Abstract
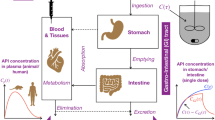
Oral dosage forms with controlled release exhibit various advantages over their immediate release counterparts, but they must be built adequately by dispersing the drug through the well-defined polymer matrix. This study is concerned with diffusion-controlled dosage forms to resolve the problems that appear: in vitro tests generally used for determining the kinetics of drug release do not take into account the nature of the drug. On the contrary, the plasma drug profiles obtained through in vivo tests strongly depend on the nature of the drug, through their typical pharmacokinetic parameters. Moreover, the effect of the stirring rate is difficult to evaluate. Following the demand from the FDA concerned with the in vitro/in vivo correlation, a numerical model was built so as to evaluate the plasma drug profile obtained with any drug delivered from a diffusion-controlled release dosage form. The results are expressed by connecting the half-life times of the drugs obtained either with bolus injection or with the dosage forms, for various values of the parameters of interest: the diffusivity of the matrix polymer and the size of the dosage form. Thus, these diagrams make it possible to promptly determine the characteristics of the dosage forms able to give the desired plasma drug profile for any drug. Of course, for each drug being defined by its pharmacokinetic parameters, the polymer matrix should be selected as a function of its diffusivity. Finally, the evaluation of the plasma drug profile is of effective help to determine quantitatively the effect of the intervariability of the patients as well as the effect of the patient’s noncompliance.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Drug concentration in the plasma
- C t , C0:
-
Drug concentration in the plasma at time t, at time 0 (Eq. 11)
- C s :
-
Drug concentration at the surface of the dosage form (Eq. 2)
- C ext :
-
Drug concentration in the GI (Eq. 2)
- D :
-
Diffusivity of the drug through the polymer dosage form cm2/s
- h :
-
Coefficient of drug transport at the dosage form–GI liquid interface
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal tract
- M t :
-
Amount of drug release by the dosage form at time t (Eqs. 3, 4)
- M ∞ :
- M t /M∞:
-
Amount of drug in the plasma at time t as a fraction of the amount initially in the dosage form (Eqs. 3, 4)
- n :
- R, r:
-
Radius of the dosage form, radial position
- t :
-
Time
- t 0.5 :
-
Half-life time of the drug in the patient’s blood obtained by iv bolus injection. Pharmacokinetic parameter (Eq. 12)
- T 0.5 :
-
Half-life of the drug in the patient’s blood with controlled release dosage form
- T ′0.5 :
-
Half-life of the drug in the patient’s blood with immediate release dosage form
- V p :
-
Apparent plasmatic volume (l) (Eq. 13)
- Y :
- Z :
- W :
-
Amount of drug eliminated at time t (Eq. 9)
References
Aïnaoui A, Vergnaud JM (2000) Effect of the nature of the polymer and the process of drug release (diffusion or erosion) for oral dosage forms. Comput Theor Polym Sci 10:383–390
Aïnaoui A, Siepmann J, Bodmeier R, Vergnaud JM (2001) Calculation of the dimensions of dosage forms with release controlled by diffusion for in vivo use. Euro J Pharm Biopharm 51:17–24
Breilh D, Pobel C, Saux MC, Maire P, Vergnaud JM, Saidna M, Jelliffe R, Barbault X (2001) Mixed pharmacokinetic population study and diffusion model to describe ciprofloxacin lung concentrations. Comput Biol Med 31:147–155
Campoli-Richards DM, Monk JP, Price A, Benfield P, Todd PA, Ward A (1998) Ciprofloxacin: a review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drug Eval Drugs 35:373–447
Cardot JM, Beyssac E (1993) In vitro/in vivo correlations: scientific implications and standardisation. Eur J Drug Metabol Pharmacol 18(1):113–120
Clissold SP (1986) Aspirin and related derivatives of salicylic acid. Drugs 32:8–26
Crump B, Wise R (1983) Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 24:784–786
Fabre D, Bressole F, Gomeni R (1991) Steady-state pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin in plasma from patients with nosocomial pneumonia: penetration of the bronchial mucosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 35:2521–2525
Heilmann K (1984) Therapeutic systems, vol 17, 2nd edn. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart
Hoppfler D, Koeppe P (1987) Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin in healthy subjects and patients with impaired renal function. Drugs 1:51–55
Nia B, Ouriemchi EM, Vergnaud JM (1995) Calculation of the blood level of a drug taken orally with a diffusion controlled dosage form. Int J Pharm 119:165–171
Ouriemchi EM, Vergnaud JM (1996a) Prediction of in vivo blood level with controlled release dosage forms. Effect of the gastrointestinal tract time. J Pharm Pharmacol 48:390–396
Ouriemchi EM, Vergnaud JM (1996b) Calculation of the plasma drug level with oral controlled release dosage forms. Effect of the dose frequency. Int J Pharm 127:177–184
Ouriemchi EM, Bouzon J, Vergnaud JM (1995) Modelling the process of controlled release of drug in in vitro and in vivo tests. Int J Pharm 113:231–240
Rosca ID, Vergnaud JM (2007) Adapting therapy with repeated short-infusions to intervariability between patients. Euro J Drug Metabol Pharmacol 32:87–99
Rosca ID, Vergnaud JM (2008) Evaluation of the characteristics of oral dosage forms with release controlled by erosion. Comput Biol Med 38(6):668–675
Siepmann J, Aïnaoui A, Vergnaud JM, Bodmeier R (1998) Calculations of the dimensions of drug-polymer devices based on diffusion parameters. J Pharm Sci 87:827–832
Siewert M (1993) Perspectives of in vitro dissolution tests in establishing in vitro/in vivo correlations. Eur J Drug Metabol Pharmacol 18(1):7–18
Skelly JP, Shiu GF (1993) In vitro/in vivo correlations in biopharmaceutics: scientific and regulatory implications. Eur J Drug Metabol Pharmacol 18(1):121–129
Skelly JP, Barr WH, Benet LZ et al (1987) Report of the workshop on controlled-release dosage forms: issues and controversies. Pharm Res 4:75–77
Skelly JP, Amidon GL, Barr WH et al (1990) In vitro and in vivo testing and correlation for oral controlled/modified release dosage forms. Pharm Res 7:975–982
Skelly JP, Van Bushirk GA, Sevello DR et al (1993) Scale-up of immediate release oral solid dosage forms. Pharm Res 10:313–316
Smith MJ, White IO, Bouryer H, Willis J, Hodson ME, Batten JC (1986) Pharmacokinetics and sputum penetration of ciprofloxacin in patients with cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 30:614–616
Sorgel F, Jaehde U, Naber K, Stephan U (1989) Pharmacokinetic disposition of quinolones in human body fluids and tissues. Clin Pharmacokin 16:5–24
Vergnaud JM (1993) Controlled drug release of oral dosage forms (chapter 1–5). Hellis Horwood, Chichester
Vergnaud JM (1996) Conference invited at the FDA, Washington DC, USA
Vergnaud JM (1999) Use of polymers in pharmacy for oral dosage forms with controlled release. Recent Res Dev Macromol Res 4:173–209
Vergnaud JM, Rosca ID (2005) Assessing bioavailability of drug delivery systems. CRC Press Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosca, I.D., Vergnaud, J.M. Survey: calculation of the characteristics of oral diffusion-controlled release dosage forms related to the drug. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 35, 29–39 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-010-0005-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-010-0005-x