Abstract
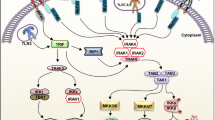
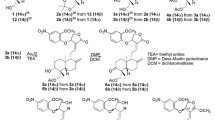
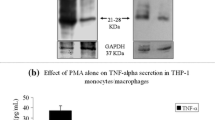
Inflammation can be initiated by invading microbial pathogens. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) recognize molecular structures derived from microbial pathogens and regulate the activation of innate immunity. TLR signaling pathways trigger the activation of nuclear factor-κB(NF-κB) transcription factor, leading to the induction of inflammatory gene products such as cyclooxygenase-2. Here, we present biochemical evidence that the fumaryl pyrrolidinone, (E)-isopropyl 4-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-butenoate (IPOP), previously synthesized in our laboratory inhibits NF-κB activation induced by TLR agonists and overexpression of two downstream signaling components of TLRs. IPOP also inhibits TLR agonist-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2. Our results suggest that IPOP can modulate TLR-mediated inflammatory responses and, potentially, the risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeda, K. & Akira, S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol 17:1–14 (2005).
Fritz, J. H. & Girardin, S. E. How Toll-like receptors and Nod-like receptors contribute to innate immunity in mammals. J Endotoxin Res 11:390–394 (2005).
Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 1:135–145 (2001).
Vogel, S. N., Fitzgerald, K. A. & Fenton, M. J. TLRs: differential adapter utilization by toll-like receptors mediates TLR-specific patterns of gene expression. Mol Interv 3:466–477 (2003).
Ospelt, C. & Gay, S. TLRs and chronic inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:495–505 (2009).
Heil, F. et al. Species-specific recognition of singlestranded RNA via toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science 303:1526–1529 (2004).
Fitzgerald, K. A. et al. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 4:491–496 (2003).
Meylan, E. et al. RIP1 is an essential mediator of Tolllike receptor 3-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat Immunol 5:503–507 (2004).
Yazdi, M. R. & Mrowietz, U. Fumaric acid esters. Clin Dermatol 26:522–526 (2008).
Schweckendiek, W. Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. Med Monatsschr 13:103–104 (1959).
Evans, D. A., Scheidt, K. A., Johnston, J. N. & Willis, M. C. Enantioselective and diastereoselective Mukaiyama-Michael reactions catalyzed by bis (oxazoline) copper (II) complexes. J Am Chem Soc 123:4480–4491 (2001).
Kang, S. H., Kang, Y. K., & Kim, D. Y. Catalytic enantioselective conjugate addition of aromatic amines to fumarate derivatives: asymmetric synthesis of aspartic acid derivatives. Tetrahedron 65:5676–5679 (2009).
Rhee, S. H. & Hwang, D. Murine TOLL-like receptor 4 confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness as determined by activation of NF kappa B and expression of the inducible cyclooxygenase. J Biol Chem 275:34035–34040 (2000).
Chi, Z. L., Hayasaka, S., Zhang, X. Y., Hayasaka, Y. & Cui, H. S. Effects of rolipram, a selective inhibitor of type 4 phosphodiesterase, on lipopolysaccharideinduced uveitis in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:2497–2502 (2004).
Katsuyama, K. et al. N2733, 1-[3-(3-pyridyl)-acryloyl]-2-pyrrolidinone hydrochloride inhibits LPS-induced TNF-alpha production and improves survival in endotoxemic mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:2177–2181 (1998).
Katsuyama, K. & Hirata, Y. A pyrrolidinone derivative inhibits cytokine-induced iNOS expression and NFkappaB activation by preventing phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB-alpha. J Biochem 129:585–591 (2001).
Youn, H. S., Ahn, S. I. & Lee, B. Y. Guggulsterone suppresses the activation of transcription factor IRF3 induced by TLR3 or TLR4 agonists. Int Immunopharmacol 9:108–112 (2009).
Ahn, S. I., Lee, J. K. & Youn, H. S. Inhibition of homodimerization of toll-like receptor 4 by 6-shogaol. Mol Cells 27:211–215 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, AN., Park, SJ., Koh, K.O. et al. Suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 expression induced by Toll-like receptor 2 or 4 agonists by (E)-isopropyl 4-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-butenoate. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 7, 39–44 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-011-0006-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-011-0006-0