Abstract
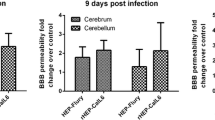
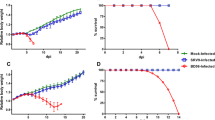
Rabies is an acute viral infection that causes encephalomyelitis in almost all warm blooded animals and is invariably fatal once the clinical signs appear. The present study was carried out to assess the effect of recombinant human interferon alpha (rhIFN α-2A) treatment on the survival of rabies infected mice and its correlation with cytokines expression. The gene expression of TNF-α and IL-6 was measured by SYBR Green Real Time PCR for two groups—“Pre-exposure” (mice were inoculated with rhIFN α-2A prior to rabies infection) and “Post-exposure” (mice were inoculated with rhIFN α-2A post rabies virus infection). Delayed mortality was observed in interferon treated infected groups. In addition, statistically significant decrease (P < 0.0001) in the expression of TNF-α and IL-6 was observed, both in the pre-exposure and post-exposure groups. These findings indicate that modulation of cytokine secretion using exogenous biologicals such as rhIFN may offer novel therapeutic approaches to treat diseases such as rabies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer GM, Moore SA, Shaddock JH, Levy HB. An effective rabies treatment in exposed monkeys: a single dose of interferon inducer and vaccine. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57(5):807–13.
Camelo S, Lafage M, Lafon M. Absence of the p55 Kd TNF-alpha receptor promotes survival in rabies virus acute encephalitis. J Neurovirol. 2000;6(6):507–18.
Carlson NG, Wieggel WA, Chen J, Bacchi A, Rogers SW, Gahring LC. Inflammatory cytokines IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha impart neuroprotection to an excitotoxin through distinct pathways. J Immunol. 1999;163(7):3963–8.
(CDC) CfDCaP. Protocol for postmortem diagnosis of rabies in animals by direct fluorescent antibody testing. A minimum standard for rabies diagnosis in the United States. Atlanta.
Dafny N, Prieto-Gomez B, Reyes-Vazquez C. Does the immune system communicate with the central nervous system? Interferon modifies central nervous activity. J Neuroimmunol. 1985;9(1–2):1–12.
Guggenheim MA, Baron S. Clinical studies of an interferon inducer, polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid [poly (I)-poly (C)], in children. J Infect Dis. 1977;136(1):50–8.
Hansen BD, Nara PL, Maheshwari RK, Sidhu GS, Bernbaum JG, Hoekzema D, et al. Loss of infectivity by progeny virus from alpha interferon-treated human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected T cells is associated with defective assembly of envelope gp120. J Virol. 1992;66(12):7543–8.
Harmon MW, Janis B. Therapy of murine rabies after exposure: efficacy of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid alone and in combination with three rabies vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1975;132(3):241–9.
Hilfenhaus J, Karges HE, Weinmann E, Barth R. Effect of administered human interferon on experimental rabies in monkeys. Infect Immun. 1975;11(5):1156–8.
Hilfenhaus J, Weinmann E, Majer M, Barth R, Jaeger O. Administration of human interferon to rabies virus-infected monkeys after exposure. J Infect Dis. 1977;135(5):846–9.
Ho M, Nash C, Morgan CW, Armstrong JA, Carroll RG, Postic B. Interferon administered in the cerebrospinal space and its effect on rabies in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1974;9(2):286–93.
Jackson AC. Update on rabies diagnosis and treatment. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2009;11(4):296–301.
Janis B, Habel K. Rabies in rabbits and mice: protective effect of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid. J Infect Dis. 1972;125(4):345–52.
Kalil AC, Devetten MP, Singh S, Lesiak B, Poage DP, Bargenquast K, et al. Use of interferon-alpha in patients with West Nile encephalitis: report of 2 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40(5):764–6.
Kuang Y, Lackay SN, Zhao L, Fu ZF. Role of chemokines in the enhancement of BBB permeability and inflammatory infiltration after rabies virus infection. Virus Res. 2009;144(1–2):18–26.
Levy HB, Baer G, Baron S, Buckler CE, Gibbs CJ, Iadarola MJ, et al. A modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex that induces interferon in primates. J Infect Dis. 1975;132(4):434–9.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Megid J, Peracolli MT, Curi PR, Zanetti CR, Cabrera WH, Vassao R, et al. Effect of vaccination and the immunomodulators “bacillus of Calmette-Guerin, avridine and Propionibacterium acnes” on rabies in mice. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998;21(4):305–18.
Megid J, Kaneno R, Nozaki CN, Brito CJ, Almeida MF. Increased interleukin-10 associated with low IL-6 concentration correlated with greater survival rates in mice infected by rabies virus vaccinated against it and immunomodulated with P. acnes. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004;27(6):393–411.
Mehta S, Mukherjee S, Balasubramanian D, Chowdhary A. Evaluation of neuroimmunomodulatory activity of recombinant human interferon alpha. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2014;21(5):250–6.
Nagaraj T, Vasanth JP, Desai A, Kamat A, Madhusudana SN, Ravi V. Ante mortem diagnosis of human rabies using saliva samples: comparison of real time and conventional RT-PCR techniques. J Clin Virol. 2006;36(1):17–23.
Nuovo GJ, Defaria DL, Chanona-Vilchi JG, Zhang Y. Molecular detection of rabies encephalitis and correlation with cytokine expression. Mod Pathol. 2005;18(1):62–7.
Phares TW, Fabis MJ, Brimer CM, Kean RB, Hooper DC. A peroxynitrite-dependent pathway is responsible for blood-brain barrier permeability changes during a central nervous system inflammatory response: TNF-α is neither necessary nor sufficient. J Immunol. 2007;178(11):7334–43.
Postic B, Fenje P. Effect of administered interferon on rabies in rabbits. Appl Microbiol. 1971;22(3):428–31.
Quaranta A, Siniscalchi M, Albrizio M, Volpe S, Buonavoglia C, Vallortigara G. Influence of behavioural lateralization on interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 gene expression in dogs before and after immunization with rabies vaccine. Behav Brain Res. 2008;186(2):256–60.
Radhakrishnan VV, Sumi MG, Reuben S, Mathai A, Nair MD. Circulating tumour necrosis factor alpha & soluble TNF receptors in patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Indian J Med Res. 2003;117:216–20.
Reyes-Vazquez C, Mendoza-Fernandez V, Herrera-Ruiz M, Dafny N. Interferon modulates glucose-sensitive neurons in the hypothalamus. Exp Brain Res. 1997;116(3):519–24.
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(6):1101–8.
Silin DS, Lyubomska OV, Ershov FI, Frolov VM, Kutsyna GA. Synthetic and natural immunomodulators acting as interferon inducers. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(11):1238–47.
Solanki A, Radotra BD, Vasishta RK. Correlation of cytokine expression with rabies virus distribution in rabies encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2009;217(1–2):85–9.
Tohamy AA, Fahmy AM, Dkhil MA, Diab MSM. Protective role of interferon against cytotoxicity induced by rabies virus in mice. Afr J Biotechnol. 2010;9(7):1097–105.
Weinmann E, Majer M, Hilfenhaus J. Intramuscular and/or intralumbar postexposure treatment of rabies virus-infected cynomolgus monkeys with human interferon. Infect Immun. 1979;24(1):24–31.
WHO. Rabies vaccines. WHO position paper. The Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2007;82(49–50):425–435.
Wiktor TJ, Postic B, Ho M, Koprowski H. Role of interferon induction in the protective activity of rabies vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972;126(4):408–18.
Willoughby RE Jr, Tieves KS, Hoffman GM, Ghanayem NS, Amlie-Lefond CM, Schwabe MJ, et al. Survival after treatment of rabies with induction of coma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(24):2508–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehta, S., Roy, S., Mukherjee, S. et al. Exogenous interferon prolongs survival of rabies infected mice. VirusDis. 26, 163–169 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-015-0269-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-015-0269-5