Abstract
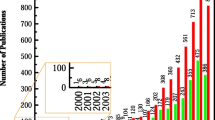
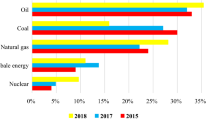
The pressure on freshwater sources increases with population, industrial, and agriculture growth. Solar desalination methods are among the technologies that show great potential for freshwater production through evaporation and condensation processes. Therefore, desalination enhancement may be achieved through enhanced evaporation, condensation, or both processes. The problems facing desalination by traditional solar stills are the low efficiency and low solar yield, around 4 L/m2·day. Many kinds of research have been implemented to enhance the yield of the solar still system at a reasonable cost. The objective of the current article is to critically review and compares the solar yield, efficiency, and production cost of the various hybrid solar desalination systems. Despite their many reviews on solar stills, this review differs from previous reviews as it focuses on the hybrid enhancement methods of solar stills. It is found that some hybrid systems achieved 20 L/m2· days by integration with thermal energy storage, external heat sources, or a combination of external heat sources and thermal energy storage. The performance of each hybrid approach is evaluated to get insight into which combination is most effective. The freshwater production cost of the hybrid solar stills is included in the analysis as a performance indication factor.






















































Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SS, SSs:
-
Solar still, solar stills
- DS:
-
Double slope
- PTC:
-
Parabolic through collector
- TES:
-
Thermal energy storage
- PCM:
-
Phase change material
- CSS:
-
Conventional solar still
- CTSS:
-
Conventional tubular solar still
- TC:
-
Total cost ($)
- TSS:
-
Tubular solar still
- CF:
-
Fixed charge ($)
- CM:
-
Maintenance cost ($)
- CO:
-
Operation cost ($)
- CPL:
-
Cost per liter ($/L/m2)
- CPC:
-
Compound parabolic collector
- ETC:
-
Evacuated tube collector
- \({T}_{\mathrm{amb}}\) :
-
Ambient temperature
- \({\dot m}_{\mathrm{ev}}\) :
-
Mass of evaporated water
- \({\eta }_{\mathrm{Thermal}}\) :
-
Thermal efficiency
- \({h}_{\mathrm{fg}}\) :
-
Evaporation latent heat
- \({A}_{\mathrm{collection}\,\mathrm{system}}\) :
-
Area of the collection system (external)
- \({A}_{\mathrm{b}}\) :
-
Area of the basin
- \({I}_{\mathrm{s}}\) :
-
Solar radiation intensity (W/m2)
- T w :
-
Temperature of water
References
Xiao, G.; Wang, X.; Ni, M.; Wang, F.; Zhu, W.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K.: A review on solar stills for brine desalination. Appl. Energy 103, 642–652 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.10.029
Distribution of Water on the Earth's Surface. https://www.e-education.psu.edu/earth103/node/701
Chang, H.: Water and Climate Change. In International Encyclopedia of Geography (pp. 1–6). Wiley (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118786352.wbieg0793.pub2
CULPAN, T. (n.d.). Making chips requires lots of water, and Taiwan has a drought. Retrieved July 16, 2021. From https://www.japantimes.co.jp/opinion/2021/03/05/commentary/world-commentary/taiwan-tsmc-semiconductors-water-drought/Distribution of Water on the Earth's Surface. (n.d.). https://www.e-education.psu.edu/earth103/node/701
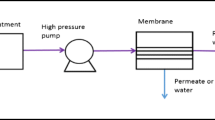
Skuse, C.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Azapagic, A.; Gorgojo, P.: Can emerging membrane-based desalination technologies replace reverse osmosis? Desalination 500, 114844 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114844
Dutta, N.; Singh, B.; Subbiah, S.; Muthukumar, P.: Performance analysis of a single and multi-staged direct contact membrane distillation module integrated with heat recovery units. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 4, 100055 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2020.100055
Emamdoost, N.; Jafarian, A.; Kouhikamali, R.: Implementing multiple-effect distillation and reverse osmosis thermal coupling to improve desalination process performance in combined water and power plants. Energy Convers. Manage. 221, 113176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113176
Kabeel, A.E.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M.: Techniques used to improve the performance of the stepped solar still—a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 46, 178–188 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.053
Amiri, H.; Aminy, M.; Lot, M.; Jafarbeglo, B.: Energy and exergy analysis of a new solar still composed of parabolic trough collector with built-in solar still. 163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.09.007
Sahota, L.; Tiwari, G.N.: Effect of nanofluids on the performance of passive double slope solar still: a comparative study using characteristic curve. Desalination 388, 9–21 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.02.039
Mahian, O.; Kianifar, A.; Heris, S.Z.; Wen, D.; Sahin, A.Z.; Wongwises, S.: Nanofluids effects on the evaporation rate in a solar still equipped with a heat exchanger. Nano Energy 36(February), 134–155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.04.025
El-maghlany, W.M.: An approach to optimization of double slope solar still geometry for maximum collected solar energy. Alex. Eng. J. 54(4), 823–828 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2015.06.010
Kabeel, A.E.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A.; Abdullah, A.S.; Arunkumar, T.; Sathyamurthy, R.: Augmentation of a solar still distillate yield via absorber plate coated with black nanoparticles. Alex. Eng. J. 56(4), 433–438 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2017.08.014
Kabeel, A.E.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A.: Enhancement of modified solar still integrated with external condenser using nanofluids: An experimental approach. Energy Convers. Manage. 78, 493–498 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.11.013
Kabeel, A.E.; Abdelgaied, M.; Mahgoub, M.: The performance of a modified solar still using hot air injection and PCM. Desalination 379, 102–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.11.007
Shoeibi, S.; Rahbar, N.; Abedini Esfahlani, A.; Kargarsharifabad, H.; Abedini, A.; Kargarsharifabad, H.: Improving the thermoelectric solar still performance by using nanofluids—experimental study, thermodynamic modeling and energy matrices analysis. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 47(June), 101339 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101339
Sharshir, S.W.; Peng, G.; Wu, L.; Yang, N.; Essa, F.A.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Mohamed, S.I.T.; Kabeel, A.E.: Enhancing the solar still performance using nanofluids and glass cover cooling: experimental study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 113, 684–693 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.11.085
Rahbar, N.; Esfahani, J.A.: Experimental study of a novel portable solar still by utilizing the heatpipe and thermoelectric module. Desalination 284, 55–61 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.08.036
Kabeel, A.E.A.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F. A.: Numerical investigation of modified solar still using nanofluids and external condenser. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 75, 77–86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.017
Tuly, S.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Sarker, M.R.I.I.; Beg, R.A.: Combined influence of fin, phase change material, wick, and external condenser on the thermal performance of a double slope solar still. J. Clean. Prod. 287, 125458 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125458
Tiwari, G.N.; Singh, H.N.; Tripathi, R.: Present status of solar distillation. Sol. Energy 75(5), 367–373 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2003.07.005
Tiwari, A.K.; Tiwari, G.N.: Effect of water depths on heat and mass transfer in a passive solar still: in summer climatic condition, 195, 78–94 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.11.014
Thakur, V.K.; Gaur, M.K.K.; Dhamneya, A.K.K.; Sagar, M.K.K.: Performance analysis of passive solar still with and without nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.539
Velmurugan, V.; Deenadayalan, C.K.; Vinod, H.; Sridhar, K.: Desalination of effluent using fin type solar still, 33, 1719–1727 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2008.07.001
Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A.; Younes, M.M.; Shanmugan, S.; Abdelgaied, M.; Amro, M.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Farouk, W.M.: Improving the performance of trays solar still using wick corrugated absorber, nano-enhanced phase change material and photovoltaics-powered heaters. J. Energy Storage 40(May), 102782 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2021.102782
Tiwari, G.N.; Sahota, L.: Advanced Solar-Distillation Systems: Basic Principles, Thermal Modeling, and its Application. Springer, Berlin (2017)
Madiouli, J.; Lashin, A.; Shigidi, I.; Badruddin, I.A.; Kessentini, A.: Experimental study and evaluation of single slope solar still combined with flat plate collector, parabolic trough and packed bed. Solar Energy 196(August 2019), 358–366 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.12.027
El-Said, E.M.S.; Elshamy, S.M.; Kabeel, A.E.: Performance enhancement of a tubular solar still by utilizing wire mesh packing under harmonic motion. Desalination, 474(October 2019), 114165 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.114165
Rashidi, S.; Abolfazli Esfahani, J.; Rahbar, N.: Partitioning of solar still for performance recovery: experimental and numerical investigations with cost analysis. Sol. Energy 153, 41–50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.05.041
Elshamy, S.M.; El-Said, E.M.S.: Comparative study based on thermal, exergetic and economic analyses of a tubular solar still with semi-circular corrugated absorber. J. Clean. Prod. 195, 328–339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.243
Kabeel, A.E.; Hamed, A.M.; El-Agouz, S.A.: Cost analysis of different solar still configurations. Energy 35(7), 2901–2908 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2010.03.021
“Cost Indices—Towering Skills.” https://www.toweringskills.com/financial-analysis/cost-indices/. Accessed Nov 16, 2022.
Kabeel, A.E.; Harby, K.; Abdelgaied, M.; Eisa, A.: Augmentation of a developed tubular solar still productivity using hybrid storage medium and CPC : an experimental approach. J. Energy Storage 28(December 2019), 101203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101203
Essa, F.A.; Alawee, W.H.; Mohammed, S.A.; Dhahad, H.A.; Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M.: Experimental investigation of convex tubular solar still performance using wick and nanocomposites. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 27(June), 101368 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2021.101368
Elashmawy, M.; Alhadri, M.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.Z.: Enhancing tubular solar still performance using novel PCM-tubes. Desalination, 500(November 2020), 114880 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114880
Yeo, S.; Lim, B.; Lee, G.; Park, C.: Experimental study of effects of different heat sources on the performance of the hybrid multiple-effect diffusion solar still. Sol. Energy 193(August), 324–334 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.09.062
Pounraj, P.; Winston, D.P.; Kabeel, A.E.; Kumar, B.P.; Manokar, A.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Christabel, S.C.: Experimental investigation on Peltier based hybrid PV/T active solar still for enhancing the overall performance. Energy Convers. Manage. 168(May), 371–381 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.05.011
Praveen, B.; Winston, D.P.; Pounraj, P.; Manokar, A.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kabeel, A.E.: Experimental investigation on hybrid PV/T active solar still with e ff ective heating and cover cooling method. Desalination, 435(August 2017), 140–151 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.11.007
Manokar, A.M.; Winston, D.P.; Kabeel, A.E.; Sathyamurthy, R.: Sustainable fresh water and power production by integrating PV panel in inclined solar still. J. Clean. Prod. 172, 2711–2719 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.140
Shafii, M.B.; Shahmohamadi, M.; Faegh, M.; Sadrhosseini, H.: Examination of a novel solar still equipped with evacuated tube collectors and thermoelectric modules. Desalination 382, 21–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.12.019
Balachandran, G.B.; David, P.W.; Vijayakumar, A.B.P.; Kabeel, A.E.; Athikesavan, M.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.: Enhancement of PV/T-integrated single slope solar desalination still productivity using water film cooling and hybrid composite insulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27(26), 32179–32190 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06131-9
Nazari, S.; Safarzadeh, H.; Bahiraei, M.: Experimental and analytical investigations of productivity, energy and exergy efficiency of a single slope solar still enhanced with thermoelectric channel and nanofluid. Renewable Energy 135, 729–744 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.12.059
Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Koleini, M.H.; Aberoumand, S.; Afrand, M.; Amidpour, M.: A renewable energy-driven thermoelectric-utilized solar still with external condenser loaded by silver/nanofluid for simultaneously water disinfection and desalination. Desalination 480(February), 114354 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114354
Sadeghi, G.; Nazari, S.: Retrofitting a thermoelectric-based solar still integrated with an evacuated tube collector utilizing an antibacterial-magnetic hybrid nanofluid. Desalination, 500(October 2020), 114871 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114871
Hafs, H.; Asbik, M.; Boushaba, H.; Koukouch, A.; Zaaoumi, A.; Bah, A.; Ansari, O.: Numerical simulation of the performance of passive and active solar still with corrugated absorber surface as heat storage medium for sustainable solar desalination technology. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 14(May), 100610 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100610
Kabeel, A.E.; Abdelgaied, M.: Observational study of modified solar still coupled with oil serpentine loop from cylindrical parabolic concentrator and phase changing material under basin. Sol. Energy 144, 71–78 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.01.007
Shehata, A.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Khairat Dawood, M.M.; Elharidi, A.M.; Abd_Elsalam, A.; Ramzy, K.; Mehanna, A.: Enhancement of the productivity for single solar still with ultrasonic humidifier combined with evacuated solar collector: An experimental study. Energy Convers. Manage. 208(October 2019), 112592 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.112592
Bianco, N.; Fragnito, A.; Iasiello, M.; Mauro, G.M.; Mongibello, L.: Multi-objective optimization of a phase change material-based shell-and-tube heat exchanger for cold thermal energy storage: experiments and numerical modeling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 119047 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.119047
Inkeri, E.; Tynjälä, T.; Nikku, M.: Numerical modeling of latent heat thermal energy storage integrated with heat pump for domestic hot water production. Appl. Therm. Eng. 214, 118819 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.118819
Hidouri, K.; ben Slama, R.; Gabsi, S.: Hybrid solar still by heat pump compression. Desalination, 250(1), 444–449 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.09.075
Omara, Z.M.; Eltawil, M.A.; ElNashar, E.S.A.: A new hybrid desalination system using wicks/solar still and evacuated solar water heater. Desalination 325, 56–64 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.06.024
Mamouri, S.J.; Derami, H.G.; Ghiasi, M.; Shafii, M.B.; Shiee, Z.: Experimental investigation of the effect of using thermosyphon heat pipes and vacuum glass on the performance of solar still. Energy 75, 501–507 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.08.005
Shukla, D.; Modi, K.: Hybrid solar still as a co-generative system and desalination system—an experimental performance evaluation. Cleaner Eng. Technol. 2(October 2020), 100063 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100063
Shoeibi, S.; Rahbar, N.; Abedini Esfahlani, A.; Kargarsharifabad, H.: Application of simultaneous thermoelectric cooling and heating to improve the performance of a solar still: an experimental study and exergy analysis. Appl. Energy 263(February), 114581 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114581
El-Sebaii, A.A.: Effect of wind speed on active and passive solar stills. Energy Convers. Manage. 45(7–8), 1187–1204 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2003.09.036
Murase, K.; Yamagishi, Y.; Iwashita, Y.; Sugino, K.: Development of a tube-type solar still equipped with heat accumulation for irrigation. Energy 33(11), 1711–1718 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2008.05.013
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge PETRONAS—Malaysia, for providing financial support under the funded project YUTP—FRG, CS: 015LC0-404. Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS is acknowledged for the technical and logistic support to conduct the research and the production of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Kayiem, H.H., Mohamed, M.M. & Gilani, S.I.U. State of the Art of Hybrid Solar Stills for Desalination. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 5709–5755 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07516-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07516-8