Abstract
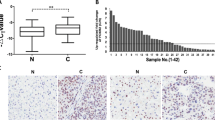
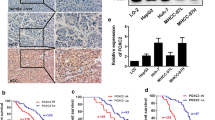
The Forkhead box M1 (FoxM1) transcription factor plays crucial roles in multiple biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and transformation. Recent studies have reported that aberrant expression of FoxM1 was found in a variety of human cancers. However, the expression pattern of FoxM1 and its clinical significance in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have not been well characterized to date. In this study, the expression of FoxM1 was evaluated in 46 pairs of human HCC, the adjacent non-tumorous liver tissues, and 12 pairs of normal liver tissues by immumohistochemistry. FoxM1 expression was upregulated in the HCC (76.09 %) compared with non-tumorous liver tissues (39.13 %) and normal liver tissues (8.33 %) (P < 0.05). FoxM1 expression was significantly associated with tumor stage, tumor size, tumor number, integrality of tumor encapsulation, tumor thrombus, and AFP level (P < 0.05). Functionally, enforced expression of FoxM1 in HCC cell line (HHCC) remarkably enhanced cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Further analysis of cell cycle-related molecules showed that FoxM1 overexpression increased expressions of cyclin B1 and cyclin D1 but reduced expressions of p27Kip1 and p21Cip1. Our findings suggest that FoxM1 overexpression promotes HCC cell proliferation by cell cycle regulation, which is a potential target for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Jia D, Jing Y, Zhang Z, Liu L, Ding J, Zhao F, et al. Amplification of MPZL1/PZR promotes tumor cell migration through Src-mediated phosphorylation of cortactin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Res. 2014;24:204–17.
Myatt SS, Lam EW. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:847–59.
Laoukili J, Stahl M, Medema RH. Foxm1: at the crossroads of ageing and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1775:92–102.
Wierstra I. FOXM1 (forkhead box M1) in tumorigenesis: overexpression in human cancer, implication in tumorigenesis, oncogenic functions, tumor-suppressive properties, and target of anticancer therapy. Adv Cancer Res. 2013;119:191–419.
Wu QF, Liu C, Tai MH, Liu D, Lei L, Wang RT, et al. Knockdown of FOXM1 by siRNA interference decreases cell proliferation, induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits cell invasion in MHCC-97h cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31:361–6.
Sun HC, Li M, Lu JL, Yan DW, Zhou CZ, Fan JW, et al. Overexpression of forkhead box M1 protein associates with aggressive tumor features and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2011;25:1533–9.
Li B, Qi XQ, Chen X, Huang X, Liu GY, Chen HR, et al. Expression of targeting protein for xenopus kinesin-like protein 2 is associated with progression of human malignant astrocytoma. Brain Res. 2010;1352:200–7.
Madureira PA, Varshochi R, Constantinidou D, Francis RE, Coombes RC, Yao KM, et al. The forkhead box M1 protein regulates the transcription of the estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:25167–76.
Zhang LL, He DL, Li X, Li L, Zhu GD, Zhang D, et al. Overexpression of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor inhibit growth of human bladder cancer cell in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28:895–900.
Korver W, Roose J, Clevers H. The winged-helix transcription factor trident is expressed in cycling cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:1715–9.
Kalinichenko VV, Major ML, Wang X, Petrovic V, Kuechle J, Yoder HM, et al. Foxm1b transcription factor is essential for development of hepatocellular carcinomas and is negatively regulated by the p19ARF tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2004;18:830–50.
Calvisi DF, Pinna F, Ladu S, Pellegrino R, Simile MM, Frau M, et al. Forkhead box M1b is a determinant of rat susceptibility to hepatocarcinogenesis and sustains ERK activity in human HCC. Gut. 2009;58:679–87.
Wakino S, Kintscher U, Kim S, Yin F, Hsueh WA, Law RE. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands inhibit retinoblastoma phosphorylation and G1→S transition in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22435–41.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30901447/C160402), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2013M532058), and Key Science and Technology Project of Shaanxi Province (2013K12-08-01).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Min Yu and Zheng Tang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Tang, Z., Meng, F. et al. Elevated expression of FoxM1 promotes the tumor cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 1289–1297 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3436-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3436-9