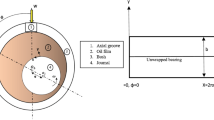
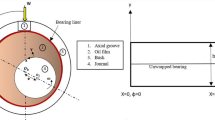
Abstract
In the present work, a 3-D CFD analysis has been implemented successfully to analyze the thermo-elastohydrodynamic (TEHD) performance of Nano-lubricated journal bearing with considering the cavitation effect. The performance of a bearing lubricated with pure oil as well as with the base oil dispersed with different volume fractions of TiO2, Al2O3, and CuO nanoparticles with and without cavitation effect has been implemented and compared. A Two-way fluid-structure interaction and Zwart–Gerber–Balamri cavitation models are used to perform the elastic deformation of the bearing material and the cavitation effects on its performance by using ANSYS-FLUENT 2019 R2. The effects of journal speed, eccentricity ratios, and different types of nano-lubricants with different volume fractions of nanoparticles on the TEHD performance of such bearing have been considered. The mathematical model is verified by comparing the results with that obtained researchers and found a good agreement. The simulation results show that the oil film pressure and hence the load carried by the bearing increased when the bearing is lubricated with nano-lubricant that has a higher volume fraction of the nanoparticles while decreased when considering the elastic deformation of the bearing material and the cavitation effect.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, Z.S.; Yang, Y.M.; Dai, X.D.; Xie, Y.B.: Effects of thermal boundary conditions on plain journal bearing thermohydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 56(5), 759–770 (2013)
Brito, F.P.; Miranda, A.S.; Claro, J.C.P.; Teixeira, J.C.; Costa, L.; Fillon, M.: The role of lubricant feeding conditions on the performance improvement and friction reduction of journal bearings. Tribol. Int. 72, 65–82 (2014)
Akbarzadeh, P.; Mikaeeli, S.Z.; Rahimiyan, M.: Multiobjective optimization of thermohydrodynamic journal bearing using MOPSO algorithm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 232(6), 657–671 (2018)
Lambha, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Verma, R.: Elastohydrodynamic analysis of couple stress lubricated cylindrical journal bearing. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1240(1), 012165 (2019)
Sekhar, P.S.; Sajja, V.S.; Murthy, V.R.K.; Parthiban, S.: A semi analytical approach in thermal analysis of Hydrodynamic lubrication of journal bearing. Mater. Today Proc. 19, 2650–2653 (2019)
Dhande, D.Y.; Pande, D.W.: Numerical analysis of multiphase flow in hydrodynamic journal bearing using CFD coupled Fluid Structure interaction with cavitation. In: 2016 International Conference on Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Techniques (ICACDOT) (pp. 964–971). IEEE (2016)
Dhande, D.Y.; Pande, D.W.: A two-way FSI analysis of multiphase flow in hydrodynamic journal bearing with cavitation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39(9), 3399–3412 (2017)
Dhande, D.Y.; Pande, D.W.: Multiphase flow analysis of hydrodynamic journal bearing using CFD coupled fluid structure interaction considering cavitation. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 30(4), 345–354 (2018)
Dhande, D.Y.; Lanjewar, G.H.; Pande, D.W.: Implementation of CFD–FSI technique coupled with response surface optimization method for analysis of three-lobe hydrodynamic journal bearing. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. C 100(6), 955–966 (2019)
Pravez, K.; Anil, D.; Garg, H.C.: Elasto-hydrodynamic analysis of journal bearing operating with Nano-lubricants. Proc. IMechE Part J. J. Eng. Tribol. 235, 963–974 (2020)
Solghar, A.A.: Investigation of nanoparticle additive impacts on thermohydrodynamic characteristics of journal bearings. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 229(10), 1176–1186 (2015)
Abdollahzadeh Jamalabadi, M.Y.; Alamian, R.; Yan, W.M.; Li, L.K.; Leveneur, S.; Safdari Shadloo, M.: Effects of nanoparticle enhanced lubricant films in thermal design of plain journal bearings at high Reynolds numbers. Symmetry 11(11), 1353 (2019)
Suryawanshi, S.R.; Pattiwar, J.T.: Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles blended with lubricating oil on the tribological performance of the journal bearing. Tribol. Ind 40(3), 370 (2018)
Ramaganesh, R.; Baskar, S.; Sriram, G.; Arumugam, S.; Ramachandran, M.: Finite element analysis of a journal bearing lubricated with nano lubricants. FME Trans. 48(2), 476–481 (2020)
Dang, R.K.; Chauhan, A.; Dhami, S.S.: Static thermal performance evaluation of elliptical journal bearings with Nano-lubricants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 235(8), 1627–1640 (2020)
Tushar, P.; Gundarneeya, D.P.; Vakharia.: Performance analysis of journal bearing with nanolubricants. Doctoral dissertation, Gujarat technological university Ahmedabad (2021)
Versteeg, H.K.; Malalasekera, W.: An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Longman Group Ltd, First edition, Pearson education (1995).
Zwart, P.; Gerber, A.; Belamri, T.: A two-phase flow model for predicting cavitation dynamics. Fifth international conference multiphase flow. Yokohama, Japan, May 30–June 3 (2004)
Kole, M.; Dey, T.K.: Effect of aggregation on the viscosity of copper oxide–gear oil nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50(9), 1741–1747 (2011)
Chen, H.; Ding, Y.; Tan, C.: Rheological behavior of nanofluids. New J. Phys. 9(10), 367 (2007)
Zenglin, G.; Toshio, H.; Gordon Kirk, R.: Application of CFD analysis for rotating machinery—part I hydrodynamic, hydrostatic bearings and squeeze film damper. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 127, 445–451 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abass, B.A., Ahmed, S.Y. & Kadhim, Z.H. Thermoelasto-Hydrodynamic Analysis of Nano-lubricated Journal Bearings Using Computational Fluid Dynamics with Two-way Fluid–Structure Interaction Considering Cavitation. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 2939–2950 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07024-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07024-9