Abstract
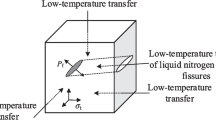
This work examined the efficacy of liquid nitrogen (LN2) both in coal fracturing, focusing on two different processes: freezing time (FT) and freezing–thawing cycle (FTC), for both dry and water-saturated specimens. Uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) with acoustic emission measurements, hardness, and modulus measurements by nanoindentation, and scanning electron microscope (SEM) imaging were conducted to comparatively analyze the cryogenic treatment efficacy of coal rocks. The outcomes indicated that in all freezing–thawing processes, water-saturated specimens have lower UCS values compared to dry ones. On the other hand, in freezing time process, water-saturated experiments have larger UCS values compared to dry ones. Moreover, it is noticed that FT experiments have greater UCS values than FTC experiments in both dry and water-saturated experiments. The hardness and reduced modulus change augment for both water-saturated and dry specimens, but in water-saturated ones, there is a sharp upward trend indicating that hardness decreases more as LN2 treatment increases. From SEM observation, it is noticed that new fractures were created, and sections of preexisting crevices expand creating fracture networks. Due to the frost force resulting from LN2 treatment, the consolidation forces among coal particles are compromised, thus creating new fractures.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Longinos, S.N.; Parlaktuna, M.: Examination of methane hydrate formation by the use of dual impeller combinations. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 133(2), 729–740 (2021)
Merey, S.; Longinos, S.N.: Investigation of gas seepages in Thessaloniki mud volcano in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 168, 81–97 (2018)
British Petroleum. Statistical review of world energy, 70th Edition (2021)
Longinos, S.N.; Parlaktuna, M.: Examination of behavior of lysine on methane (95%)–propane (5%) hydrate formation by the use of different impellers. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 11(4), 1823–1831 (2021)
Longinos, S.N.; Parlaktuna, M.: Are the amino acids inhibitors or promoters on methane (95%)–propane (5%) hydrate formation? React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 132(2), 795–809 (2021)
Cander, H.: PS what are unconventional resources? A simple definition using viscosity and permeability. In: AAPG Annual Convention and Exhibition. American Association of Petroleum Geologists and Society for Sedimentary Geology, Tulsa, US (2012)
Gunningham, N.: A shale gas revolution for China? AU—Gunningham. Neil. Clim. Policy 14(2), 302–320 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/14693062.2014.842857
Anna, S.; Krystyna, C.: Reducing life-cycle environmental impacts of coal-power by using coal-mine methane. Int. J. Energy Res. 37(9), 1044–1058 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.2908
Moore, T.A.: Coalbed methane: a review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 101, 36–81 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2012.05.011
Longinos, S.; Wang, L.; Loskutova, A.; Zhang, D,; Hazlett, R.: Cyclic LN2 treatment of coal samples from coal basin in Kazakhstan. In: SPE EuropEC-Europe Energy Conference featured at the 83rd EAGE Annual Conference & Exhibition. OnePetro (2022)
Sun, Y.; Zhai, C.; Xu, J.; Cong, Y.; Zheng, Y.: Experimental study on pore structure evolution of coal in macroscopic, mesoscopic, and microscopic scales during liquid nitrogen cyclic cold-shock fracturing. Fuel 291, 120150 (2021)
Cai, C.Z.; Li, G.; Huang, Z.; Tian, S.; Shen, Z.; Fu, X.: Experiment of coal damage due to super-cooling with liquid nitrogen. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 22, 42–48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2014.11.016
Qin, L.; Zhai, C.; Liu, S.M.; Xu, J.Z.; Tang, Z.Q.; Yu, G.Q.: Failure mechanism of coal after cryogenic freezing with cyclic liquid nitrogen and its influences on coalbed methane exploitation. Energy Fuels 30(10), 8567–8578 (2016)
Du, M.; Gao, F.; Cai, C.; Su, S.; Wang, Z.: Experimental study on the damage and cracking characteristics of bedded coal subjected to liquid nitrogen cooling. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 54(11), 5731–5744 (2021)
Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Chang, X.: Fracture stiffness evaluation with waterless cryogenic treatment and its implication in fluid flowability of treated coals. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 142, 104727 (2021)
Sinal, M.L.; Lancaster, G.: Liquid CO2 fracturing: advantages and limitation. J Can Pet. 26(5), 26–30 (1987). https://doi.org/10.2118/87-05-01
Jackson, R.E.; Gorody, A.W.; Mayer, B.; Roy, J.W.; Ryan, M.C.; van Stempvoort, D.R.: Groundwater protection and unconventional gas extraction: the critical need for field-based hydrogeological research. Groundwater 51(4), 488–510 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12074
Qin, L.; Ma, C.; Li, S.; Lin, H.; Wang, P.; Long, H.; Yan, D.: Mechanical damage mechanism of frozen coal subjected to liquid nitrogen freezing. Fuel 309, 122124 (2022)
Hilary, B.; Christopher, C.; Dylan, B.; Edward, M.; Connie, R.; Anthony, L.: ”Fracking” controversy and communication: using national survey data to understand public perceptions of hydraulic fracturing. Energy Policy 65, 57–67 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.10.017
Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.: Liquid nitrogen gasification fracturing technology for shale gas development. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 138, 253–256 (2016)
Hou, P.; Su, S.; Gao, F.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Cai, C.: Influence of liquid nitrogen cooling state on mechanical properties and fracture characteristics of coal. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 55, 3817 (2022)
Yuan, Y.; Cai, F.; Yang, L.: Pore structure characteristics and fractal structure evaluation of medium-and high-rank coal. Energy Explor. Exploit. 40(1), 328–342 (2022)
Mundi index, 2014. Average precipitation in depth (mm per year) - Country Ranking.
Longinos, S.N.; Wang, L.; Hazlett, R.: Advances in cryogenic fracturing of coalbed methane reservoirs with LN2. Energies 15(24), 9464 (2022)
Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, M.: Experimental study on the seepage characteristics of bituminous coal under the conditions of liquid nitrogen fracturing. Energy Sci. Eng. 7(5), 2138–2154 (2019)
Qin, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, C.; Lin, H.; Lin, S.; Wang, P.; Li, S.: Advances in liquid nitrogen fracturing for unconventional oil and gas development: a review. Energy Fuels 36(6), 2971–2992 (2022)
Wang, S.; Su, S.; Wang, D.; Hou, P.; Xue, Y.; Liang, X.; Cai, C.; Gao, X.; Jin, Y.; Yang, S.; Jiang, X.: Experimental study on fracture characteristics of coal due to liquid nitrogen fracturing. Geomech. Energy Environ. 13, 100438 (2023)
Yang, R.; Wen, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Dubinya, N.: Experimental investigation on fracture characteristics by liquid nitrogen compound fracturing in coal. Fuel 340, 127434 (2023)
Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, R.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Hung, P.: A review of liquid nitrogen fracturing technology. Fuel 266, 117040 (2020)
Cai, C.; Li, G.; Huang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Tian, S.; Wei, J.: Experimental study of the effect of liquid nitrogen cooling on rock pore structure. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 21, 507–517 (2014)
Cai, C.; Gao, F.; Li, G.; Huang, Z.; Hou, P.: Evaluation of coal damage and cracking characteristics due to liquid nitrogen cooling on the basis of the energy evolution laws. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 29, 30–36 (2016)
Lin, H.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Li, S.; Qin, L.; Zhang, Y.: Damage caused by freeze-thaw treatment with liquid nitrogen on pore and fracture structures in a water-bearing coal mass. Energy Sci. Eng. 8(5), 1667–1680 (2020)
Qin, L.; Zhai, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhong, C.; Yu, G.: Evolution of the pore structure in coal subjected to freeze− thaw using liquid nitrogen to enhance coalbed methane extraction. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 175, 129–139 (2019)
Yin, G.; Shang, D.; Li, M.; Huang, J.; Gong, T.; Song, Z., et al.: Permeability evolution and mesoscopic cracking behaviors of liquid nitrogen cryogenic freeze fracturing in low permeable and heterogeneous coal. Powder Technol. 325, 234–246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.10.058
Zhang, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, C.: Experimental study of thermal-crack characteristics on hot dry rock impacted by liquid nitrogen jet. Geothermics 76, 253–260 (2018)
Zhang, S.; Huang, Z.; Huang, P.; Wu, X.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, C.: Numerical and experimental analysis of hot dry rock fracturing stimulation with high-pressure abrasive liquid nitrogen jet. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 163, 156–165 (2018)
Wang, L.; Yao, B.; Cha, M.; Alqahtani, N.B.; Patterson, T.W.; Kneafsey, T.J.; Miskimins, J.L.; Yin, X.; Wu, Y.S.: Waterless fracturing technologies for unconventional reservoirs-opportunities for liquid nitrogen. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 35, 160–174 (2016)
Liew, M.S.; Danyaro, K.U.; Zawawi, N.A.: A comprehensive guide to different fracturing technologies: a review. Energies 13, 3326 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133326
Sabitova, D.K.: Exploration potential of coalbed methane in Karaganda field. Mod. Appl. Sci. 9(6), 145–159 (2015)
Andrei petrovich, 1980, Technical report of TOO RAPID Company (In Russian)
Acknowledgements
This research is financially supported by Nazarbayev University (Funder Project Reference: 021220CRP2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Longinos, S.N., Serik, A., Zhang, D. et al. Experimental Evaluation of Liquid Nitrogen Fracturing on the Coal Rocks in Karaganda Basin, Kazakhstan. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 16623–16638 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07857-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07857-y