Abstract
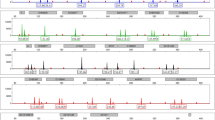
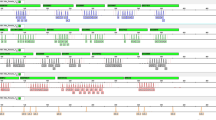
The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of using short tandem repeats (STRs) to diagnose Edwards’ syndrome (ES). Quantitative fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (QF-PCR) was performed to amplify STR loci on chromosome 18, specifically D18S53, D18S59, and D18S488. The amplified products were subjected to a fluorescence signal analysis and their application to ES diagnosis was examined. Among the 807 cases that showed normal results in the karyotype analysis, 793 showed one or two fluorescence bands with a fluorescence intensity ratio of 1:1, and 14 cases showed 3 bands, which were false-positive results. ES was diagnosed in 9 samples. The sensitivities of D18S53, D18S59, and D18S488 for the diagnosis of ES were 77.78, 44.44, and 55.56 % and the specificities were 96.16, 96.03, and 96.28 %, respectively. The combined sensitivity of the three loci for diagnosing DS was 100 % (9/9), with a specificity of 98.27 % (793/807). QF-PCR amplification of STR loci had high sensitivity, strong specificity, and was simple and rapid. Thus, it might have wide clinical applications, and could be an ideal tool for large-scale genetic and prenatal diagnosis of ES.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruns DA (2010) Neonatal experiences of newborns with full trisomy 18. Adv Neonatal Care 10:25–31
Cereda A, Carey JC (2012) The trisomy 18 syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 7:81
Cirigliano V, Voglino G, Ordoñez E, Marongiu A, Paz Cañadas M, Ejarque M, Rueda L, Lloveras E, Fuster C, Adinolfi M (2009) Rapid prenatal diagnosis of common chromosome aneuploidies by QF-PCR, results of 9 years of clinical experience. Prenat Diagn 29:40–49
Elsayed GM, El Assiouty L, El Sobky ES (2013) The importance of rapid aneuploidy screening and prenatal diagnosis in the detection of numerical chromosomal abnormalities. Springerplus 2:490
Gekas J, van den Berg DG, Durand A, Vallée M, Wildschut HI, Bujold E, Forest JC, Rousseau F, Reinharz D (2011) Rapid testing versus karyotyping in Down’s syndrome screening: cost-effectiveness and detection of clinically significant chromosome abnormalities. Eur J Hum Genet 19:3–9
Hills A, Donaghue C, Waters J, Waters K, Sullivan C, Kulkarni A, Docherty Z, Mann K, Ogilvie CM (2010) QF-PCR as a stand-alone test for prenatal samples: the first 2 years’ experience in the London region. Prenat Diagn 30:509–517
Houlihan OA, O’Donoghue K (2013) The natural history of pregnancies with a diagnosis of trisomy 18 or trisomy 13; a retrospective case series. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 13:209–217
Hultén MA, Dhanjal S, Pertl B (2003) Rapid and simple prenatal diagnosis of common chromosome disorders: advantages and disadvantages of the molecular methods FISH and QF-PCR. Reproduction 126:279–297
Irving C, Richmond S, Wren C, Longster C, Embleton ND (2011) Changes in fetal prevalence and outcome for trisomies 13 and 18: a population-based study over 23 years. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 24:137–141
Jain S, Agarwal S, Panigrahi I, Tamhankar P, Phadke S (2010) Diagnosis of Down syndrome and detection of origin of nondisjunction by short tandem repeat analysis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 14:489–491
Kamyab AR, Shahrokhi F, Shamsian E, Hayat Nosaied M, Dibajnia P, Hashemi M, Mahdian R (2012) Determination of sensitivity and specificity of a novel gene dosage assay for prenatal screening of trisomy 21 syndrome. Clin Biochem 45:267–271
Lakovschek IC, Streubel B, Ulm B (2011) Natural outcome of trisomy 13, trisomy 18, and triploidy after prenatal diagnosis. Am J Med Genet A 155A:2626–2633
Loane M, Morris JK, Addor MC et al (2013) Twenty-year trends in the prevalence of Down syndrome and other trisomies in Europe: impact of maternal age and prenatal screening. Eur J Hum Genet 21:27–33
Lubin MB, Elashoff JD, Wang SJ, Rotter JI, Toyoda H (1991) Precise gene dosage determination by polymerase chain reaction: theory, methodology, and statistical approach. Mol Cell Probes 5:307–317
Mann K, Ogilvie CM (2012) QF-PCR: application, overview and review of the literature. Prenat Diagn 32:309–314
Mansfield ES (1993) Diagnosis of Down syndrome and other aneuploidies using quantitative polymerase chain reaction and small tandem repeat polymorphisms. Hum Mol Genet 2:43–50
Papageorgiou EA, Karagrigoriou A, Tsaliki E, Velissariou V, Carter NP, Patsalis PC (2011) Fetal-specific DNA methylation ratio permits noninvasive prenataldiagnosis of trisomy 21. Nat Med 17:510–513
Parker SE, Mai CT, Canfield MA, Rickard R, Wang Y, Meyer RE, Anderson P, Mason CA, Collins JS, Kirby RS, Correa A, Network National Birth Defects Prevention (2010) Updated National Birth Prevalence estimates for selected birth defects in the United States, 2004-2006. Birth Defects Res A 88:1008–1016
Putzova M, Soldatova I, Pecnova L, Dvorakova L, Jencikova N, Goetz P, Stejskal D (2008) QF-PCR-based prenatal detection of common aneiploidies in the Czech population: five years of experience. Eur J Med Genet 51:209–218
Rasmussen SA, Wong LY, Yang Q, May KM, Friedman JM (2003) Population-based analyses of mortality in trisomy 13 and trisomy 18. Pediatrics 111:777–784
Sibiude J, Gavard L, Floch-Tudal C, Mandelbrot L (2011) Perinatal care and outcome of fetuses with trisomies 13 and 18 following a parental decision not to terminate the pregnancy. Fetal Diagn Ther 29:233–237
Tekcan A, Tural S, Elbistan M, Kara N, Guven D, Kocak I (2014) The combined QF-PCR and cytogenetic approach in prenatal diagnosis. Mol Biol Rep 41:7431–7436
Wilkinson DJ, de Crespigny L, Lees C, Savulescu J, Thiele P, Tran T, Watkins A (2014) Perinatal management of trisomy 18: a survey of obstetricians in Australia, New Zealand and the UK. Prenat Diagn 34:42–49
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Education Commission of Tianjin (20050229) and Science and Technology Foundation in Tackle Key Problems of Tianjin (06YFSYSF01800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this paper.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Sun, L., Shi, Y. et al. Use of the STR loci D18S53, D18S59, and D18S488 in the diagnosis of Edwards’ syndrome. Genes Genom 38, 639–644 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0412-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0412-8