Abstract
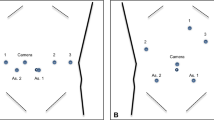
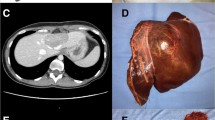
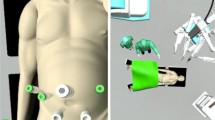
Minimally invasive liver surgery is performed with increasing frequency by hepatic surgeons. Laparoscopy was the first approach to be used and it is currently safely feasible in selected patients by experienced surgeons. Minor and major laparoscopic hepatectomies are now performed as a routine procedure in tertiary referral centers, with increasing evidence of long-term results comparable to traditional surgery together with the advantages of a minimally invasive approach. Robotic surgery, first developed for military purposes, showed to overcome some of the limits of laparoscopy, with an improved visual magnification, a 3-dimensional view and enhanced dexterity with better movement control. This allows an easier approach for resections in the posterior segments and for lesions close to major vessels. We present our preliminary experience of 20 consecutive robotic liver resection. Indications were colo-rectal liver metastasis (n = 7), hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 6), liver hemangioma (n = 2), biliary cystoadenoma (n = 2), breast cancer liver metastasis (n = 1), lung cancer liver metastasis (n = 1), symptomatic left liver lithiasis (n = 1). No conversion to laparotomy have been made and no hepatic pedicle clamping has been performed. The median duration of surgery was 141 min. There was no mortality, global morbidity was 10 %. Median tumor size was 36 mm. Median post-operative length of stay was 5.7 days. Robotic surgery can be safely performed by experienced hepatic surgeons, resections of lesions in the posterior segments and close to the major vessels seem to be the best indication. Further studies are needed to clarify the exact role of robotics in liver surgery.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reich H, McGlynn F, DeCaprio J, Budin R (1991) Laparoscopic excision of benign liver lesions. Obstet Gynecol 78:956–958
Gagner M, Rheault M, Dubuc J (1992) Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy for liver tumor (abstract). Surg Endosc 6:99
Dagher I, Di Giuro G, Dubrez J et al (2009) Laparoscopic versus open right hepatectomy: a comparative study. Am J Surg 198:173–177
Laurent A, Cherqui D, Lesurtel M et al (2003) Laparoscopic liver resection for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma complicating chronic liver disease. Arch Surg 138:763–769
Cai XJ, Yang J, Yu H et al (2008) Clinical study of laparoscopic versus open hepatectomy for malignant liver tumors. Surg Endosc 22:2350–2356
Guerron AD, Aliyev S, Agcaoglu O et al (2013) Laparoscopic versus open resection of colorectal liver metastasis. Surg Endosc 27:1138–1143
Tsung A, Geller DA, Sukato DC et al (2013) Robotic versus laparoscopic hepatectomy: a matched comparison. Ann Surg 259:549–555
Yoon YS, Han HS, Cho JY et al (2013) Laparoscopic liver resection for centrally located tumors close to the hilum, major hepatic veins, or inferior vena cava. Surgery 153:502–509
Cherqui D, LaurentA Tayar C et al (2006) Laparoscopic liver resection for peripheral hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: midterm results and perspectives. Ann Surg 243:499–550
Kazaryan AM, Marangos IP, Rosok BI et al (2010) Laparoscopic resection of colorectal liver metastases: surgical and long-term oncologic outcome. Ann Surg 252:1005–1012
Castaing D, Vibert E, Ricca L et al (2009) Oncologic results of laparoscopic versus open hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases in two specialized centers. Ann Surg 250:849–855
Nguyen KT, Laurent A, Dagher I et al (2009) Minimally invasive liver resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multi-institutional, international report of safety, feasibility, and early outcomes. Ann Surg 250:842–848
Sasaki A, Nitta H, Otsuka K et al (2009) Ten-year experience of totally laparoscopic liver resection in a single institution. Br J Surg 96:274–279
Nguyen KT, Gamblin TC, Geller DA (2009) World review of laparoscopic liver resection-2,804 patients. Ann Surg 250:831–841
Giulianotti PC, Coratti A, Sbrana F et al (2011) Robotic liver surgery: results for 70 resections. Surgery 149:29–39
National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v. 4.0; 2010. Available at: http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm. Accessed 27 Feb 2015
Reggiani BA, Rossi G (2013) Robotic surgery of the liver: Italian experience and review of the literature. Ecancer 7:358
Casciola L, Patriti A, Ceccarelli G et al (2011) Robot-assisted parenchymal-sparing liver surgery including lesions located in the posterosuperior segments. Surg Endosc 25:3815–3824
de Haas RJ, Wicherts MD, Flores E, Azoulay D et al (2008) R1 resection by necessity for colorectal liver metastases: Is it still a contraindication to surgery? Ann Surg 248:626–637
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standard
All the procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felli, E., Santoro, R., Colasanti, M. et al. Robotic liver surgery: preliminary experience in a tertiary hepato-biliary unit. Updates Surg 67, 27–32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-015-0285-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-015-0285-4