Abstract
Background
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common degenerative disease of the nervous system in the elderly.
Objectives
To investigate the effect of protocadherin 8 (PCDH8) on PD and explore the underlying mechanism.
Results
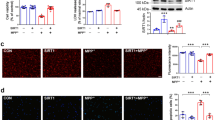
PCDH8 was down-regulated in PD. Silencing PCDH8 inhibited cell viability, increased cell cytotoxicity and apoptosis, but overexpression of PCDH8 acted the opposed effects. Then, silencing PCDH8 increased the levels of IL-1β, IL-8, TNF-α and ROS production, but decreased SOD and CAT activity, while up-regulation of PCDH8 acted the opposed effects. In addition, down-regulation of PCDH8 activated MAPK pathway, but up-regulation of PCDH8 inhibited MAPK pathway. Furthermore, in SH-SY5Y cells treated by MPP+, SB203580 reversed cell injuries induced by silencing PCDH8.
Conclusion
PCDH8 was down-regulated in PD, and PCDH8 protected MPP+-induced neuronal injury in SH-SY5Y cells via inhibiting MAPK pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar RS, Ness JM, Roth KA (2004) Bcl-2 family regulation of neuronal development and neurodegeneration. Biochem Biophys Acta 1644(2–3):189–203
Bai H et al (2020) Polydatin protects SH-SY5Y in models of Parkinson’s disease by promoting Atg5-mediated but parkin-independent autophagy. Neurochem Int 134:104671
Benassi B et al (2019) 50-Hz MF does not affect global DNA methylation of SH-SY5Y cells treated with the neurotoxin MPP(). Bioelectromagnetics 40(1):33–41
Campbell BC (2017) Thrombolysis and thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: strengths and synergies. Semin Thromb Hemost 43(2):185–190
Chen ZJ et al (2021) Association of Parkinson’s disease with microbes and microbiological therapy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:619354
Cirmi S et al (2021) A flavonoid-rich extract of mandarin juice counteracts 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells and modulates Parkinson-related genes. Antioxidants 10(4):539
Correa SA, Eales KL (2012) The role of p38 MAPK and its substrates in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disease. J Signal Transduct 2012:649079
Cruz-Monteagudo M et al (2016) Efficient and biologically relevant consensus strategy for Parkinson’s disease gene prioritization. BMC Med Genomics 9:12
Ding XM et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA-p21 regulates MPP(+)-induced neuronal injury by targeting miR-625 and derepressing TRPM2 in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem Biol Interact 307:73–81
Dorsey ER et al (2007) Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 68(5):384–386
El Hajj N, Dittrich M, Haaf T (2017) Epigenetic dysregulation of protocadherins in human disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 69:172–182
Fecher LA, Amaravadi RK, Flaherty KT (2008) The MAPK pathway in melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol 20(2):183–189
Gao JX et al (2019) Overexpression of microRNA-183 promotes apoptosis of substantia nigra neurons via the inhibition of OSMR in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Med 43(1):209–220
Gong P et al (2017) Tectorigenin attenuates the MPP(+)-induced SH-SY5Y cell damage, indicating a potential beneficial role in Parkinson’s disease by oxidative stress inhibition. Exp Ther Med 14(5):4431–4437
Gonzalez-Latapi P, Bhowmick SS, Saranza G, Fox SH (2020) Non-dopaminergic treatments for motor control in Parkinson’s disease: an update. CNS Drugs 34(10):1025–1044
Guo C et al (2019) Neuroprotective effects of protocatechuic aldehyde through PLK2/p-GSK3beta/Nrf2 signaling pathway in both in vivo and in vitro models of Parkinson’s disease. Aging 11(21):9424–9441
Kim SY et al (2010) The expression of non-clustered protocadherins in adult rat hippocampal formation and the connecting brain regions [comparative study research support, Non-U S Gov’t]. Neuroscience. 170(1):189–199
Lee DS, Kwon KH, Cheong SH (2017) Taurine chloramine suppresses LPS-induced neuroinflammatory responses through Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression in mouse BV2 microglial cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 975(Pt 1):131–143
Lesnick TG et al (2007) A genomic pathway approach to a complex disease: axon guidance and Parkinson disease [Research Support, N I H, Extramural Research Support, Non-U S Gov’t]. PLoS Genet 3(6):0030098
Li Z, Gou J, Jia J, Zhao X (2015) MicroRNA-429 functions as a regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Pcdh8 during murine embryo implantation [Research Support, Non-U S Gov’t]. Hum Reprod 30(3):507–518
Luo SH et al (2010) In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of silver-containing borate bioactive glass. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 95(2):441–448
Miralles CP et al (2020) Expression of protocadherin-gammaC4 protein in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 528(5):840–864
Ola MS, Nawaz M, Ahsan H (2011) Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 351(1–2):41–58
Poewe W et al (2017) Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim 3:17013
Qian Y, Xu S, Yang X, Xiao Q (2018) Purinergic receptor P2Y6 contributes to 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced oxidative stress and cell death in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells [Research Support, Non-U S Gov’t]. J Neurosci Res 96(2):253–264
Radhakrishnan DM, Goyal V (2018) Parkinson’s disease: a review. Neurol India 66(Supplement):S26–S35
Robinson KA et al (1999) Redox-sensitive protein phosphatase activity regulates the phosphorylation state of p38 protein kinase in primary astrocyte culture. J Neurosci Res 55(6):724–732
Schapira AHV, Chaudhuri KR, Jenner P (2017) Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(7):435–450
Shao Z et al (2019) Dysregulated protocadherin-pathway activity as an intrinsic defect in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cortical interneurons from subjects with schizophrenia. Nat Neurosci 22(2):229–242
Sznejder-Pacholek A et al (2017) The effect of alpha-synuclein on gliosis and IL-1alpha, TNFalpha, IFNgamma, TGFbeta expression in murine brain. Pharmacol Rep: PR 69(2):242–251
Tysnes OB, Storstein A (2017) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 124(8):901–905
Weidner WS, Barbarino P (2019) The state of the art of dementia research: new frontiers. Alzheimers Dement 15(7):P1473
Weng L et al (2017) Ampelopsin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through the inhibition of the NF-kappaB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways in microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 44:1–8
Wu F et al (2013) p38(MAPK)/p53-mediated bax induction contributes to neurons degeneration in rotenone-induced cellular and rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 63(3):133–140
Xia D, Sui R, Zhang Z (2019) Administration of resveratrol improved Parkinson’s disease-like phenotype by suppressing apoptosis of neurons via modulating the MALAT1/miR-129/SNCA signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 120(4):4942–4951
Xu J et al (2018) Urolithins attenuate LPS-induced neuroinflammation in BV2Microglia via MAPK, Akt, and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem 66(3):571–580
Yasuda S et al (2007) Activity-induced protocadherin arcadlin regulates dendritic spine number by triggering N-cadherin endocytosis via TAO2beta and p38 MAP kinases. Neuron 56(3):456–471
Yoo YM, Jung EM, Ahn C, Jeung EB (2018) Nitric oxide prevents H2O2-induced apoptosis in SK-N-MC human neuroblastoma cells. Int J Biol Sci 14(14):1974–1984
Yu JS et al (2008) PCDH8, the human homolog of PAPC, is a candidate tumor suppressor of breast cancer. Oncogene 27(34):4657–4665
Yu H et al (2020) Protocadherin 8 (PCDH8) inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Sci Monitor: Int Med J Exp Clin Res 26:e920665
Yue Y, Qiao B, Jiang X (2020) Tormentic acid confers protection against oxidative stress injury in rats with Parkinson’s disease by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol 66(1):32–36
Zhu J, Wang S, Liang Y, Xu X (2018) Inhibition of microRNA-505 suppressed MPP+-induced cytotoxicity of SHSY5Y cells in an in vitro Parkinson’s disease model. Eur J Pharmacol 835:11–18
Zhu YL et al (2019) Neuroprotective effects of astilbin on MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mice: glial reaction, α-synuclein expression and oxidative stress. Int Immunopharmacol 66:19–27
Zong Z, Pang H, Yu R, Jiao Y (2017) PCDH8 inhibits glioma cell proliferation by negatively regulating the AKT/GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 14(3):3357–3362
Acknowledgements
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huaming Wei designed the study and wrote the paper; Huaming Wei and Yuping Wu provided technical support and obtained the data; Hongyi Su and Huanxia Zhuang analyzed data; Final approval of the version to be published: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Huaming Wei declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yuping Wu Wei declares that he has no conflict of interest. Huanxia Zhuang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Hongyi Su declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., Wu, Y., Zhuang, H. et al. PCDH8 protects MPP+-induced neuronal injury in SH-SY5Y cells by inhibiting MAPK pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 19, 293–302 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00257-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00257-7