Abstract
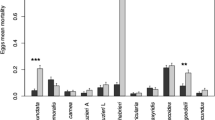
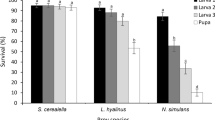
The multicoloured Asian ladybird, Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) is a generalist predator of aphids and other soft-bodied insects. Its diet leads to negative impacts on non-target species, despite its beneficial effects offered as biocontrol agent. Herein, we evaluated prey preferences and predation success of H. axyridis adults and 4th instar larvae exposed to binary prey combinations of insects commonly found in Italian vineyards. These binary combinations included a classic prey, Aphis craccivora (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and an alternative prey, i.e., first instar larvae of the European grapevine moth Lobesia botrana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), second instar larvae of H. axyridis, to evaluate cannibalistic behaviour of H. axyridis, fourth instar larvae of the non-target ladybird Scymnus apetzi (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), to evaluate intra-guild predation. Results showed that H. axyridis larvae and adults can act as potential predators of the moth pest L. botrana. They were also able to predate the non-target coccinellid species S. apetzi, thus adversely affecting aphidophagous guilds. Harmonia axyridis larvae did not significantly prefer to predate A. craccivora over the other tested preys. Harmonia axyridis adults did not show significant preferences on A. craccivora over S. apetzi larvae, whereas they prefer A. craccivora over L. botrana and H. axyridis larvae. As a general trend, the prey selection time was shorter in H. axyridis larvae, if compared to adults. Overall, our study adds basic knowledge to the prey location behaviour of H. axyridis larvae and adults, showing main differences in predation parameters of larvae and adults of this species evaluating selected binary combinations of potential preys.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Salam AH, Abdel-Baky NF (2001) Life table and biological studies of Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Col., Coccinellidae) reared on the grain moth eggs of Sitotroga cerealella Olivier (Lep., Gelechiidae). J Appl Entomol 125:455–462
Acar EB, Medina JC, Lee ML, Booth GM (2001) Olfactory behaviour of convergent lady beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to alarm pheromone of green peach aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Can Entomol 133:389–397
Ayer WA, Browne LM (1977) The ladybug alkaloids including synthesis and biosynthesis. Heterocycles 7:685–707
Bahlai CA, Welsman JA, Macleod EC, Schaafsma AW, Hallett RH, Sears MK (2008) Role of visual and olfactory cues from agricultural hedgerows in the orientation behavior of multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Environ Entomol 37:973–979
Barratt BIP, Howarth FG, Withers TM, Kean JM, Ridley GS (2010) Progress in risk assessment for classical biological control. Biol Control 52:245–254
Benelli G, Stefanini C, Giunti G, Geri S, Messing RH, Canale A (2014) Associative learning for danger avoidance nullifies innate positive chemotaxis to host olfactory stimuli in a parasitic wasp. Naturwissenschaften 101:753–757
Berkvens N, Bonte J, Berkvens D, Deforce K, Tirry L, De Clercq P (2008) Pollen as an alternative food for Harmonia axyridis. Biocontrol 53:201–210
Botezatu A, Kotseridis Y, Inglis D, Pickering G (2013) Occurrence and contribution of alkyl methoxypyrazines in wine tainted by Harmonia axyridis and Coccinella septempunctata. J Sci Food Agric 93:803–810
Brown PMJ, Thomas CE, Lombaert E, Jeffries DL, Estoup A, Lawson Handley LJ (2011) The global spread of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): distribution, dispersal and routes of invasion. Biocontrol 56:623–641
Bugg RL, Giusti GA, Merenlende A, Harrison SP, McGourty GT, Baumgartner K (2011) Biodiversity, habitat, and natural resource issues in winegrape production. In McGourty GT (ed) Organic winegrowing manual. UCANR Publications, Davis. University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources. Part 4: Organic Vineyards and the Environment, pp 155–180
Burgio G, Santi F, Maini S (2002) On intra-guild predation and cannibalism in Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) and Adalia bipunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 24:110–116
Cooper M, Varela LG, Smith RJ, Whitmer DR, Simmons GA, Lucchi A, Broadway R, Steinhauer R (2014) Growers, scientists and regulators collaborate on European grapevine moth program. Calif Agric 4:125–133
Cottrell TE (2004) Suitability of exotic and native lady beetle eggs (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) for development of lady beetle larvae. Biol Control 31:362–371
Daloze D, Braekman JC, Pateels JM (1995) Ladybird defense alkaloids: structural chemotaxonomic and biosynthetic aspects (Col.: Coccinellidae). Chemoecology 5–6:173–183
Evans EW, Dixon AFG (1986) Cues for oviposition by ladybird beetles (Coccinellidae): response to aphids. J Anim Ecol 55:1027–1034
Evans EW, Richards DR (1997) Managing the dispersal of ladybird beetles (Col.: Coccinellidae): use of artificial honeydew to manipulate spatial distributions. Entomophaga 42:93–102
Ferran A, Gambier J, Parent S, Legendre K, Tourniere R, Giuge L (1997) The effect of rearing the ladybird Harmonia axyridis on Ephestia kuehniella eggs on the response of its larvae to aphid tracks. J Insect Behav 10:129–144
Francis F, Lognay G, Haubruge E (2004) Olfactory responses to aphid and host plant volatile releases: (E)-β-farnesene an effective kairomone for the predator Adalia bipunctata. J Chem Ecol 30:741–755
Fu W, Yu X, Ahmed N, Zhang S, Liu T (2017) Intraguild predation on the aphid parasitoid Aphelinus asychis by the ladybird Harmonia axyridis. Biocontrol 62:61–70
Guo JY, Wan FH (2001) Effect of three diets on development and fecundity of the ladybeetles Harmonia axyridis and Propylaea japonica. Chin J Biol Control 17:116–120
Heidari M, Copland MJW (1992) Host finding by Cryptolaemus montrouzieri (Col., Coccinellidae) a predator of mealybugs (Hom., Pseudococcidae). Entomophaga 37:621–625
Hemptinne JL, Dixon AFG, Gauthier C (2000a) Nutritive cost of intraguild predation on eggs of Coccinella septempunctata and Adalia bipunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur J Entomol 97:559–562
Hemptinne JL, Lognay G, Gauthier C, Dixon AFG (2000b) Role of surface chemical signals in egg cannibalism and intraguild predation in ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemoecology 10:123–128
Hoddle MS (2002) Classical biological control of arthropods in the 21st century. In: Hoddle MS (eds) Proceedings of the 1st international symposium on biological control of arthropods, Honolulu, Hawaii, 14–18 January 2002. Washington, United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, p 3
Hodek I (1973) Biology of Coccinellidae. Academia, Prague & Dr. W. Junk, The Hague
Hodek I (1996) Food relationships. In: Hodek I, Honĕk A (eds) Ecology of Coccinellidae. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 143–238
Hukushima S, Itoh K (1976) Pollen and fungus as food for some Coccinellids beetles. Res Bull Fac Agric Gifu Univ 39:31–37
Ioriatti C, Anfora G, Tasin M, De Cristofaro A, Witzgall P, Lucchi A (2011) Chemical ecology and management of Lobesia botrana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J Econ Entomol 104:1125–1137
Jetter K, Klonsky K, Pickett CH (1997) A cost/benefit analysis of the ash whitefly biological control program in California. J Arboric 23:65
Joseph SB, Snyder WE, Moore AJ (1999) Cannibalizing Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) larvae use endogenous cues to avoid eating relatives. J Evol Biol 12:792–797
Kalaskar A, Evans EW (2001) Larval responses of aphidophagous lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to weevil larvae versus aphid as prey. Ann Entomol Soc Am 94:76–81
Kawai A (1976) Analysis of the aggregation behavior in the larvae of Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to prey colony. Res Popul Ecol 18:123–134
Kenis M, Adriaens T, Brown PM, Katsanis A, San Martin G, Branquart E et al (2017) Assessing the ecological risk posed by a recently established invasive alien predator: Harmonia axyridis as a case study. Biocontrol 62:341–354
Kesten U (1969) Zur Morphologie und Biologie von Anatis ocellata (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Z Angew Entomol 63:412–445
King AG, Meinwald J (1996) Review of the defensive chemistry of coccinellids. Chem Rev 96:1105–1122
Koch RL (2003) The multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis: a review of its biology, use in biological control and no-targets impacts. J Insect Sci 3:1–16
Koch RL, Costamagna AC (2017) Reaping benefits from an invasive species: role of Harmonia axyridis in natural biological control of Aphis glycines in North America. Biocontrol 62:331–340
Koch RL, Galvan TL (2008) Bad side of a good beetle: the North American experience with Harmonia axyridis. Biocontrol 53:23–35
Koch RL, Hutchison WD, Venette RC, Heimpel GE (2003) Susceptibility of immature monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae: Danainae), to predation by Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 28:265–270
Koch R, Burkness E, Burkness SJW, Hutchison WD (2004) Phytophagous preferences of the multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) for autumn-ripening fruit. J Econ Entomol 97:539–544
Lambin M, Ferran A, Maugan K (1996) Perception of visual information in the ladybird Harmonia axyridis Pallas. Entomol Exp Appl 79:121–130
Lucas E, Coderre D, Vincent C (1997) Voracity and feeding preferences of two aphidophagous coccinellids on Aphis citricola and Tetranychus urticae. Entomol Exp Appl 85:151–159
Lucas E, Coderre D, Brodeur J (1998) Intraguild predation among aphid predators: characterization and influence of extraguild prey density. Ecology 79:1084–1092
Lucas E, Demougeot S, Vincent C, Coderre D (2004) Predation upon the oblique-banded leafroller, Choristoneura rosaceana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), by two aphidophagous coccinellids (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in the presence and absence of aphids. Eur J Entomol 101:37–42
Lucchi A, Benelli G (2018) Towards pesticide-free farming? Sharing needs and knowledge promotes Integrated Pest Management. Environ Sci Poll Res 25:13439–13445
Lucchi A, Ladurner E, Iodice A, Savino F, Ricciardi R, Cosci F, Conte G, Benelli G (2018) Eco-friendly pheromone dispensers—a green route to manage the European grapevine moth? Environ Sci Poll Res 25:9426–9442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1248-3
Majerus MEN (1989) Coccinella magnifica (Redtenbacher): a myrmecophilous ladybird. Br J Entomol Nat Hist 2:97–106
Majerus MEN, Strawson W, Roy H (2006) The potential impacts of the arrival of the harlequin ladybird, Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), in Britain. Ecol Entomol 31:207–215
McClure MS (1986) Role of predator in regulation of endemic populations of Matsucoccus matsumarae (Homoptera: Margarodidae) in Japan. Environ Entomol 15:976–983
Meiracker RAF, Hammond WNO, Alphen JJM (1990) The role of kairomones in prey finding by Diomus sp. and Exochomus sp., two coccinellid predators of the cassava mealybug Phenacoccus manihoti. Entomol Exp Appl 56:209–217
Meisner MH, Harmon JP, Harvey CT, Ives AR (2011) Intraguild predation on the parasitoid Aphidius ervi by the generalist predator Harmonia axyridis: the threat and its avoidance. Entomol Exp Appl 138:193–201
Messing RH, Wright MG (2006) Biological control of invasive species: solution or pollution? Front Ecol Environ 4:132–140
Michaud JP (2001) Numerical response of Olla v-nigrum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to infestations of Asian Citrus Psyllid, (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in Florida. Fla Entomol 84:608–612
Michaud JP (2002) Biological control of Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in Florida: a preliminary report. Entomol News 113:216–222
Mirande L, Desneux N, Haramboure M, Schneider MI (2015) Intraguild predation between an exotic and native coccinellid in Argentina: the role of prey density. J Pest Sci 88:155–162
Naidu RA, Kimmins FM, Deom CM, Subrahmanyam P, Chiyembekeza AJ, Van der Merwe PJA (1999) Groundnut rossette: a virus disease affecting groundnut production in sub-saharan Africa. Plant Dis 83:700–709
Nakamuta K (1984) Visual orientation of a ladybird Coccinella septempunctata (L.) (Col.: Coccinellidae), towards its prey. Appl Entomol Zool 22:434–442
Nakamuta K, Saito T (1985) Recognition of aphid prey by the lady beetle, Coccinella septempunctata bruckii Mulsant (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Appl Entomol Zool 20:479–483
Ninkovic V, Al Abassi S, Petersson J (2001) The influence of aphid induced plant volatiles on ladybirds Beetle searching behavior. Biol Control 21:191–195
Obata S (1986) Mechanisms of prey finding in the aphidophagous ladybird beetle, Harmonia axyridis [Coleoptera: Coccinellidae]. Entomophaga 31:303–311
Obata S (1997) The influence of aphids in the behaviour of adult ladybird beetle, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Entomophaga 42:103–106
Omkar, Pervez A, Gupta AK (2004) Role of surface chemicals in egg cannibalism and intraguild predation by neonates of two aphidophagous ladybirds, Propylea dissecta and Coccinella transversalis. J Appl Entomol 128:691–695
Osawa N (1989) Sibling and non-sibling cannibalism by larvae of a lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in the field. Res Popul Ecol 31:153–160
Osawa N (1992a) Sibling cannibalism in the ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis fitness consequences for mother and offspring. Res Popul Ecol 34(1):45–55
Osawa N (1992b) A life table of the ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in relation to aphid abundance. Jpn J Entomol 60:575–579
Osawa N (1992c) Effect of pupation site on pupal cannibalism and parasitism in the ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae). Jpn J Entomol 60:131–135
Osawa N (1993) Population field studies of the aphidophagous ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): life tables and key factor analysis. Res Popul Ecol 35:335–348
Pasteels JM, Deroe C, Tursch B, Braeakman JC, Daloze D, Hootele C (1973) Distribution et activités des alcaloides défensifs des Coccinellidae. J Insect Physiol 19:1771–1784
Pearson DE, Callaway RM (2003) Indirect effects of host-specific biological control agents. Trends Ecol Evol 18:456–461
Pell JK, Baverstock J, Roy HE, Ware RL, Majerus MEN (2008) Intraguild predation involving Harmonia axyridis: a review of current knowledge and future persectives. Biocontrol 53:147–168
Pervez A, Omkar (2006) Ecology and biological control application of multicoloure Asian ladybird, Harmonia axyridis: a rewiev. Biocontrol Sci Technol 16:111–128
Polis GA (1981) The evolution and dynamics of intraspecific predation. Annu Rev Ecol Sys 12:225–251
Polis GA, Myers CA, Holt RD (1989) The ecology and the evolution of intra-guild predation: potential competitor that eat each other. Annu Rev Entomol 20:297–330
Ponsonby DJ, Copland MJW (1995) Olfactory responses by the scale insect predator Chilocorus nigritus (F.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 5:83–94
Provost C, Lucas E, Coderre D, Chouinard G (2006) Prey selection by the lady beetle Harmonia axyridis: The influence of prey mobility and prey species. J Insect Behav 19:265–277
Riddick EW (2017) Spotlight on the positive effects of the ladybird Harmonia axyridis on agriculture. Biocontrol 62:319–330
Rondoni G, Onofri A, Ricci C (2012) Laboratory studies on intraguild predation and cannibalism among coccinellid larvae (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur J Entomol 109:353–362
Rosenheim JA, Kaya HK, Ehler LE, Marois JJ, Jaffee BA (1995) Intraguild predation among biological control agents: theory and evidence. Biol Control 5:303–335
Roy H, Wajnberg E (2008) From biological control to invasion: the ladybird Harmonia axyridis as a model species. Biocontrol 53:1–4
Roy HE, Baverstock J, Ware RL, Clark SJ, Majerus MEN, Baverstock KE, Pell JK (2008) Intraguild predation of the aphid pathogenic fungus Pandora neoaphidis by the invasive coccinellid Harmonia axyridis. Ecol Entomol 33:1–8
Roy HE, Brown PM, Adriaens T, Berkvens N, Borges I, Clusella-Trullas S et al (2016) The harlequin ladybird, Harmonia axyridis: global perspectives on invasion history and ecology. Biol Invasions 18:997–1044
Růžička Z, Zemek R (2008) Deterrent effects of larval tracks on conspecific larvae in Cycloneda limbifer. Biocontrol 53:763–771
Santi F, Burgio G, Maini S (2003) Intra-guild predation and cannibalism of Harmonia axyridis and Adalia bipunctata in choice conditions. Bull Insectol 56:207–210
Santos AA, Almeida LM, Castro-Guedes CF, Penteado SRC (2014) Life table analysis and consumption capacity for Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), feeding on Cinara atlantica (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Fla Entomol 97:1702–1709
Sato S, Dixon AF (2004) Effect of intraguild predation on the survival and development of three species of aphidophagous ladybirds: consequences for invasive species. Agric For Entomol 6:21–24
Şengonca Ç, Liu B (1994) Responses of the different instar predator, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), to the kairomones produced by the prey and non-prey insects as well as the predator itself. Zeit Pflanzenk Pflanzensch 101:173–177
Shu CR, Yu CY (1985) An investigation on the natural enemies of Hyphantria cunea. Nat Enem Insects 7:91–99
Sloggett JJ, Davis AJ (2010) Eating chemically defended prey: alkaloid metabolism in an invasive ladybird predator of other ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Exp Biol 213:237–241
Sloggett JJ, Magro A, Verheggen FJ, Hemptinne JL, Hutchison WD, Riddick EW (2011) The chemical ecology of Harmonia axyridis. Biocontrol 56:643–661
Snyder WE, Joseph SB, Preziosi RF, Moore AJ (2000) Nutritional benefits of cannibalism for the lady beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) when prey quality is poor. Environ Entomol 29:1173–1179
Storch RH (1976) Prey detection by fourth stage Coccinella transversoguttata larvae (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Anim Behav 24:690–693
Stuart RJ, Michaud JP, Olsen L, Mc Coy CW (2002) Lady beetles as potential predators of the root weevil Diaprepes abbreviatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Florida citrus. Fla Entomol 85:409–416
Stubbs M (1980) Another look at prey detection by coccinellids. Ecol Entomol 5:179–182
Tasin M, Lucchi A, Ioriatti C, Mraihi M, De Cristofaro A, Boger Z, Anfora G (2011) Oviposition response of the moth Lobesia botrana to sensory cues from a host plant. Chem Senses 36:633–639
Tedders WL, Schaefer PW (1994) Release and establishment of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in the southeastern United States. Entomol News 105:228–243
Thomas MB, Willis AJ (1998) Biocontrol—risky but necessary? Trends Ecol Evol 13:325–329
Van Driesche R, Hoddle M, Center TD (2008) Control of pests and weeds by natural enemies: an introduction to biological control. Blackwell, Malden, MA
Van Lenteren JC (2012) The state of commercial augmentative biological control: plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. Biocontrol 57:1–20
Van Lenteren JC, Babendreier D, Bigler F, Burgio G, Hokkanen HMT, Kuske S et al (2003) Environmental risk assessment of exotic natural enemies used in inundative biological control. Biocontrol 48:3–38
Völkl W (1990) Fortpflanzungsstrategien von Blattlausparasitoiden (Hymenoptera, Aphidiidae): Konsequenzen ihrer Interaktionen mit Wirten und Ameisen. Dissertation, University of Bayreuth
Völkl W, Vohland K (1996) Wax covers in larvae of two Scymnus species: do they enhance coccinellid larval survival? Oecologia 107:498–503
Wagner JD, Glover MD, Moseley JB, Moore AJ (1999) Hereditability and fitness consequences of cannibalism in Harmonia axyridis. Evol Ecol Res 1:375–388
Wang XM, Yang X, Zang LS, Wang Z, Ruan CC, Liu XJ (2017) Effect of geographic variation on biology and cold tolerance of Harmonia axyridis in China. Entomol Gen 36:239–250
Yamatsu K, Watanabe C (1964) A tentative catalogue of insects natural enemies of injurious insects in Japan—part 1. Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, Parasite-Predator Host Catalogue, p 166
Yang YW, Zhang KM, Du L, Qu AJ (2006) Study on selective preferences of Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) collected from different habitats to predating aphids. China Plant Prot 26:5–7
Yasuda H, Onuma N (1999) Effect of cannibalism and predation on the larval performance of two ladybird beetles. Entomol Exp Appl 93:63–67
Yasuda H, Shinia Y (1997) Cannibalism and interspecific predation in two predatory ladybirds in relation to prey abundance in the field. Entomophaga 42:153–163
Yasuda H, Takagi T, Kogi K (2000) Effects of conspecific and heterospecific larval tracks on the oviposition behaviour of the predatory ladybird, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur J Entomol 97:551–554
Yasuda H, Kikuchi T, Kindlmann P, Sato S (2001) Relationships between attack and escape rates, cannibalism, and intraguild predation in larvae of two predatory ladybirds. J Insect Behav 14:373–384
Zhu J, Cossé AA, Obrycki JJ, Boo KS, Baker TC (1999) Olfactory reactions of the twelve-spotted lady beetle, Coleomegilla maculata and the green lacewing, Chrysoperla carnea to semiochemicals released from their prey and host plant: electroantennogram and behavioral responses. J Chem Ecol 25:1163–1177
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Associate Editor and the anonymous reviewers for kindly improving an earlier version of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canovai, R., Benelli, G., Ceragioli, T. et al. Prey selection behaviour in the multicoloured Asian ladybird, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Appl Entomol Zool 54, 213–222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-019-00615-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-019-00615-3