Abstract
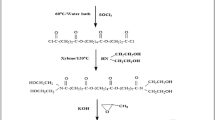
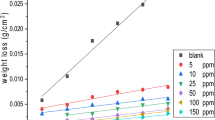
A number of gemini surfactants from the series of 1,2-alkane-bis-(ethyl ammonium bromide) were synthesized and their inhibitive effects on mild steel corrosion in acetic acid were evaluated by weight loss and electrochemical polarization measurements. Their critical micelle concentrations at equilibrium in water at 30°C were also determined. The results obtained revealed that all the studied gemini surfactants are effective in reducing corrosion of mild steel in acetic acid media. The adsorption of the inhibitors on the mild steel surface obeys Langmuir’s adsorption isotherm. The thermodynamic parameters of adsorption revealed a strong interaction between the inhibitors and the corroding mild steel surface. The influence of inhibitor concentration, solution temperature, immersion time and acid concentration on the corrosion of mild steel has also been investigated.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garverich L (1994) Corrosion in petrochemical industry. ASM International, The Materials Information Society, p 197
Maeng WY, Macdonald DD (2008) The effect of acetic acid on the stress corrosion cracking of 3.5 NiCrMoV turbine steels in high temperature water. Corros Sci 50: 2239
Bermudez XC, Jacomino OC, Aguilar PJV (1997) Inhibition of the corrosion of middle steel in solutions of hydrochloric and acetic acid mixed at different temperatures. Afinidad 54: 469
Veloz MA, González I (2002) Electrochemical study of carbon steel corrosion in buffered acetic acid solutions with chlorides and H2S. Electrochim Acta 48: 135
Bastidas DM, La Iglesia VM (2007) Organic acid vapours and their effect on corrosion of copper: a review. Corros Eng Sci Technol 42: 272
Heitz E (1974) Corrosion of metals in organic solvents. Plenum Press, New York, p 226
Singh MM, Gupta A (2000) Corrosion behavior of mild steel in acetic acid solutions. Corrosion 56: 371
Singh VB, Singh RN (1997) Organo-tin compounds as corrosion inhibitor for nickel in acetic acid solution. Mater Trans Jim 38: 49
Quraishi MA, Ansari FA (2006) Fatty acid oxadiazole as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in formic acid. J Appl Electrochem 36: 309
Quraishi MA, Sharma HK (2005) Thiazoles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in formic and acetic acid solution. J Appl Electrochem 35: 33
Branzoi V, Branzoi F, Baibarac M (2000) The inhibition of the corrosion of Armco iron in HCl solution in the presence of surfactant of the type N-alkyl-quaternary ammonium salts. Mater Chem Phys 65: 288
Ma H, Chen SH, Yin BS, Zhao SY, Liu XQ (2003) Impedance spectroscopic study of corrosion inhibition of copper by surfactants in the acidic solution. Corros Sci 45: 867
Guo R, Liu TQ, Wei X (2002) Effect of SDS and some alcohols on the inhibition efficiency of corrosion of nickel. Colloids Surf A 209: 37
Qiu LG, Xie AJ, Shen YH (2005) A novel triazole-based cationic gemini surfactant: synthesis and effect on corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid. Mater Chem Phys 91: 269
Menger FM, Littau CA (1993) Gemini surfactant: a new class of self assembling molecule. J Am Chem Soc 115: 10083
Zana R (2002) Dimeric and Oligomerin surfactants behavior at interface and in aqueous solution; a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 97: 205
De S, Aswal VK, Goyal PS, Bhattacharya S (1996) Role of spacer chain length in dimeric micellar organization, small angle neutron scattering and fluroscene studies. J Phys Chem 100: 11664
Bernheim-Groswasser A, Zana R, Talmon Y (2000) Sphere-to-cylinder transition in aqueous micellar solution of dimeric (gemini) surfactant. J Phys Chem B 104: 4005
Achouri ME, Infante MR, Izquierdo F, Kertit S, Gouttaya HM, Nciri B (2001) Synthesis of some cationic gemini surfactants and their inhibitive effect on iron corrosion in hydrochloric acid medium. Corros Sci 43: 19
ASTM (1990) Standard practice for laboratory immersion corrosion testing of metals annual book of standards. G 31-72, 3.02
Shukla SK, Quraishi MA (2010) The effects of pharmaceutically active compound doxycycline on the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros Sci 52: 314
Lebrini M, Traisnel M, Lagrenee M, Mernari B, Bentiss F (2008) Inhibitive properties, adsorption and a theoretical study of 3,5-bis(n-pyridyl)-4-amino-1,2,4-triazoles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in perchloric acid. Corros Sci 50: 473
Oguzie EE, Njoku VO, Enenbebeaku CK, Akalezi CO, Obi C (2008) Effect of hexamethyl pararosaniline chloride (crystal violet) on mild steel corrosion in acidic media. Corros Sci 50: 3480
Ferreira ES, Giancomelli C, Giacomelli FC, Spinelli A (2004) Evaluation of the inhibitor effect of L-ascorbic acid on the corrosion of mild steel. Mater Chem Phys 83: 129
Putilova IN, Blazin SA, Baranik UP (1960) Metal corrosion inhibitors. Pergamon Press, New York, p 31
Branzoi V, Branzoi F, Baibarac M (2000) The inhibition of the corrosion of Armco iron in HCl solutions in the presence of surfactants of the type of N-alkyl quaternary ammonium salts. Mater Chem Phys 65: 288
Abiola OK (2006) Adsorption of 3-(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidyl methyl)-4-methyl thiazolium chloride on mild steel. Corros Sci 48: 3078
Olivares O, Likhanova NV, Gomez B, Navarrete J, Llanos-Serrano ME, Arce E, Hallen JM (2006) Electrochemical and XPS studies of decylamides of α-amino acids adsorption on carbon steel in acidic environment. Appl Surf Sci 252: 2894
Singh AK, Quraishi MA (2010) The effect of some bis-thiadiazole derivatives on the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Corros Sci. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2010.01.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, F.A., Quraishi, M.A. Inhibitive Effect of Some Gemini Surfactants as Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acetic Acid Media. Arab J Sci Eng 36, 11–20 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-010-0008-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-010-0008-6