Abstract
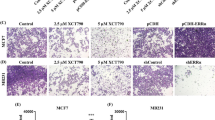
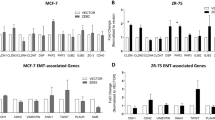
More and more studies have reported that epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) involved in the process of cancer development and progression occurs. The EMT also plays an important role in the movement and transfer of the tumors. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) could induce the EMT in some cancer cell types. However, the mechanism underlying this transition process has also not been entirely clarified. In this study, the results indicated that TGF-β1-mediated EMT in the tumor was associated with the estrogen receptor (ER). The decreased expression of vimentin and snail resulted in the decrease of the ER expression by small interfering RNA-mediated silencing and preventing the TGF-β-induced EMT. In conclusion, our results indicated that TGF-β1 is an estrogen receptor signaling and essential novel downstream targets and could act as an important factor in the TGF-β-induced EMT.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng J, Li C, Wu X, Yang Y, Hao M, Sheng S, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel biomarker of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in two China regions. Tumor Biol. 2014;35(3):2265–9.
Lue HW, Yang X, Wang R, Qian W, Xu RZ, Lyles R, et al. LIV-1 promotes prostate cancer epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis through HB-EGF shedding and EGFR-mediated ERK signaling. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27720.
Di Cello F, Li H, Vecchio-Pagán B, Gordon B, Harbom K, Shin J, et al. Cigarette smoke induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition and increases the metastatic ability of breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2013;12(1):90.
Vervoort SJ, Lourenco AR, van Boxtel R, Coffer PJ. SOX4 mediates TGF-β-induced expression of mesenchymal markers during mammary cell epithelial to mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53238.
Lenferink AEG, Cantin C, Nantel A, Wang E, Durocher Y, Banville M, et al. Transcriptome profiling of a TGF-β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition reveals extracellular clusterin as a target for therapeutic antibodies. Oncogene. 2010;29(6):831–44.
Balanis N, Wendt MK, Schiemann BJ, Wang Z, Schiemann WP, Carlin CR. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition promotes breast cancer progression via a fibronectin-dependent STAT3 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(25):17954–67.
Mak P, Chang C, Pursell B, Mercurio AM. Estrogen receptor β sustains epithelial differentiation by regulating prolyl hydroxylase 2 transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(12):4708–13.
Lam SS, Mak AS, Yam JW, Cheung AN, Ngan HY, Wong AS. Targeting estrogen-related receptor alpha inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties of ovarian cancer cells. Mol Ther. 2014;22(4):743–51.
Shao R, Shi J, Liu H, Shi X, Du X, Klocker H, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and estrogen receptor alpha mediated epithelial dedifferentiation mark the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate. 2014;74(9):970–82.
Asiedu MK, Ingle JN, Behrens MD, Radisky DC, Knutson KL. TGFβ/TNFα-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition generates breast cancer stem cells with a claudin-low phenotype. Cancer Res. 2011;71(13):4707–19.
Romagnoli M, Belguise K, Yu Z, Wang X, Landesman-Bollag E, Seldin DC, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-β1 is mediated by Blimp-1–dependent repression of BMP-5. Cancer Res. 2012;72(23):6268–78.
Chua KN, Poon KL, Lim J, Sim WJ, Huang RYJ, Thiery JP. Target cell movement in tumor and cardiovascular diseases based on the epithelial–mesenchymal transition concept. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2011;63(8):558–67.
Xu K, Wang X, Shi Q, Chen C, Tian C, Li XL, et al. Human prion protein mutants with deleted and inserted octarepeats undergo different pathways to trigger cell apoptosis. J Mol Neurosci. 2011;43(3):225–34.
Takebe N, Warren RQ, Ivy SP. Breast cancer growth and metastasis: interplay between cancer stem cells, embryonic signaling pathways and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(3):211.
Farabaugh SM, Micalizzi DS, Jedlicka P, Zhao R, Ford HL. Eya2 is required to mediate the pro-metastatic functions of Six1 via the induction of TGF-β signaling, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and cancer stem cell properties. Oncogene. 2012;31(5):552–62.
Wik E, Ræder MB, Krakstad C, Trovik J, Birkeland E, Hoivik EA, et al. Lack of estrogen receptor-α is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and PI3K alterations in endometrial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(5):1094–105.
Stadler SC, Vincent CT, Fedorov VD, Patsialou A, Cherrington BD, Wakshlag JJ, et al. Dysregulation of PAD4-mediated citrullination of nuclear GSK3β activates TGF-β signaling and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(29):11851–6.
Stankic M, Pavlovic S, Chin Y, Brogi E, Padua D, Norton L, et al. TGF-β-Id1 signaling opposes Twist1 and promotes metastatic colonization via a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. Cell Rep. 2013;5(5):1228–42.
Sivadas VP, Kannan S. The microRNA networks of TGF-beta signaling in cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014;35(4):1857–2869.
Azhar M, Runyan RB, Gard C, Sanford LP, Miller ML, Andringa A, et al. Ligand-specific function of transforming growth factor beta in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in heart development. Dv Cyn. 2009;238(2):431–42.
Medici D, Hay ED, Olsen BR. Snail and slug promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition through beta-catenin T cell factor-4-dependent expression of transforming growth factor-beta 3. Mol Bil Cell. 2008;19(1):4875–87.
Yu Y, Xiao CH, Tan LD, Wang QS, Li XQ, Feng YM. Cancer-associated fibroblast induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cells through paracrine TGF-β signaling. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(3):724–32.
Acknowledgements
The present study was financially granted by the projects of Henan Health Bureau (ID. 201203077)
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dong-Mei Fan and Peng-Wei Qi contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, DM., Qi, PW., Gao, SG. et al. TGF-β1 mediates estrogen receptor-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in some tumor lines. Tumor Biol. 35, 11277–11282 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2166-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2166-8