskite absorbers for PSCs.
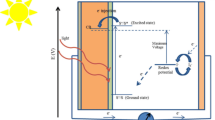
Graphical Abstract


Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons

Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society

Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society

Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society

Copyright 2016 John Wiley & Sons

Copyright 2016 John Wiley & Sons

Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society

Copyright 2017, Elsevier

Copyright 2017, Royal Society of Chemistry

Copyright 2017, Royal Society of Chemistry

Copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry

Copyright 2016, Nature Publishing Group

Copyright 2015, Royal Society of Chemistry

Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society

Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society

Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. (Color figure online)

Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima, A., Teshima, K., Shirai, Y., Miyasaka, T.: Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 6050–6051 (2009)
Im, J.-H., Lee, C.-R., Lee, J.-W., Park, S.-W., Park, N.-G.: 6.5% efficient perovskite quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell. Nanoscale 3, 4088–4093 (2011)
Kim, H.-S., Lee, C.-R., Im, J.-H., Lee, K.-B., Moehl, T., Marchioro, A., Moon, S.-J., Humphry-Baker, R., Yum, J.-H., Moser, J.E.: Lead iodide perovskite sensitized all-solid-state submicron thin film mesoscopic solar cell with efficiency exceeding 9%. Sci. Rep. 2, 591 (2012)
Lee, M.M., Teuscher, J., Miyasaka, T., Murakami, T.N., Snaith, H.J.: Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 338, 643–647 (2012)
Burschka, J., Pellet, N., Moon, S.-J., Humphry-Baker, R., Gao, P., Nazeeruddin, M.K., Grätzel, M.: Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature 499, 316–319 (2013)
Chen, Q., Zhou, H., Hong, Z., Luo, S., Duan, H.-S., Wang, H.-H., Liu, Y., Li, G., Yang, Y.: Planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells via vapor-assisted solution process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 622–625 (2013)
Wu, Y., Islam, A., Yang, X., Qin, C., Liu, J., Zhang, K., Peng, W., Han, L.: Retarding the crystallization of PbI2 for highly reproducible planar-structured perovskite solar cells via sequential deposition. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 2934–2938 (2014)
Son, D.-Y., Im, J.-H., Kim, H.-S., Park, N.-G.: 11% efficient perovskite solar cell based on ZnO nanorods: an effective charge collection system. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 16567–16573 (2014)
Eperon, G.E., Burlakov, V.M., Docampo, P., Goriely, A., Snaith, H.J.: Morphological control for high performance, solution-processed planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 151–157 (2014)
Kumar, M.H., Yantara, N., Dharani, S., Graetzel, M., Mhaisalkar, S., Boix, P.P., Mathews, N.: Flexible, low-temperature, solution processed ZnO-based perovskite solid state solar cells. Chem. Commun. 49, 11089–11091 (2013)
Gilfillan, S.C.: Lead poisoning and the fall of Rome. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 7, 53–60 (1965)
Noel, N.K., Stranks, S.D., Abate, A., Wehrenfennig, C., Guarnera, S., Haghighirad, A.-A., Sadhanala, A., Eperon, G.E., Pathak, S.K., Johnston, M.B.: Lead-free organic–inorganic tin halide perovskites for photovoltaic applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3061–3068 (2014)
Park, B.W., Philippe, B., Zhang, X., Rensmo, H., Boschloo, G., Johansson, E.M.: Bismuth based hybrid perovskites A3Bi2I9 (A: methylammonium or cesium) for solar cell application. Adv. Mater. 27, 6806–6813 (2015)
Cortecchia, D., Dewi, H.A., Yin, J., Bruno, A., Chen, S., Baikie, T., Boix, P.P., Grätzel, M., Mhaisalkar, S., Soci, C.: Lead-free MA2CuClxBr 4–x hybrid perovskites. Inorg. Chem. 55, 1044–1052 (2016)
Hebig, J.-C., Kühn, I., Flohre, J., Kirchartz, T.: Optoelectronic properties of (CH3NH3)3Sb2I9 thin films for photovoltaic applications. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 309–314 (2016)
Chen, W., Wu, Y., Yue, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, W., Yang, X., Chen, H., Bi, E., Ashraful, I., Grätzel, M.: Efficient and stable large-area perovskite solar cells with inorganic charge extraction layers. Science 2015(350), 944–948 (2015)
Wu, Y., Yang, X., Chen, W., Yue, Y., Cai, M., Xie, F., Bi, E., Islam, A., Han, L.: Perovskite solar cells with 18.21% efficiency and area over 1 cm2 fabricated by heterojunction engineering. Nat. Energy 1, 16148 (2016)
Mitzi, D., Feild, C., Harrison, W., Guloy, A.: Conducting tin halides with a layered organic-based perovskite structure. Nature 369, 467–469 (1994)
Mitzi, D.B., Feild, C., Schlesinger, Z., Laibowitz, R.: Transport, optical, and magnetic properties of the conducting halide perovskite CH3NH3SnI3. J. Solid State Chem. 114, 159–163 (1995)
Kumar, M.H., Dharani, S., Leong, W.L., Boix, P.P., Prabhakar, R.R., Baikie, T., Shi, C., Ding, H., Ramesh, R., Asta, M.: Lead-free halide perovskite solar cells with high photocurrents realized through vacancy modulation. Adv. Mater. 26, 7122–7127 (2014)
Eperon, G.E., Stranks, S.D., Menelaou, C., Johnston, M.B., Herz, L.M., Snaith, H.J.: Formamidinium lead trihalide: a broadly tunable perovskite for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 982–988 (2014)
Hao, F., Stoumpos, C.C., Guo, P., Zhou, N., Marks, T.J., Chang, R.P., Kanatzidis, M.G.: Solvent-mediated crystallization of CH3NH3SnI3 films for heterojunction depleted perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 11445–11452 (2015)
Liao, W., Zhao, D., Yu, Y., Shrestha, N., Ghimire, K., Grice, C.R., Wang, C., Xiao, Y., Cimaroli, A.J., Ellingson, R.J.: Fabrication of efficient low-bandgap perovskite solar cells by combining formamidinium tin iodide with methylammonium lead iodide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 12360–12363 (2016)
Wang, Z.K., Li, M., Yang, Y.G., Hu, Y., Ma, H., Gao, X.Y., Liao, L.S.: High efficiency Pb–In binary metal perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 28, 6695–6703 (2016)
Liao, W., Zhao, D., Yu, Y., Grice, C.R., Wang, C., Cimaroli, A.J., Schulz, P., Meng, W., Zhu, K., Xiong, R.G.: Lead-free inverted planar formamidinium tin triiodide perovskite solar cells achieving power conversion efficiencies up to 6.22%. Adv. Mater. 28, 9333–9340 (2016)
Tsai, C.-M., Wu, H.-P., Chang, S.-T., Huang, C.-F., Wang, C.-H., Narra, S., Yang, Y.-W., Wang, C.-L., Hung, C.-H., Diau, E.W.-G.: Role of tin chloride in tin-rich mixed-halide perovskites applied as mesoscopic solar cells with a carbon counter electrode.”. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 1086–1093 (2016)
Zhang, J., Shang, M.-H., Wang, P., Huang, X., Xu, J., Hu, Z., Zhu, Y., Han, L.: n-Type Doping and Energy States Tuning in CH3NH3Pb1–x Sb2 x/3I3 Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 535–541 (2016)
Ogomi, Y., Morita, A., Tsukamoto, S., Saitho, T., Fujikawa, N., Shen, Q., Toyoda, T., Yoshino, K., Pandey, S.S., Ma, T.: CH3NH3SnxPb(1–x)I3 perovskite solar cells covering up to 1060 nm. J phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 1004–1011 (2014)
Stoumpos, C.C., Malliakas, C.D., Kanatzidis, M.G.: Semiconducting tin and lead iodide perovskites with organic cations: phase transitions, high mobilities, and near-infrared photoluminescent properties. Inorg. Chem. 52, 9019–9038 (2013)
Kayesh, M.E., Chowdhury, T.H., Matsuishi, K., Kaneko, R., Kazaoui, S., Lee, J.J., Noda, T., Islam, A.: Enhanced photovoltaic performance of FASnI3-based perovskite solar cells with hydrazinium chloride coadditive. ACS Energy Lett. 3(7), 1584–1589 (2018)
Hao, F., Stoumpos, C.C., Chang, R.P., Kanatzidis, M.G.: Anomalous band gap behavior in mixed Sn and Pb perovskites enables broadening of absorption spectrum in solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 8094–8099 (2014)
Yang, L., Cappel, U.B., Unger, E.L., Karlsson, M., Karlsson, K.M., Gabrielsson, E., Sun, L., Boschloo, G., Hagfeldt, A., Johansson, E.M.: Comparing spiro-OMeTAD and P3HT hole conductors in efficient solid state dye-sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 779–789 (2012)
Zuo, F., Williams, S.T., Liang, P.W., Chueh, C.C., Liao, C.Y., Jen, A.K.Y.: Binary-metal perovskites toward high-performance planar-heterojunction hybrid solar cells. Adv. Mater. 26, 6454–6460 (2014)
Chen, Q., Zhou, H., Fang, Y., Stieg, A.Z., Song, T.-B., Wang, H.-H., Xu, X., Liu, Y., Lu, S., You, J.: The optoelectronic role of chlorine in CH3NH3PbI3(Cl)-based perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 6, 7269 (2015)
Docampo, P., Hanusch, F.C., Stranks, S.D., Döblinger, M., Feckl, J.M., Ehrensperger, M., Minar, N.K., Johnston, M.B., Snaith, H.J., Bein, T.: Solution deposition-conversion for planar heterojunction mixed halide perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 1400355 (2014)
Lee, S.J., Shin, S.S., Kim, Y.C., Kim, D., Ahn, T.K., Noh, J.H., Seo, J., Seok, S.I.: Fabrication of efficient formamidinium tin iodide perovskite solar cells through SnF2–pyrazine complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 3974–3977 (2016)
Koh, T.M., Krishnamoorthy, T., Yantara, N., Shi, C., Leong, W.L., Boix, P.P., Grimsdale, A.C., Mhaisalkar, S.G., Mathews, N.: Formamidinium tin-based perovskite with low Eg for photovoltaic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 14996–15000 (2015)
Koh, T.M., Fu, K., Fang, Y., Chen, S., Sum, T., Mathews, N., Mhaisalkar, S.G., Boix, P.P., Baikie, T.: Formamidinium-containing metal-halide: an alternative material for near-IR absorption perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 16458–16462 (2013)
Wetzelaer, G.J.A., Scheepers, M., Sempere, A.M., Momblona, C., Ávila, J., Bolink, H.J.: Trap-assisted non-radiative recombination in organic–inorganic perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 27, 1837–1841 (2015)
Yang, Z., Rajagopal, A., Jo, S.B., Chueh, C.-C., Williams, S., Huang, C.-C., Katahara, J.K., Hillhouse, H.W., Jen, A.K.-Y.: Stabilized wide bandgap perovskite solar cells by tin substitution. Nano Lett. 16, 7739–7747 (2016)
Zhang, M., Lyu, M., Yu, H., Yun, J.H., Wang, Q., Wang, L.: Stable and low-cost mesoscopic CH3NH3PbI2Br perovskite solar cells by using a thin poly(3-hexylthiophene) layer as a hole transporter. Chem. Eur. J. 21, 434–439 (2015)
Colella, S., Mosconi, E., Fedeli, P., Listorti, A., Gazza, F., Orlandi, F., Ferro, P., Besagni, T., Rizzo, A., Calestani, G.: MAPbI3-xClx mixed halide perovskite for hybrid solar cells: the role of chloride as dopant on the transport and structural properties. Chem. Mater. 25, 4613–4618 (2013)
Yang, Z., Chueh, C.-C., Liang, P.-W., Crump, M., Lin, F., Zhu, Z., Jen, A.K.-Y.: Effects of formamidinium and bromide ion substitution in methylammonium lead triiodide toward high-performance perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 22, 328–337 (2016)
Hu, M., Bi, C., Yuan, Y., Bai, Y., Huang, J.: Stabilized wide bandgap MAPbBrxI3–x perovskite by enhanced grain size and improved crystallinity. Adv. Sci. 3(6), 1500301 (2016)
Braly, I.L., Hillhouse, H.W.: Optoelectronic quality and stability of hybrid perovskites from MAPbI3 to MAPbI2Br using composition spread libraries. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 893–902 (2016)
Goldschmidt, V.M.: Die gesetze der krystallochemie. Naturwissenschaften 14, 477–485 (1926)
Hesse, S., Zimmermann, J., Von Seggern, H., Ehrenberg, H., Fuess, H., Fasel, C., Riedel, R.: CsEuBr 3: crystal structure and its role in the photostimulation of Cs Br:Eu2+. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 083506 (2006)
Shirwadkar, U., van Loef, E., Hawrami, R., Mukhopadhyay, S., Glodo, J., Shah, K.: New promising scintillators for gamma-ray spectroscopy: Cs (Ba,Sr)(Br,I)3. In: IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, 1583-1585 (2011)
Stoumpos, C.C., Kanatzidis, M.G.: The renaissance of halide perovskites and their evolution as emerging semiconductors. Acc. Chem. Res. 48, 2791–2802 (2015)
Frolova, L.A., Anokhin, D.V., Gerasimov, K.L., Dremova, N.N., Troshin, P.A.: Exploring the effects of the Pb2+ substitution in MAPbI3 on the photovoltaic performance of the hybrid perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 4353–4357 (2016)
Zhang, W., Saliba, M., Moore, D.T., Pathak, S.K., Hörantner, M.T., Stergiopoulos, T., Stranks, S.D., Eperon, G.E., Alexander-Webber, J.A., Abate, A.: Ultrasmooth organic–inorganic perovskite thin-film formation and crystallization for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells. Nat. Commun. 6, 6142 (2015)
Unger, E.L., Bowring, A.R., Tassone, C.J., Pool, V.L., Gold-Parker, A., Cheacharoen, R., Stone, K.H., Hoke, E.T., Toney, M.F., McGehee, M.D.: Chloride in lead chloride-derived organo-metal halides for perovskite-absorber solar cells. Chem. Mater. 26, 7158–7165 (2014)
Colella, S., Mosconi, E., Pellegrino, G., Alberti, A., Guerra, V.L., Masi, S., Listorti, A., Rizzo, A., Condorelli, G.G., De Angelis, F.: Elusive presence of chloride in mixed halide perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 3532–3538 (2014)
Pérez-del-Rey, D., Forgács, D., Hutter, E.M., Savenije, T.J., Nordlund, D., Schulz, P., Berry, J.J., Sessolo, M., Bolink, H.J.: Strontium Insertion in methylammonium lead iodide: long charge carrier lifetime and high fill-factor solar cells. Adv. Mater. 28, 9839–9845 (2016)
Yin, W.J., Chen, H., Shi, T., Wei, S.H., Yan, Y.: Origin of high electronic quality in structurally disordered CH3NH3PbI3 and the passivation effect of Cl and O at grain boundaries. Adv. Electron. Mater. 1(6), 1500044 (2015)
Zhao, W., Yang, D., Yang, Z., Liu, S.F.: Zn-doping for reduced hysteresis and improved performance of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite hybrid solar cells. Mater. Today Energy 5, 205–213 (2017)
Klug, M.T., Osherov, A., Haghighirad, A.A., Stranks, S.D., Brown, P.R., Bai, S., Wang, J.T.-W., Dang, X., Bulović, V., Snaith, H.J.: Tailoring metal halide perovskites through metal substitution: influence on photovoltaic and material properties. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 236–246 (2017)
Heo, J.H., Han, H.J., Kim, D., Ahn, T.K., Im, S.H.: Hysteresis-less inverted CH3NH 3PbI3 planar perovskite hybrid solar cells with 18.1% power conversion efficiency. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 1602–1608 (2015)
Xiao, Z., Bi, C., Shao, Y., Dong, Q., Wang, Q., Yuan, Y., Wang, C., Gao, Y., Huang, J.: Efficient, high yield perovskite photovoltaic devices grown by interdiffusion of solution-processed precursor stacking layers. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 2619–2623 (2014)
Ahn, N., Son, D.-Y., Jang, I.-H., Kang, S.M., Choi, M., Park, N.-G.: Highly reproducible perovskite solar cells with average efficiency of 18.3% and best efficiency of 19.7% fabricated via Lewis base adduct of lead (II) iodide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 8696–8699 (2015)
Im, J.-H., Jang, I.-H., Pellet, N., Grätzel, M., Park, N.-G.: Growth of CH3NH3PbI3 cuboids with controlled size for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 927–932 (2014)
Qing, J., Chandran, H.-T., Cheng, Y.-H., Liu, X.-K., Li, H.-W., Tsang, S.-W., Lo, M.-F., Lee, C.-S.: Chlorine incorporation for enhanced performance of planar perovskite solar cell based on lead acetate precursor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 23110–23116 (2015)
Forgács, D., Sessolo, M., Bolink, H.J.: Lead acetate precursor-based pin perovskite solar cells with enhanced reproducibility and low hysteresis. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 14121–14125 (2015)
Zhu, L., Yuh, B., Schoen, S., Li, X., Aldighaithir, M., Richardson, B.J., Alamer, A., Yu, Q.: Solvent-molecule-mediated manipulation of crystalline grains for efficient planar binary lead and tin triiodide perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 8, 7621–7630 (2016)
Yang, Z., Rajagopal, A., Chueh, C.C., Jo, S.B., Liu, B., Zhao, T., Jen, A.K.Y.: Stable low-bandgap Pb–Sn binary perovskites for tandem solar cells. Adv. Mater. 28, 8990–8997 (2016)
Liu, X., Yang, Z., Chueh, C.-C., Rajagopal, A., Williams, S.T., Sun, Y., Jen, A.K.-Y.: Improved efficiency and stability of Pb–Sn binary perovskite solar cells by Cs substitution. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 17939–17945 (2016)
Liu, C., Fan, J., Li, H., Zhang, C., Mai, Y.: Highly efficient perovskite solar cells with substantial reduction of lead content. Sci. Rep. 6, 35705 (2016)
Li, Y., Sun, W., Yan, W., Ye, S., Rao, H., Peng, H., Zhao, Z., Bian, Z., Liu, Z., Zhou, H.: 50% Sn-based planar perovskite solar cell with power conversion efficiency up to 13.6%. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1601353 (2016)
Chen, Q., Chen, L., Ye, F., Zhao, T., Tang, F., Rajagopal, A., Jiang, Z., Jiang, S., Jen, A.K.-Y., Xie, Y.: Ag-incorporated organic–inorganic perovskite films and planar heterojunction solar cells. Nano Lett. 17, 3231–3237 (2017)
Ohishi, Y., Oku, T., Suzuki, A.: Fabrication and characterization of perovskite-based CH3NH3Pb1-xGexI3, CH3NH3Pb1-xTlxI3 and CH3NH3Pb1-xInxI3 photovoltaic devices. AIP Conf. Proc. 1709(1), 20020 (2016)
Hamatani, T., Shirahata, Y., Ohishi, Y., Fukaya, M., Oku, T.: Arsenic and chlorine co-doping to CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 7(01), 1 (2017)
Oku, T., Ohishi, Y., Suzuki, A.: Effects of SbBr 3 addition to CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells. AIP Conf Proc 1807(1), 020007 (2017)
Eperon, G.E., Leijtens, T., Bush, K.A., Prasanna, R., Green, T., Wang, J.T.-W., McMeekin, D.P., Volonakis, G., Milot, R.L., May, R.: Perovskite-perovskite tandem photovoltaics with optimized band gaps. Science 354, 861–865 (2016)
Zuo, C., Ding, L.: An 80.11% FF record achieved for perovskite solar cells by using the NH4Cl additive. Nanoscale 6, 9935–9938 (2014)
Li, X., Bi, D., Yi, C., Décoppet, J.-D., Luo, J., Zakeeruddin, S.M., Hagfeldt, A., Grätzel, M.: A vacuum flash–assisted solution process for high-efficiency large-area perovskite solar cells. Science 353(6294), 58–62 (2016)
Saliba, M., Matsui, T., Domanski, K., Seo, J.-Y., Ummadisingu, A., Zakeeruddin, S.M., Correa-Baena, J.-P., Tress, W.R., Abate, A., Hagfeldt, A.: Incorporation of rubidium cations into perovskite solar cells improves photovoltaic performance. Science 354, 206–209 (2016)
Aharon, S., Cohen, B.E., Etgar, L.: Hybrid lead halide iodide and lead halide bromide in efficient hole conductor free perovskite solar cell. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 17160–17165 (2014)
Wehrenfennig, C., Eperon, G.E., Johnston, M.B., Snaith, H.J., Herz, L.M.: High charge carrier mobilities and lifetimes in organolead trihalide perovskites. Adv. Mater. 26, 1584–1589 (2014)
Hao, F., Stoumpos, C.C., Cao, D.H., Chang, R.P., Kanatzidis, M.G.: Lead-free solid-state organic–inorganic halide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 8, 489–494 (2014)
Nie, W., Tsai, H., Asadpour, R., Blancon, J.-C., Neukirch, A.J., Gupta, G., Crochet, J.J., Chhowalla, M., Tretiak, S., Alam, M.A.: High-efficiency solution-processed perovskite solar cells with millimeter-scale grains. Science 347, 522–525 (2015)
Kim, H.-B., Choi, H., Jeong, J., Kim, S., Walker, B., Song, S., Kim, J.Y.: Mixed solvents for the optimization of morphology in solution-processed, inverted-type perovskite/fullerene hybrid solar cells. Nanoscale 6, 6679–6683 (2014)
Yang, W.S., Noh, J.H., Jeon, N.J., Kim, Y.C., Ryu, S., Seo, J., Seok, S.I.: High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science 348, 1234–1237 (2015)
Meillaud, F., Shah, A., Droz, C., Vallat-Sauvain, E., Miazza, C.: Efficiency limits for single-junction and tandem solar cells. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 90(18–19), 2952–2959 (2006)
Ke, W., Stoumpos, C.C., Logsdon, J.L., Wasielewski, M.R., Yan, Y., Fang, G., Kanatzidis, M.G.: TiO2–ZnS cascade electron transport layer for efficient formamidinium tin iodide perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 14998–15003 (2016)
Gur, I., Fromer, N.A., Geier, M.L., Alivisatos, A.P.: Air-stable all-inorganic nanocrystal solar cells processed from solution. Science 310, 462–465 (2005)
Shin, B., Gunawan, O., Zhu, Y., Bojarczuk, N.A., Chey, S.J., Guha, S.: Thin film solar cell with 8.4% power conversion efficiency using an earth-abundant Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 21, 72–76 (2013)
Chuang, C.-H.M., Brown, P.R., Bulović, V., Bawendi, M.G.: Improved performance and stability in quantum dot solar cells through band alignment engineering. Nat. Mater. 13, 796 (2014)
Chen, L.-J., Lee, C.-R., Chuang, Y.-J., Wu, Z.-H., Chen, C.: Synthesis and optical properties of lead-free cesium tin halide perovskite quantum rods with high-performance solar cell application. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 5028–5035 (2016)
Biswas, A., Bayer, I.S., Biris, A.S., Wang, T., Dervishi, E., Faupel, F.: Advances in top–down and bottom–up surface nanofabrication: techniques, applications & future prospects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 170, 2–27 (2012)
Cavallini, M., Facchini, M., Massi, M., Biscarini, F.: Bottom–up nanofabrication of materials for organic electronics. Synth. Metals 146, 283–286 (2004)
Ariga, K., Hill, J.P., Ji, Q.: Layer-by-layer assembly as a versatile bottom-up nanofabrication technique for exploratory research and realistic application. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9, 2319–2340 (2007)
Green, M.A., Ho-Baillie, A., Snaith, H.J.: The emergence of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 8, 506–514 (2014)
Miller, O.D., Yablonovitch, E., Kurtz, S.R.: Strong internal and external luminescence as solar cells approach the Shockley-Queisser limit. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2, 303–311 (2012)
Krishnamoorthy, T., Ding, H., Yan, C., Leong, W.L., Baikie, T., Zhang, Z., Sherburne, M., Li, S., Asta, M., Mathews, N.: Lead-free germanium iodide perovskite materials for photovoltaic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 23829–23832 (2015)
Fabian, D.M., Ardo, S.: Hybrid organic–inorganic solar cells based on bismuth iodide and 1, 6-hexanediammonium dication. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 6837–6841 (2016)
Yokoyama, T., Cao, D.H., Stoumpos, C.C., Song, T.-B., Sato, Y., Aramaki, S., Kanatzidis, M.G.: Overcoming short-circuit in lead-free CH3NH3SnI3 perovskite solar cells via kinetically controlled gas-solid reaction film fabrication process. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 776–782 (2016)
Zhang, M., Lyu, M., Yun, J.-H., Noori, M., Zhou, X., Cooling, N.A., Wang, Q., Yu, H., Dastoor, P.C., Wang, L.: Low-temperature processed solar cells with formamidinium tin halide perovskite/fullerene heterojunctions. Nano Res. 9, 1570–1577 (2016)
Gupta, S., Bendikov, T., Hodes, G., Cahen, D.: CsSnBr 3, a lead-free halide perovskite for long-term solar cell application: insights on SnF2 addition. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 1028–1033 (2016)
Hsu, H.-Y., Ji, L., Du, M., Zhao, J., Edward, T.Y., Bard, A.J.: Optimization of lead-free organic–inorganic tin (II) halide perovskite semiconductors by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Electrochim. Acta 220, 205–210 (2016)
Yu, Y., Zhao, D., Grice, C.R., Meng, W., Wang, C., Liao, W., Cimaroli, A.J., Zhang, H., Zhu, K., Yan, Y.: Thermally evaporated methylammonium tin triiodide thin films for lead-free perovskite solar cell fabrication. RSC Adv. 6, 90248–90254 (2016)
Jung, M.-C., Raga, S.R., Qi, Y.: Properties and solar cell applications of Pb-free perovskite films formed by vapor deposition. RSC Adv. 6, 2819–2825 (2016)
Song, T.-B., Yokoyama, T., Stoumpos, C.C., Logsdon, J.L., Cao, D.H., Wasielewski, M.R., Aramaki, S., Kanatzidis, M.G.: Importance of reducing vapor atmosphere in the fabrication of tin-based perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(2), 836–842 (2017)
Li, W., Li, J., Li, J., Fan, J., Mai, Y., Wang, L.: Addictive-assisted construction of all-inorganic CsSnIBr 2 mesoscopic perovskite solar cells with superior thermal stability up to 473 K. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 17104–17110 (2016)
Qiu, X., Cao, B., Yuan, S., Chen, X., Qiu, Z., Jiang, Y., Ye, Q., Wang, H., Zeng, H., Liu, J.: From unstable CsSnI3 to air-stable Cs2SnI6: a lead-free perovskite solar cell light absorber with bandgap of 1.48 eV and high absorption coefficient. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 159, 227–234 (2017)
Sourisseau, S., Louvain, N., Bi, W., Mercier, N., Rondeau, D., Boucher, F., Buzaré, J.-Y., Legein, C.: Reduced band gap hybrid perovskites resulting from combined hydrogen and halogen bonding at the organic–inorganic interface. Chem. Mater. 19, 600–607 (2007)
Takahashi, Y., Obara, R., Nakagawa, K., Nakano, M., Tokita, J.-Y., Inabe, T.: Tunable charge transport in soluble organic–inorganic hybrid semiconductors. Chem. Mater. 19, 6312–6316 (2007)
Knutson, J.L., Martin, J.D., Mitzi, D.B.: Tuning the band gap in hybrid tin iodide perovskite semiconductors using structural templating. Inorg. Chem. 44, 4699–4705 (2005)
Acknowledgements
Ashraful Islam acknowledges support from JSPS KAKENHI Grant 18H02079. Ashraful Islam and Jae-Joon Lee also acknowledge support from NRF-2016M1A2A2940912 and 2015M1A2A2054996. This work was partly supported by the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) Malaysia research grant with code- FRGS/1/2017/TK07/UKM/02/9. I. Bedja extends his appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through research group NO (RG-1438-041) and RSSU at King Saud University for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wadi, M.A.A., Chowdhury, T.H., Bedja, I.M. et al. Evolution of Pb-Free and Partially Pb-Substituted Perovskite Absorbers for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Electron. Mater. Lett. 15, 525–546 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00149-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00149-4