Abstract
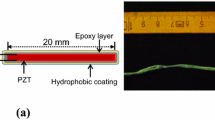
This study developed an innovative device, “IoT Corr,” to monitor rebar corrosion’s physical and chemical characteristics in concrete. A corrosion potential sensor (solid-phase pseudo-reference electrode) and a resistance pressure sensor printed with a 3D printer utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) technology were employed for the device’s development. Also, a wireless power transfer (WPT) system was used to overcome charging and other issues associated with power supply systems. The 1.2-mm IoT Corr thickness caused it to be inserted into the concrete cover above the structure’s rebar. Two 3D-printed pressure sensors—one next to the IoT Corr sample rebar and one above the structural rebar—measured the pressure of the corrosion products. Sensors designed for this work were measured up to 1 MPa with a linear function. It was found that IoT Corr demonstrated a maximum difference of 2 mV in corrosion potential and 380 nA in corrosion current density compared to the PGSTAT101 potentiostat device.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angst, U.M.: Challenges and opportunities in corrosion of steel in concrete. Mater. Struct. 51(1), 1–20 (2018)
Kadakolmath, S.; Gurav, R.S.; Misale, V.N.: Role of non-destructive testing and evaluation (NDTE) in water resource engineering. J. Destr. Test. Eval. JNDE 19(1), 31–37 (2022)
Jin, M., et al.: Fabrication and characterization of pseudo reference electrode based on graphene-cement composites for corrosion monitoring in reinforced concrete structure. Constr. Build. Mater. 204, 144–157 (2019)
Duffó, G.; Farina, S.; Giordano, C.: Embeddable reference electrodes for corrosion monitoring of reinforced concrete structures. Mater. Corros. 61(6), 480–489 (2010)
Duffó, G.; Farina, S.; Giordano, C.: Characterization of solid embeddable reference electrodes for corrosion monitoring in reinforced concrete structures. Electrochim. Acta 54(3), 1010–1020 (2009)
Fan, L.; Shi, X.: Techniques of corrosion monitoring of steel rebar in reinforced concrete structures: a review. Struct. Health Monit. 21(4), 1879–1905 (2022)
Tang, Y.-B., et al.: Preparation and properties of embeddable Ag/AgCl gelling reference electrode for rebars corrosion monitoring in concrete. China Ocean Eng. 29(6), 925–932 (2015)
Leon-Salas, W.D.; Halmen, C.: A RFID sensor for corrosion monitoring in concrete. IEEE Sens. J. 16(1), 32–42 (2015)
Figueira, R.B.: Electrochemical sensors for monitoring the corrosion conditions of reinforced concrete structures: a review. Appl. Sci. 7(11), 1157 (2017)
Wang, X.-P., et al.: Study on corrosion inhibition of reinforcing steel in simulated concrete pore solutions by scanning microelectrode technique. ECS Trans. 80(10), 655 (2017)
Mei, K., et al.: Study on electrochemical characteristics of reinforced concrete corrosion under the action of carbonation and chloride. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 17, e01351 (2022)
Qiao, G., et al.: Remote corrosion monitoring of the RC structures using the electrochemical wireless energy-harvesting sensors and networks. NDT E Int. 44(7), 583–588 (2011)
Li, Z., et al.: Combined application of novel electromagnetic sensors and acoustic emission apparatus to monitor corrosion process of reinforced bars in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 245, 118472 (2020)
Cheng, Y., et al.: Simulation of a novel capacitive sensor for rebar corrosion detection. Constr. Build. Mater. 174, 613–624 (2018)
Xie, L., et al.: A rebar corrosion sensor embedded in concrete based on surface acoustic wave. Measurement 165, 108118 (2020)
Su, D.; Xia, Y.; Yuan, R.: Self-powered wireless sensor network for automated corrosion prediction of steel reinforcement. J. Sens. 2018, 1–10 (2018)
Wang, Z.L.: Nanopiezotronics. Adv. Mater. 19(6), 889–892 (2007)
Tan, C., et al.: Fiber Bragg grating based sensing system: early corrosion detection for structural health monitoring. Sens. Actuators A 246, 123–128 (2016)
Mao, J., et al.: An optical fiber sensor method for simultaneously monitoring corrosion and structural strain induced by loading. J. Test. Eval. 46(4), 1443–1451 (2018)
Fan, L., et al.: In-situ monitoring of corrosion-induced expansion and mass loss of steel bar in steel fiber reinforced concrete using a distributed fiber optic sensor. Compos. B Eng. 165, 679–689 (2019)
Rahmatian, A., et al.: Modeling of supplemental bar-mounted fiber optic strain sensor for structural health monitoring applications. J Test Eval 50(2), 1165–1181 (2021)
Li, Z., et al.: Coupled application of innovative electromagnetic sensors and digital image correlation technique to monitor corrosion process of reinforced bars in concrete. Cem Concr. Compos. 113, 103730 (2020)
Li, Z., et al.: Use of a novel electro-magnetic apparatus to monitor corrosion of reinforced bar in concrete. Sens. Actuators A 286, 14–27 (2019)
Ai, D., et al.: Corrosion damage identification for reinforced concrete beam using embedded piezoelectric transducer: numerical simulation. Measurement 192, 110925 (2022)
Yu, Y.; Qiao, G.; Ou, J.: Self-powered wireless corrosion monitoring sensors and networks. IEEE Sens. J. 10(12), 1901–1902 (2010)
Fan, L., et al.: Monitoring corrosion of steel bars in reinforced concrete based on helix strains measured from a distributed fiber optic sensor. Eng. Struct. 204, 110039 (2020)
Raupach, M.; Gulikers, J.; Reichling, K.: Condition survey with embedded sensors regarding reinforcement corrosion. Mater. Corros. 64(2), 141–146 (2013)
Lu, S., Ba, H., Yang, Y.: In-suit monitoring electrical resistiviy in cover-zone concrete by Tower Type Sensor. In: 2009 International Conference on Test and Measurement. IEEE (2009)
Sun, X., et al.: A novel method for steel bar all-stage pitting corrosion monitoring using the feature-level fusion of ultrasonic direct waves and coda waves. Struct. Health Monit. 22(1), 714–729 (2023)
Jin, M., et al.: Electrochemical characterization of solid Ag/AgCl reference electrode with different electrolytes for corrosion monitoring of steel in concrete. Electrochemistry 84(6), 383–389 (2016)
Karthick, S., et al.: Long-term relative performance of embedded sensor and surface mounted electrode for corrosion monitoring of steel in concrete structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 192, 303–309 (2014)
Alamin, M., et al.: Corrosion detection using low-frequency RFID technology. Insight Destruct. Test. Cond. Monit. 54(2), 72–75 (2012)
Leon-Salas, W., Kanneganti, S., Halmen, C.: Development of a smart RFID-based corrosion sensor. In: Sensors, 2011. IEEE (2011)
Sunny, A.I., et al.: Low frequency (LF) RFID sensors and selective transient feature extraction for corrosion characterisation. Sens. Actuators A 241, 34–43 (2016)
Santamaria, A.F., et al.: Data analysis and integration of environmental sensors to meet human needs. In: Wireless Sensing, Localization, and Processing IX. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2014)
Civerchia, F., et al.: Industrial Internet of Things monitoring solution for advanced predictive maintenance applications. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 7, 4–12 (2017)
Santamaria, A.F., et al.: SmartHome: a domotic framework based on smart sensing and actuator network to reduce energy wastes. In: Wireless Sensing, Localization, and Processing IX. SPIE (2014)
Wang, M.: Embedded strain sensor with power scavenging from bridge vibration. University of Maryland, College Park (2004)
Carkhuff, B.; Cain, R.: Corrosion sensors for concrete bridges. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 6(2), 19–24 (2003)
Gallucci, L., et al.: An embedded wireless sensor network with wireless power transmission capability for the structural health monitoring of reinforced concrete structures. Sensors 17(11), 2566 (2017)
Chen, J., et al.: Q-charge: a quadcopter-based wireless charging platform for large-scale sensing applications. IEEE Netw. 31(6), 56–61 (2017)
Georgakopoulos, S.V., Jiang, S.: Wireless powering of sensors embedded in concrete. In: 2010 IEEE 11th Annual Wireless and Microwave Technology Conference (WAMICON). IEEE (2010)
Andrade, C.; Muñoz, A.; Torres-Acosta, A.: Correlación entre ancho de grieta del recubrimiento del concreto y corrosión del refuerzo en elementos expuestos a un ambiente natural contaminado por cloruros. Concr. Cem. Invest. Desarro. 1(2), 30–41 (2010)
Munoz, A.; Andrade, C.; Torres, A.: Corrosion products pressure needed to crack the concrete cover. Adv. Constr. Mater. 2007, 359–370 (2007)
Torres-Acosta, A.A.: Cracking induced by localized corrosion of reinforment in chloride contaminated concrete. University of South Florida (1999)
Shevtsov, D., et al.: Progress in sensors for monitoring reinforcement corrosion in reinforced concrete structures—a review. Sensors 22(9), 3421 (2022)
Elsener, B.: Corrosion rate of steel in concrete—Measurements beyond the Tafel law. Corros. Sci. 47(12), 3019–3033 (2005)
Andrade, C.: Propagation of reinforcement corrosion: principles, testing and modelling. Mater. Struct. 52(1), 2 (2019)
Rodrigues, R., et al.: Reinforced concrete structures: a review of corrosion mechanisms and advances in electrical methods for corrosion monitoring. Constr. Build. Mater. 269, 121240 (2020)
International A. ASTM C876-15 Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete. ASTM International West Conshohocken, PA (2015)
Jin, L., et al.: Cracking of cover concrete due to non-uniform corrosion of corner rebar: a 3D meso-scale study. Constr. Build. Mater. 245, 118449 (2020)
Alonso, C., et al.: Factors controlling cracking of concrete affected by reinforcement corrosion. Mater. Struct. 31(7), 435–441 (1998)
Liang, Y.; Wang, L.: Prediction of corrosion-induced cracking of concrete cover: a critical review for thick-walled cylinder models. Ocean Eng. 213, 107688 (2020)
Allan, M.; Cherry, B.: Factors controlling the amount of corrosion for cracking in reinforced concrete. Corrosion 48(5), 426–430 (1992)
Williamson, S.; Clark, L.: Pressure required to cause cover cracking of concrete due to reinforcement corrosion. Mag. Concr. Res. 52(6), 455–467 (2000)
Stern, M.; Geary, A.L.: Electrochemical polarization: I. A theoretical analysis of the shape of polarization curves. J. Electrochem. Soci. 104(1), 56 (1957)
Andrade, C.; González, J.: Quantitative measurements of corrosion rate of reinforcing steels embedded in concrete using polarization resistance measurements. Mater. Corros. 29(8), 515–519 (1978)
Gonzalez, J., et al.: Some questions on the corrosion of steel in concrete—Part I: when, how and how much steel corrodes. Mater. Struct. 29(1), 40–46 (1996)
Andrade, C.; Alonso, C.: Test methods for on-site corrosion rate measurement of steel reinforcement in concrete by means of the polarization resistance method. Mater. Struct. 37(9), 623–643 (2004)
Chang, Z.-T.; Cherry, B.; Marosszeky, M.: Polarisation behaviour of steel bar samples in concrete in seawater. Part 1: experimental measurement of polarisation curves of steel in concrete. Corros. Sci. 50(2), 357–364 (2008)
Scuro, C., et al.: IoT for structural health monitoring. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 21(6), 4–14 (2018)
Ali, S.H., et al.: Wireless sensor network-based structural health monitoring of bridges using advanced signal processing techniques. J. Test. Eval. 49(2), 1266–1283 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malaekeh, S., Shirzadi Javid, A.A. & Sasani Babak, S. Detection of the Rebar Corrosion in Concrete Using a New IOT-Based Device Constructed by the Solid-Phase Electrodes and Pressure Sensors. Arab J Sci Eng 49, 4929–4946 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08282-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08282-x